|
NDUFS8
NADH dehydrogenase biquinoneiron-sulfur protein 8, mitochondrial also known as NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 23 kDa subunit, Complex I-23kD (CI-23kD), or TYKY subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NDUFS8'' gene. The NDUFS8 protein is a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) also known as Complex I, which is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and is the largest of the five complexes of the electron transport chain. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Leigh syndrome. Structure NDUFS8 is located on the q arm of chromosome 11 in position 13.2. The NDUFS8 gene produces a 23.7 kDa protein composed of 210 amino acids. The encoded protein, TYKY, contains two 4Fe4S ferredoxin consensus patterns which are believed to be iron-sulfur cluster N-2 binding sites. Studies of other subunits of Complex I have suggested that the subunits TYKY, PSST, 49 kDa, ND1, and ND5 interact with iron-sulfur clusters to form the catalytic core of NADH dehydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADH Dehydrogenase (ubiquinone)
Respiratory complex I, (also known as NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase, Type I NADH dehydrogenase and mitochondrial complex I) is the first large protein complex of the respiratory chains of many organisms from bacteria to humans. It catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and translocates protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes or the plasma membrane of bacteria. This enzyme is essential for the normal functioning of cells, and mutations in its subunits lead to a wide range of inherited neuromuscular and metabolic disorders. Defects in this enzyme are responsible for the development of several pathological processes such as ischemia/reperfusion damage (stroke and cardiac infarction), Parkinson's disease and others. Function Complex I is the first enzyme of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. There are three energy-transducing enzymes in the electron transport chain - NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex I
Respiratory complex I, (also known as NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase, Type I NADH dehydrogenase and mitochondrial complex I) is the first large protein complex of the Electron transport chain, respiratory chains of many organisms from bacteria to humans. It catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and translocates protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes or the plasma membrane of bacteria. This enzyme is essential for the normal functioning of cells, and mutations in its subunits lead to a wide range of inherited neuromuscular and metabolic disorders. Defects in this enzyme are responsible for the development of several pathological processes such as Reperfusion injury, ischemia/reperfusion damage (stroke and Myocardial infarction, cardiac infarction), Parkinson's disease and others. Function Complex I is the first enzyme of the Electron transport chain#Mitochondrial electron transport chains, mitochondrial electron tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leigh Syndrome
Leigh syndrome (also called Leigh disease and subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy) is an inherited neurometabolic disorder that affects the central nervous system. It is named after Archibald Denis Leigh, a British neuropsychiatrist who first described the condition in 1951. Normal levels of thiamine, thiamine monophosphate, and thiamine diphosphate are commonly found but there is a reduced or absent level of thiamine triphosphate. This is thought to be caused by a blockage in the enzyme thiamine-diphosphate kinase, and therefore treatment in some patients would be to take thiamine triphosphate daily. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of Leigh syndrome are classically described as beginning in infancy and leading to death within a span of several years; however, as more cases are recognized, it is apparent that symptoms can emerge at any age—including adolescence or adulthood—and patients can survive for many years following diagnosis. Symptoms are often first seen after a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NDUFS7
NADH dehydrogenase biquinoneiron-sulfur protein 7, mitochondrial, also knowns as NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 20 kDa subunit, Complex I-20kD (CI-20kD), or PSST subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NDUFS7'' gene. The NDUFS7 protein is a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) also known as Complex I, which is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and is the largest of the five complexes of the electron transport chain. Structure The NDUFS7 gene is located on the p arm of chromosome 19 in position 13.3. The NDUFS7 gene produces a 25 kDa protein composed of 238 amino acids. The PSST subunit is highly conserved across evolutionary distances. Crystal structures and mutational studies indicate that it is one of the ubiquinone binding sites of Complex I, together with the TYKY (NDUFS8) subunit. It has been proposed that PSST, along with TYKY, 49 kDa, ND1 and ND5 subunits interact with iron-sulfur clusters as part of the catalytic core of NADH dehydroge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise Intolerance
Exercise intolerance is a condition of inability or decreased ability to perform physical exercise at the normally expected level or duration for people of that age, size, sex, and muscle mass. It also includes experiences of unusually severe post-exercise pain, fatigue, nausea, vomiting or other negative effects. Exercise intolerance is not a disease or syndrome in and of itself, but can result from various disorders. In most cases, the specific reason that exercise is not tolerated is of considerable significance when trying to isolate the cause down to a specific disease. Dysfunctions involving the pulmonary, cardiovascular or neuromuscular systems have been frequently found to be associated with exercise intolerance, with behavioural causes also playing a part. Signs and symptoms Exercise in this context means physical activity, not specifically exercise in a fitness program. For example, a person with exercise intolerance after a heart attack may not be able to sustain the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptosis (eyelid)
Ptosis, also known as blepharoptosis, is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid. The drooping may be worse after being awake longer when the individual's muscles are tired. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to the condition amblyopia. If severe enough and left untreated, the drooping eyelid can cause other conditions, such as amblyopia or astigmatism. This is why it is especially important for this disorder to be treated in children at a young age, before it can interfere with vision development. The term is from Greek 'fall, falling'. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms typically seen in this condition include: * The eyelid(s) may appear to droop. * Droopy eyelids can give the face a false appearance of being fatigued, disinterested, or even sinister. * The eyelid may not protect the eye as effectively, allowing it to dry out. * Sagging upper eyelids can partially block the person's field of view. * Obstructed vision may cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia
Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) is a type of eye disorder characterized by slowly progressive inability to move the eyes and eyebrows. It is often the only feature of mitochondrial disease, in which case the term CPEO may be given as the diagnosis. In other people suffering from mitochondrial disease, CPEO occurs as part of a syndrome involving more than one part of the body, such as Kearns–Sayre syndrome. Occasionally CPEO may be caused by conditions other than mitochondrial diseases. Signs and symptoms CPEO is a rare disease that may affect those of all ages, but typically manifests in the young adult years. CPEO is the most common manifestation of mitochondrial myopathy, occurring in an estimated two-thirds of all cases of mitochondrial myopathy. Patients typically present with ptosis (drooping eyelids). Other diseases like Graves' disease, myasthenia gravis and glioma that may cause an external ophthalmoplegia must be ruled out. CPEO itself CPEO is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
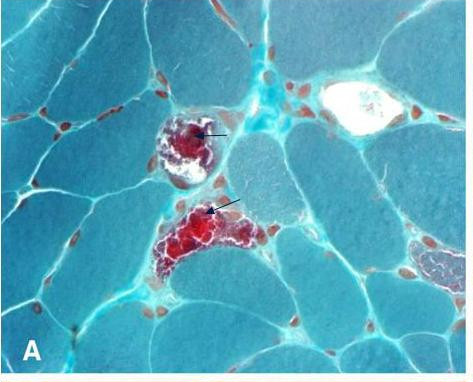
Myopathy
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. This results in muscular weakness. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease (Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia '' -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meaning implies that the primary defect is within the muscle, as opposed to the nerves ("neuropathies" or "neurogenic" disorders) or elsewhere (e.g., the brain). Muscle cramps, stiffness, and spasm can also be associated with myopathy. Capture myopathy can occur in wild or captive animals, such as deer and kangaroos, and leads to morbidity and mortality. It usually occurs as a result of stress and physical exertion during capture and restraint. Muscular disease can be classified as neuromuscular or musculoskeletal in nature. Some conditions, such as myositis, can be considered both neuromuscular and musculoskeletal. Signs and symptoms Common symptoms include muscle weakness, cramps, stiffness, and tetany. Systemic diseases Myopathies i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Atrophy
Optic neuropathy is damage to the optic nerve from any cause. The optic nerve is a bundle of millions of fibers in the retina that sends visual signals to the brain. Damage and death of these nerve cells, or neurons, leads to characteristic features of optic neuropathy. The main symptom is loss of vision, with colors appearing subtly washed out in the affected eye. A pale disc is characteristic of long-standing optic neuropathy. In many cases, only one eye is affected and patients may not be aware of the loss of color vision until the doctor asks them to cover the healthy eye. Optic neuropathy is often called optic atrophy, to describe the loss of some or most of the fibers of the optic nerve. Ischemic optic neuropathy In ischemic optic neuropathies, there is insufficient blood flow (ischemia) to the optic nerve. The anterior optic nerve is supplied by the short posterior ciliary artery and choroidal circulation, while the retrobulbar optic nerve is supplied intraorbitally by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An irregular heart beat and fainting may occur. Those affected are at an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. Types of cardiomyopathy include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (broken heart syndrome). In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy the heart muscle enlarges and thickens. In dilated cardiomyopathy the ventricles enlarge and weaken. In restrictive cardiomyopathy the ventricle stiffens. In many cases, the cause cannot be determined. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually inherited, whereas dilated cardiomyopathy is inherited in about one third of cases. Dilated cardiomyopathy may also result from alcohol, heavy m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear or sensory organ (cochlea and associated structures) or the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). SNHL accounts for about 90% of reported hearing loss . SNHL is usually permanent and can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total. Various other descriptors can be used depending on the shape of the audiogram, such as high frequency, low frequency, U-shaped, notched, peaked, or flat. ''Sensory'' hearing loss often occurs as a consequence of damaged or deficient cochlear hair cells. Hair cells may be abnormal at birth or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, including infection, and ototoxic drugs, as well as intrinsic causes, including genetic mutations. A common cause or exacerbating factor in SNHL is prolonged exposure to environmental noise, or noise-induced hearing loss. Exposure to a single very loud noise such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)