|
Nahal Gerar
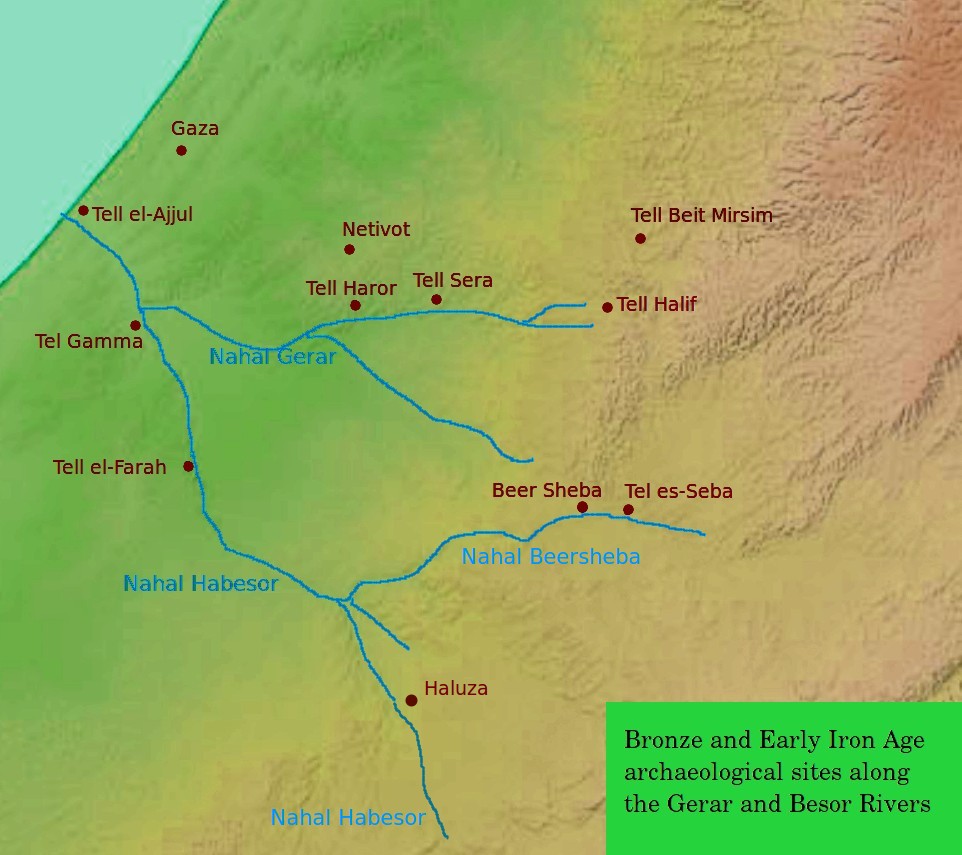
Nahal Gerar, also ''Nachal Grar'' ( he, נחל גרר) is a wadi in Israel, in the Negev desert. Its Arabic name is Wadi esh-Sheri'a (also Wady el Sharia and other variations). Along this wadi, there are several important ancient Bronze Age archaeological sites. During the Early Iron Age this was an area of Philistine settlement. Geography Nahal Gerar begins on the border between the northern Negev and the southwest foothills of Judaean Mountains, near the village of Lahav (ancient site of Tel Halif). Then the wadi flows west near the city of Lehavim, and along the southern edge of a large Bedouin town of Rahat. Then it flows west along the northwestern edge of the Negev towards the town of Netivot, an agricultural area. Near the village of Re'im, it flows into Nahal Besor, of which it is the main affluent. Nature reserve The lower river area is now part of the Eshkol National Park, a nature reserve used by tourists. Forest have been replanted there, and hiking trails developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerar
Gerar ( ''Gərār'', "lodging-place") was a Philistine town and district in what is today south central Israel, mentioned in the Book of Genesis and in the Second Book of Chronicles of the Hebrew Bible. Identification According to the International Standard Bible Encyclopedia, the biblical ''valley of Gerar'' () was probably located in the area of a valley known in Arabic as Wady Sheri'a, and in Modern Hebrew as Nahal Gerar. Most commentators see the mound of Tel Haror (Hebrew) or Tell Abu Hureyra (Arabic) as representing the ancient Gerar. Some older commentaries, such as Smith's Bible Dictionary, stated simply that Gerar was located "south of Gaza". Also, a ninth century rabbinical source (Saadia Gaon) identified Gerar with Haluza, located along the Besor River in the Negev.Rabbi Saadia Gaon's Judeo-Arabic Translation of the word Gerar (Judeo-Arabic: אלכ'לוץ = ''al-Khalūṣ'') in the Pentateuch (''Tafsir''), s.v. Genesis 10:19, Genesis 20:2, Genesis 26:17, 20. On Haluza' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharuhen
Sharuhen ( he, שָׁרוּחֶן) was an ancient town in the Negev Desert or perhaps in Gaza. Following the expulsion of the Hyksos from Egypt in the second half of the 16th century BCE, they fled to Sharuhen and fortified it. The armies of Pharaoh Ahmose I seized and razed the town after a three-year siege. History The destruction of Sharuhen was merely the first stage of a new policy of pre-emptive warfare waged by the Egyptians. Because the Egyptians of the 17th Dynasty felt deeply humiliated by the 15th and 16th Dynasty rule of the Hyksos (ca. 1650 BCE – ca. 1540 BCE), the Theban dynasty launched an ambitious war, led by Seqenenre Tao, against the foreign king, Apepi, to reclaim lost territory. Though his own campaign to expel the Hyksos from Egypt failed, and he himself was killed in battle, his son, Kamose, launched an attack on the Hyksos capital of Avaris. It was his much younger brother, Ahmose I, however, who finally succeeded in capturing Avaris, razing it, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Beit Mirsim
Tell Beit Mirsim is an archaeological site in Israel, on the border between the lowlands of Shfela and Mount Hebron. It is located in the eastern region of Lachish about 20 kilometers southwest of Hebron and about 13 kilometers southeast of Lachish. Excavations It was excavated for four seasons (1926, 1928, 1930 and 1932) by William F. Albright. The excavation revealed 10 or 11 strata dating from the late 3rd millennium BC to around 589 BC. The site is of particular importance for the archeology of Palestine, since the ceramics in the individual layers were observed particularly well and published quickly. This pottery corpus has long been considered the standard for archeology in the region. :"The strict separation of earth layers, or archaeological sediments, also allowed the strict separation of ceramic assemblages".Herr, Larry G. (2002)"W.F. Albright and the History of Pottery in Palestine".''Near Eastern Archaeology'' 65.1 (2002), 53. Town plan The site has "a town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell El-Khuweilifeh
Tel H̱alif, formerly Tel H̱alifa ( he, תל חליף, Arabic name: Tel el-Khuweilifeh) is an archaeological site, a mound ( tell) in northern Negev area, west from kibbutz Lahav, Israel. Albrecht Alt suggested that it is the location of the biblical town of Ziklag. Other evidence suggests Rimmon. Excavcations around Tel Halif was among the research activities of the Cobb Institute of Archaeology as part of the Lahav Research Project arranged by Joe Seger in 1974. See also *Battle of Tel el Khuweilfe The Battle of Tel el Khuweilfe, part of the Southern Palestine Offensive, began on 1 November 1917, the day after the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) victory at the Battle of Beersheba (1917), Battle of Beersheba during the Sinai and Palestine ... References {{infobox mapframe, coord={{coord, 31.383062, 34.866140, zoom=14 archaeological sites in Israel Negev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Haror
Tel Haror (Hebrew Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ... name) or Tell Abu Hureyra (Arabic name; also spelled Hureira and Hareira), also known as ''Tel Heror'', is an archaeological site in the western Negev Desert, Israel, northwest of Beersheba, about 20 km east of the Mediterranean Sea, situated on the north bank of Nahal Gerar, Wadi Gerar, a wadi known in Arabic as Wadi esh-Sheri'a. During the List of archaeological periods (Levant), Middle Bronze Age II it was one of the largest urban centres in the area, occupying about 40 acres. The city contains substantial remains of History of Israel#Bronze and Iron Ages, Middle Bronze Age II through to Persian-period settlement strata. Excavations W.F. Albright suggested as early as 1924 that there was a Cush (Bible), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian New Kingdom
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radiocarbon dating places the beginning of the New Kingdom between 1570 BC and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period. It was Egypt's most prosperous time and marked the peak of its power. The concept of a "New Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The later part of this period, under the Nineteenth and Twentieth dynasties (1292–1069 BC), is also known as the ''Ramesside period''. It is named after the eleven pharaohs who took the name Ramesses, after Ramesses I, the founder of the Nineteenth Dynasty. Possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Middle Kingdom
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately 2040 to 1782 BC, stretching from the reunification of Egypt under the reign of Mentuhotep II in the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Twelfth Dynasty. The kings of the Eleventh Dynasty ruled from Thebes and the kings of the Twelfth Dynasty ruled from el-Lisht. The concept of the Middle Kingdom as one of three golden ages was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition evolved significantly throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. Some scholars also include the Thirteenth Dynasty of Egypt wholly into this period, in which case the Middle Kingdom would end around 1650 BC, while others only include it until Merneferre Ay around 1700 BC, last king of this dynasty to be attested in both Upper and Lower Egypt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Antiquities Authority
The Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA, he, רשות העתיקות ; ar, داﺌرة الآثار, before 1990, the Israel Department of Antiquities) is an independent Israeli governmental authority responsible for enforcing the 1978 Law of Antiquities. The IAA regulates excavation and conservation, and promotes research. The Director-General is Mr. Eli Escusido, and its offices are housed in the Rockefeller Museum. The Israel Antiquities Authority plans to move into a new building for the National Campus for the Archaeology of Israel in Jerusalem, next to the Israel Museum. History The Israel Department of Antiquities and Museums (IDAM) of the Ministry of Education was founded on July 26, 1948, after the establishment of the State of Israel. It took over the functions of the Department of Antiquities of the British Mandate in Israel and Palestine. Originally, its activities were based on the British Mandate Department of Antiquities ordinances. IDAM was the statutory aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranen
Ranen ( he, רנן, lit. ''Singing'') is a moshav in southern Israel. Located in the north-western Negev two kilometres north of Ofakim, it falls under the jurisdiction of Merhavim Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The moshav was established in 1950 by immigrants from Yemen and was originally named ''Bitha''. In 1952 the residents moved to the site of the Hakam Ha-107 ma'abara and converted it to a moshav, taking the name Bitha. A group of Karaite Jews from Egypt moved onto the moshav, renaming it Ranen, which like the names of two other moshavim (Tifrah, Gilat Gilat ( he, גִּילַת, , Joy) is a moshav in southern Israel. Located in the western Negev desert between Beersheba and Ofakim, it falls under the jurisdiction of Merhavim Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The moshav ...) in the area, is taken from the Book of Isaiah 35:2, (The desert,) ''it shall blossom abundantly, and rejoice, even with joy and singing; the glory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1926._Excavating_house_at_east_gate_LOC_matpc.05732.jpg)



