|
Moldovan Ground Forces
'' , image= Flag of the Armed Forces of Moldova.svg , image_size = , caption = Moldovan Ground Forces flag , start_date = 25 December 2008 , country= , allegiance = , branch = , type = Army , role = Land warfare , size = 4,000 , command_structure = National Army , garrison = Chișinău , garrison_label = Headquarters , nickname = Moldovan Army , patron = , motto = , colors = , colors_label = , march = Marș de Întîmpinare «La Mulți ani» , mascot = , notable_commanders =Brigadier General Mihail Buclis , current_commander = , current_commander_label = , equipment = SSh-68PASGT , equipment_label = , battles = Transnistria War , decorations = , battle_honours = , identification_symbol = , identification_symbol_label = , identification_symbol_2 = , identification_symbol_2_label = The Moldovan Ground Forces, known officially as Land Forces Command is the land armed-forces branch of the National Army of the Moldovan Armed Forces. The Moldovan Gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by possessing an army aviation component. Within a national military force, the word army may also mean a field army. In some countries, such as France and China, the term "army", especially in its plural form "armies", has the broader meaning of armed forces as a whole, while retaining the colloquial sense of land forces. To differentiate the colloquial army from the formal concept of military force, the term is qualified, for example in France the land force is called ''Armée de terre'', meaning Land Army, and the air and space force is called ''Armée de l'Air et de l’Espace' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPG-9
The SPG-9 Kopyo (''Spear'') ( Russian: СПГ-9 Копьё) is a tripod-mounted man-portable, 73 millimetre calibre recoilless gun developed by the Soviet Union. It fires fin-stabilised, rocket-assisted HE and HEAT projectiles similar to those fired by the 73 mm 2A28 Grom low pressure gun of the BMP-1 armored vehicle. It was accepted into service in 1962, replacing the B-10 recoilless rifle. Description The projectile is launched from the gun by a small charge, which gives it an initial velocity of between 250 and 400 metres per second. The launch charge also imparts spin to the projectile by a series of offset holes. Once the projectile has traveled approximately 20 meters (65.6 feet) from the launcher, a rocket motor in its base ignites. For the PG-9 projectile, this takes it to a velocity of 700 metres per second (2,297 feet per second) before the motor burns out. The SPG-9 is heavy (~60 kg), and is normally transported by vehicle, and carried into position by it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moldova Military Location Map
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistria lies across the Dniester river on the country's eastern border with Ukraine. Moldova's capital and largest city is Chișinău. Most of Moldovan territory was a part of the Principality of Moldavia from the 14th century until 1812, when it was ceded to the Russian Empire by the Ottoman Empire (to which Moldavia was a vassal state) and became known as Bessarabia. In 1856, southern Bessarabia was returned to Moldavia, which three years later united with Wallachia to form Romania, but Russian rule was restored over the whole of the region in 1878. During the 1917 Russian Revolution, Bessarabia briefly became an autonomous state within the Russian Republic, known as the Moldavian Democratic Republic. In February 1918, the Moldavian Democ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recoilless Rifle
A recoilless rifle, recoilless launcher or recoilless gun, sometimes abbreviated "RR" or "RCL" (for ReCoilLess) is a type of lightweight artillery system or man-portable launcher that is designed to eject some form of countermass such as propellant gas from the rear of the weapon at the moment of firing, creating forward thrust that counteracts most of the weapon's recoil. This allows for the elimination of much of the heavy and bulky recoil-counteracting equipment of a conventional cannon as well as a thinner-walled barrel, and thus the launch of a relatively large projectile from a platform that would not be capable of handling the weight or recoil of a conventional gun of the same size. Technically, only devices that use spin-stabilized projectiles fired from a rifled barrel are recoilless rifles, while smoothbore variants (which can be fin-stabilized or unstabilized) are recoilless guns. This distinction is often lost, and both are often called recoilless rifles. Though sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-tank Missile
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder-launched weapons, which can be transported by a single soldier, to larger tripod-mounted weapons, which require a squad or team to transport and fire, to vehicle and aircraft mounted missile systems. Earlier man-portable anti-tank weapons like anti-tank rifles and magnetic anti-tank mines, generally had very short range, sometimes on the order of metres or tens of metres. Rocket-propelled high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) systems appeared in World War II and extended range to the order of hundreds of metres, but accuracy was low and hitting targets at these ranges was largely a matter of luck. It was the combination of rocket propulsion and remote wire guidance that made the ATGM much more effective than these earlier weapons, and gave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MT-LB
The MT-LB (russian: Многоцелевой Тягач Легкий Бронированный, translit=Mnogotselevoy tyagach legky bronirovanny, literally "multi-purpose towing vehicle light armored") is a Soviet multi-purpose, fully amphibious, tracked armored fighting vehicle in use since the 1950s. It was also produced in Poland, where (starting in the mid-1990s) its YaMZ engine was replaced by a Polish 6-cylinder SW 680 diesel engine. Development In the 1950s, the Soviet Central Auto and Tractor Directorate began a development program to replace the AT-P series of artillery tractors (which were based on the ASU-57 airborne self-propelled gun) with a new generation of vehicles. The MT-L was developed to meet this requirement based on the PT-76 amphibious light tank chassis. The MT-LB is the armored variant of the MT-L. Entering production in the early 1970s, it was cheap to build, being based on many existing components, e.g. the engine, which was originally developed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAB-71
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers (APCs). It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen in public for the first time in 1961. BTR stands for ''Bronetransporter'' (БТР, Бронетранспортер, literally "armoured transporter"). History Origins The BTR-152 and BTR-40, the first two Soviet mass-produced APCs developed after the Second World War, gave the Soviet Army useful experience with wheeled armoured personnel carriers. However, even as they were designed, they were not suited for the needs of the Soviet Army as they lacked a roof (which was added in later versions designated BTR-152K and BTR-40B respectively). The low combat values of the BTR-152 and BTR-40 were exposed when the Egyptian Army used them during the Suez Crisis and also when the Soviet Army used them in the fighting on the streets of Budapest during the Hungarian Revolution of 1956. These were among t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Personnel Carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world. According to the definition in the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, an APC is "an armoured combat vehicle which is designed and equipped to transport a combat infantry squad and which, as a rule, is armed with an integral or organic weapon of less than 20 millimetres calibre." Compared to infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs), which are also used to carry infantry into battle, APCs have less armament and are not designed to provide direct fire support in battle. Infantry units which travel in APCs are known as mechanized infantry. Some militaries also make a distinction between infantry units which use APCs and infantry units which use IFVs, with the latter being known as armoured infantry in such militaries. History The genesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle, in service 1966–present. BMP stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1'' (russian: link=no, Боевая Машина Пехоты 1; БМП-1), meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st serial model". The BMP-1 was the first mass-produced infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) of the Soviet Union. It was called the M-1967, BMP and BMP-76PB by NATO before its correct designation was known. The Soviet military leadership saw any future wars as being conducted with nuclear, chemical and biological weapons. A new design, like the BMP, combining the properties of an armored personnel carrier (APC) and a light tank would allow infantry to operate from the relative safety of its armoured, radiation-shielded interior in contaminated areas and to fight alongside it in uncontaminated areas. It would increase infantry squad mobility, provide fire support to them, and also be able to fight alongside main battle tanks. The BMP-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IISS
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) is a British research institute or think tank in the area of international affairs. Since 1997, its headquarters have been Arundel House in London, England. The 2017 Global Go To Think Tank Index ranked IISS as the tenth-best think tank worldwide and the second-best Defence and National Security think tank globally, while Transparify ranked it third-largest UK think tank by expenditure, but gave it its lowest rating, "deceptive", on funding transparency. Overview The current director-general and chief executive is John Chipman. Sir Michael Howard, the British military historian, founded the institute together with the British Labour MP Denis Healey ( Defence Secretary, 1964–1970 and Chancellor, 1974–1979) and University of Oxford academic Alastair Francis Buchan. Based in London, the IISS is both a private company limited by guarantee in UK law and a registered charity. Research The institute has worked w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
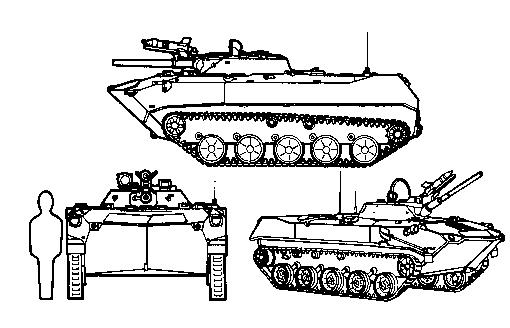
BMD-1
The BMD-1 is a Soviet airborne amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle, which was introduced in 1969 and first seen by the West in 1970. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десанта, which literally translates to "Combat Vehicle of the Airborne"). It can be dropped by parachute and although it resembles the BMP-1 it is in fact much smaller. The BMD-1 was used as an IFV by the Soviet Army's airborne divisions. An improved variant of the BMD-1 was developed, the BMD-2. The BMD-1 also provided a basis for the BTR-D airborne multi-purpose tracked APC. Development In the wake of the Cuban Missile Crisis, the army was instructed to consider putting more emphasis on means to project power outside of the normal sphere of Soviet influence. As a result, there was a major effort to develop the VDV (Soviet airborne forces) as a rapid deployment force. Soviet studies of airborne operations had shown that lightly armed paratroops were unable to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a predominantly temperate-continental climate, and an area of , with a population of around 19 million. Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe and the sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, followed by Iași, Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, and Galați. The Danube, Europe's second-longest river, rises in Germany's Black Forest and flows in a southeasterly direction for , before emptying into Romania's Danube Delta. The Carpathian Mountains, which cross Romania from the north to the southwest, include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Settlement in what is now Romania began in the Lower Paleolithic, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |