|
NA31 Experiment
NA31 is a CERN experiment which was proposed in 1982 as a "Measurement of , η00 /η+-, 2 by the CERN-Edinburgh-Mainz-Pisa-Siegen collaboration. It took data between 1986 and 1989, using a proton beam from the SPS through the K4 neutral beam-line. Its aim was to experimentally prove direct CP-violation. CP violation While charge symmetry and parity symmetry are both violated for any transformation under the weak interaction, the CP violation is known only to appear in particular phenomena - kaon and B-meson decays - under the weak interaction. CP-violation was first theoretically developed for the Standard Model by Kobayashi and Maskawa in 1973 when they introduced a third generation of quark (bottom and top) and thus extended the Cabibbo matrix to the 3x3 CKM matrix, parameterizing the couplings between quark-mass eigenstates and the charge weak gauge bosons. CP violation then appears through the presence of complex parameters in this matrix. Determined from the rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 23 member states, and Israel (admitted in 2013) is currently the only non-European country holding full membership. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2019, it had 2,660 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,400 users from institutions in more than 70 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research — consequently, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN through international collaborations. CERN is the site of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermilab
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been operated by the Fermi Research Alliance, a joint venture of the University of Chicago, and the Universities Research Association (URA). Fermilab is a part of the Illinois Technology and Research Corridor. Fermilab's Main Injector, two miles (3.3 km) in circumference, is the laboratory's most powerful particle accelerator. The accelerator complex that feeds the Main Injector is under upgrade, and construction of the first building for the new PIP-II linear accelerator began in 2020. Until 2011, Fermilab was the home of the 6.28 km (3.90 mi) circumference Tevatron accelerator. The ring-shaped tunnels of the Tevatron and the Main Injector are visible from the air and by satellite. Fermilab aims to become a world center in neutri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as carbon dioxide (400 ppmv), and more than 500 times as abundant as neon (18 ppmv). Argon is the most abundant noble gas in Earth's crust, comprising 0.00015% of the crust. Nearly all of the argon in Earth's atmosphere is radiogenic argon-40, derived from the decay of potassium-40 in Earth's crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, as it is the most easily produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas. The name "argon" is derived from the Greek word , neuter singular form of meaning 'lazy' or 'inactive', as a reference to the fact that the element undergoes almost no chemical reactions. The complete octe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, and plasma), and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. A liquid is made up of tiny vibrating particles of matter, such as atoms, held together by intermolecular bonds. Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Most liquids resist compression, although others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly constant density. A distinctive property of the liquid state is surface tension, leading to wetting phenomena. Water is by far the most common liquid on Earth. The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than that of a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are both termed condensed matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively). Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects. Electric charge is a conserved property; the net charge of an isolated system, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge, cannot change. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Space
In dynamical system theory, a phase space is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state corresponding to one unique point in the phase space. For mechanical systems, the phase space usually consists of all possible values of position and momentum variables. It is the outer product of direct space and reciprocal space. The concept of phase space was developed in the late 19th century by Ludwig Boltzmann, Henri Poincaré, and Josiah Willard Gibbs. Introduction In a phase space, every degree of freedom or parameter of the system is represented as an axis of a multidimensional space; a one-dimensional system is called a phase line, while a two-dimensional system is called a phase plane. For every possible state of the system or allowed combination of values of the system's parameters, a point is included in the multidimensional space. The system's evolving state over time traces a path (a phase-space trajectory for the system) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interaction Point
In particle physics, an interaction point (IP) is the place where particles collide in an accelerator experiment. The ''nominal'' interaction point is the design position, which may differ from the ''real'' or ''physics'' interaction point, where the particles actually collide. A related, but distinct, concept is the ''primary vertex'': the reconstructed location of an individual particle collision. For fixed target experiments, the interaction point is the point where beam and target interact. For colliders, it is the place where the beams interact. Experiments (detectors) at particle accelerators are built around the nominal interaction points of the accelerators. The whole region around the interaction point (the experimental hall) is called an interaction region. Particle colliders such as LEP, HERA, RHIC, Tevatron The Tevatron was a circular particle accelerator (active until 2011) in the United States, at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (also known as ''F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calorimetry
In chemistry and thermodynamics, calorimetry () is the science or act of measuring changes in ''state variables'' of a body for the purpose of deriving the heat transfer associated with changes of its state due, for example, to chemical reactions, physical changes, or phase transitions under specified constraints. Calorimetry is performed with a calorimeter. Scottish physician and scientist Joseph Black, who was the first to recognize the distinction between heat and temperature, is said to be the founder of the science of calorimetry. Indirect calorimetry calculates heat that living organisms produce by measuring either their production of carbon dioxide and nitrogen waste (frequently ammonia in aquatic organisms, or urea in terrestrial ones), or from their consumption of oxygen. Lavoisier noted in 1780 that heat production can be predicted from oxygen consumption this way, using multiple regression. The dynamic energy budget theory explains why this procedure is correct. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Chambers
A wire chamber or multi-wire proportional chamber is a type of proportional counter that detects charged particles and photons and can give positional information on their trajectory, by tracking the trails of gaseous ionization. was located via Dr. C.N. BootPHY304 Particle Physics Sheffield University/ref> Description The multi-wire chamber uses an array of wires at high voltage (anode), which run through a chamber with conductive walls held at ground potential (cathode). Alternatively, the wires may be at ground potential and the cathode held at a high negative voltage; the important thing is that a uniform electric field draws extra electrons or negative ions to the anode wires with little lateral motion. The chamber is filled with carefully chosen gas, such as an argon/methane mix, such that any ionizing particle that passes through the tube will ionize surrounding gaseous atoms. The resulting ions and electrons are accelerated by the electric field across the chamber, causi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
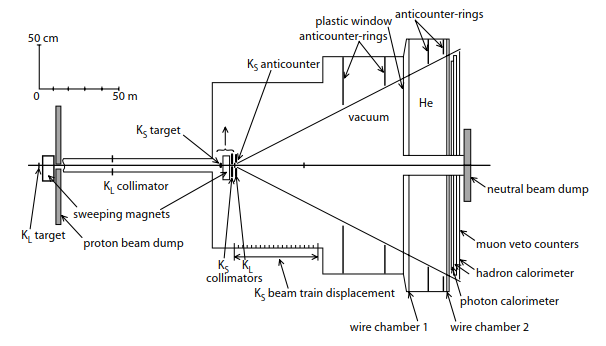
Layout Of The NA31 Experiment
Layout may refer to: * Page layout, the arrangement of visual elements on a page ** Comprehensive layout (comp), a proposed page layout presented by a designer to their client * Layout (computing), the process of calculating the position of objects in space * Layout engine, another name for web browser engine, the core software that displays content in a web browser * Automobile layout, a description of the locations of the engine and drive wheels on a vehicle * Integrated circuit layout, the representation of an integrated circuit in geometric shapes * Keyboard layout, an arrangement of the keys on a typographic keyboard * Model railroad layout, a diorama with tracks for operating scaled-down trains *Layout (dominoes), the tableau in a domino game * Layout or marking out, the transfer of a design onto a workpiece in manufacturing * Plant layout study, an engineering study to analyze physical configurations for a manufacturing plant * Layout, a specific version of the splits, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Energy And Particle Physics Prize
The High Energy and Particle Physics Prize, established in 1989, is awarded every two years by the European Physical Society (EPS) for an outstanding contribution to high energy and particle physics. :) Enjoy Recipients Source: * 1989 Georges Charpak * 1991 Nicola Cabibbo * 1993 Martinus Veltman * 1995 Paul Söding, Bjørn Wiik, , Sau Lan Wu * 1997 Robert Brout, François Englert, Peter Higgs * 1999 Gerard ’t Hooft * 2001 Don Perkins * 2003 David Gross, David Politzer, Frank Wilczek * 2005 and the NA31 Collaboration * 2007 Makoto Kobayashi, Toshihide Maskawa * 2009 The Gargamelle collaboration * 2011 Sheldon Glashow, John Iliopoulos, Luciano Maiani * 2013 The ATLAS and CMS collaborations, Michel Della Negra, Peter Jenni, Tejinder Virdee * 2015 James D. Bjorken, Guido Altarelli, , Lev Lipatov, Giorgio Parisi * 2017 , , * 2019 The CDF and D0 collaborations * 2021 Torbjörn Sjöstrand, Bryan Webber See also * List of physics awards This list of physics awards is an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |