|
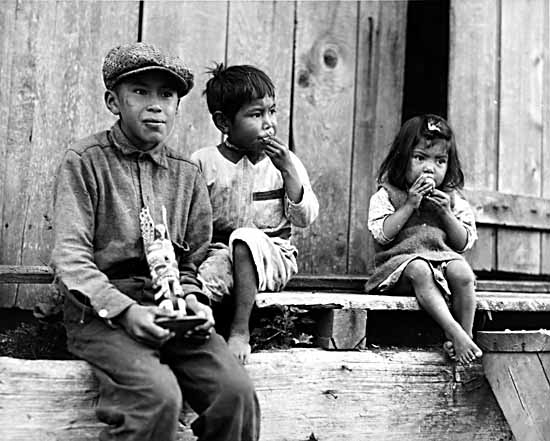
Mowachaht
The Mowachaht/Muchalaht First Nations are a First Nations government on the west coast of Vancouver Island in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The Mowachaht/Muchalaht First Nations are a member nation of the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council, which spans all Nuu-chah-nulth-aht peoples (incorrectly known as "Nootka") except for the Pacheedaht First Nation. Their main reserve is at Gold River, British Columbia but the Mowachaht are originally from Yuquot on Nootka Sound, known to history as Friendly Cove, scene of the Nootka Incident and, later, the negotiations and eventual implementation of the Nootka Conventions between Britain and Spain, hosted by the Mowachaht chief Maquinna. Name The Mowachaht (pronounced ), which translates to people of the deer, originate from a place called Friendly Cove, or Yuquot (translates to "Wind comes from all directions"). The name Muchalaht translates to the people who hover over the river or the people over the river. History In the mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuquot, British Columbia
Yuquot , also known as Friendly Cove, is a small settlement of around six people—the Williams family of the Mowachaht band—plus two full-time lighthouse keepers, located on Nootka Island in Nootka Sound, just west of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It was the summer home of Chief Maquinna and the Mowachaht/Muchalaht (Nuu-chah-nulth) people for generations, housing approximately 1,500 people in 20 traditional wooden longhouses. The name means "Wind comes from all directions" in Nuu-chah-nulth. The community is located within the Strathcona Regional District but like all Indian Reserve communities is not governed by nor represented in the regional district. The Mowchaht/Muchalaht First Nations are rather part of the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council, which unites the governments of the indigenous communities of the Island's West Coast. The Canadian government declared Friendly Cove a National Historic Site in 1923, with recognition of the significance of the Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuquot
Yuquot , also known as Friendly Cove, is a small settlement of around six people—the Williams family of the Mowachaht band—plus two full-time lighthouse keepers, located on Nootka Island in Nootka Sound, just west of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It was the summer home of Maquinna, Chief Maquinna and the Mowachaht/Muchalaht First Nations, Mowachaht/Muchalaht (Nuu-chah-nulth people, Nuu-chah-nulth) people for generations, housing approximately 1,500 people in 20 traditional wooden longhouses. The name means "Wind comes from all directions" in Nuu-chah-nulth language, Nuu-chah-nulth. The community is located within the Strathcona Regional District, British Columbia, Strathcona Regional District but like all Indian Reserve communities is not governed by nor represented in the regional district. The Mowchaht/Muchalaht First Nations are rather part of the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council, which unites the governments of the indigenous communities of the Island's West Coas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna (Orca)
Luna ( – March 10, 2006) also known as L98 or Tsux'iit, was a killer whale (orca) born in Puget Sound. After being separated from his mother while still young, Luna spent five years in Nootka Sound, an ocean inlet of western Vancouver Island, where he had extensive human contact and became recognized internationally. Although Luna was healthy and his presence in the area attracted extensive publicity, there were concerns that his behavior could endanger watercraft and people. After years of debate, the Canadian Department of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) authorized an effort in June 2004 to rescue Luna and return him to his pod. The plan was opposed by the Mowachaht/Muchalaht First Nations, who believed Luna was the reincarnation of a former chief. Remaining alone in Nootka Sound, Luna was killed accidentally by a tugboat propeller in March 2006. Early life Luna was born into a population known as the Southern Resident community, consisting of three families called "pods": J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuu-chah-nulth Governments
The Nuu-chah-nulth (; Nuučaan̓uł: ), also formerly referred to as the Nootka, Nutka, Aht, Nuuchahnulth or Tahkaht, are one of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast in Canada. The term Nuu-chah-nulth is used to describe fifteen related tribes whose traditional home is on the west coast of Vancouver Island. In precontact and early post-contact times, the number of tribes was much greater, but the smallpox epidemics and other consequences of settler colonization resulted in the disappearance of some groups and the absorption of others into neighbouring groups. The Nuu-chah-nulth are related to the Kwakwaka'wakw, the Haisla, and the Ditidaht First Nation. The Nuu-chah-nulth language belongs to the Wakashan family. The governing body is the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council. History Contact with Europeans When James Cook first encountered the villagers at Yuquot in 1778, they directed him to "come around" (Nuu-chah-nulth ''nuutkaa'' is "to circle around")C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuu-chah-nulth People
The Nuu-chah-nulth (; Nuučaan̓uł: ), also formerly referred to as the Nootka, Nutka, Aht, Nuuchahnulth or Tahkaht, are one of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast in Canada. The term Nuu-chah-nulth is used to describe fifteen related tribes whose traditional home is on the west coast of Vancouver Island. In precontact and early post-contact times, the number of tribes was much greater, but the smallpox epidemics and other consequences of settler colonization resulted in the disappearance of some groups and the absorption of others into neighbouring groups. The Nuu-chah-nulth are related to the Kwakwaka'wakw, the Haisla, and the Ditidaht First Nation. The Nuu-chah-nulth language belongs to the Wakashan family. The governing body is the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council. History Contact with Europeans When James Cook first encountered the villagers at Yuquot in 1778, they directed him to "come around" (Nuu-chah-nulth ''nuutkaa'' is "to circle around" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maquinna
Maquinna (also transliterated Muquinna, Macuina, Maquilla) was the chief of the Nuu-chah-nulth people of Nootka Sound, during the heyday of the maritime fur trade in the 1780s and 1790s on the Pacific Northwest Coast. The name means "possessor of pebbles". His people are today known as the Mowachaht and reside today with their kin, the Muchalaht, at Gold River, British Columbia, Canada. History Maquinna was a powerful chief whose summer coastal village, Yuquot, became the first important anchorage in the European jockeying for power and commerce as the era of the maritime fur trade began. Yuquot became known as Friendly Cove after the British explorer Captain James Cook visited in 1778. Cook did not record the name of the chief of Yuquot, who may not have been Maquinna in 1778, even though writers have often assumed it was. Imperial Spain had sent two voyages to the region before Cook's visit, including Juan Pérez, who in 1774 had anchored in or near the entrance of Nootka Soun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuu-chah-nulth Language
Nuu-chah-nulth (), Nootka (), is a Wakashan language in the Pacific Northwest of North America on the west coast of Vancouver Island, from Barkley Sound to Quatsino Sound in British Columbia by the Nuu-chah-nulth peoples. Nuu-chah-nulth is a Southern Wakashan language related to Nitinaht and Makah. It is the first language of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast to have documentary written materials describing it. In the 1780s, Captains Vancouver, Quadra, and other European explorers and traders frequented Nootka Sound and the other Nuu-chah-nulth communities, making reports of their voyages. From 1803–1805 John R. Jewitt, an English blacksmith, was held captive by chief '' Maquinna'' at Nootka Sound. He made an effort to learn the language, and in 1815 published a memoir with a brief glossary of its terms. Name The provenance of the term "Nuu-chah-nulth", meaning "along the outside f Vancouver Island dates from the 1970s, when the various groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council
The Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council is a First Nations Tribal Council in the Canadian province of British Columbia, located on the west coast of Vancouver Island. The organization is based in Port Alberni, British Columbia. History The Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council began as the West Coast Allied Tribes in 1958, but then incorporated as a non-profit society called the West Coast District Society of Indian Chiefs in 1973. In 2009, the name was changed to the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council (NTC) (NTC, 2008). The northern boundary of Nuu-chah-nulth territory begins on the west coast of Vancouver Island at Brooks Peninsula and the southern boundary is at Port Renfrew. The territory extends inland about halfway across the island to encompass Gold River and Port Alberni. There are fourteen tribes that comprise the Nuu-chah-nulth Nations. These tribes share many aspects of their culture, language and traditions. Each Nation can have several "houses" that are centered on a Ha’wiih (heredi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold River, British Columbia
Gold River is a village municipality located close to the geographic centre of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. In terms of the Island's human geography it is considered to be part of the "North Island", even though it technically is on the Island's west coast. History Taking advantage of its deep water and abundant forests, Gold River developed in 1967 as a prototypical logging and pulp and paper industry community. Gold River quickly sprang into prosperity and established excellent community facilities. When shifting world markets brought the mill closure in 1998, many of Gold River's inhabitants were forced to relocate. Since then, the village has attempted to capitalize on its idealistic setting among picturesque mountains, lakes, rivers, ocean, and forests to develop tourism and sport fishing as its main economic supports. Currently, Gold River serves as a base for such famous activities as the Nootka Island trek, hiking the Elk Lake trail and mountain climbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Reserve
In Canada, an Indian reserve (french: réserve indienne) is specified by the '' Indian Act'' as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty, that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band." Indian reserves are the areas set aside for First Nations, an indigenous Canadian group, after a contract with the Canadian state ("the Crown"), and are not to be confused with land claims areas, which involve all of that First Nations' traditional lands: a much larger territory than any reserve. Demographics A single "band" (First Nations government) may control one reserve or several, while other reserves are shared between multiple bands. In 2003, the Department of Indian and Northern Affairs stated there were 2,300 reserves in Canada, comprising . According to Statistics Canada in 2011, there are more than 600 First Nations/Indian bands in Canada and 3,100 Indian reserves across Canada. Examples include the Driftpile First Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Province
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the '' Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the '' British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territorial governments are creatures of statute with powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada. The powers flowing fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |