|
Military Activity In The Antarctic
As Antarctica has never been permanently settled by humans, there has historically been little military activity in the Antarctic as the Antarctic Treaty, which came into effect on June 23, 1961, bans military activity in Antarctica. Military personnel and equipment may only be used for scientific research or any other peaceful purpose (such as delivering supplies) on the continent. The Antarctic Treaty specifically prohibits military activity on land or ice shelves below 60°S. While the use of nuclear weapons is absolutely prohibited, the Treaty does not apply to naval activity within these bounds (in the Southern Ocean) so long as it takes place on the high seas. Notable operations Military forces from many countries have provided support to scientific expeditions and bases in Antarctica. Notable operations and expeditions have included: * Commander James Cook's second voyage (United Kingdom, 1773) * USS ''Vincennes surveys of Antarctica (United States, 1839 and 1840) * In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
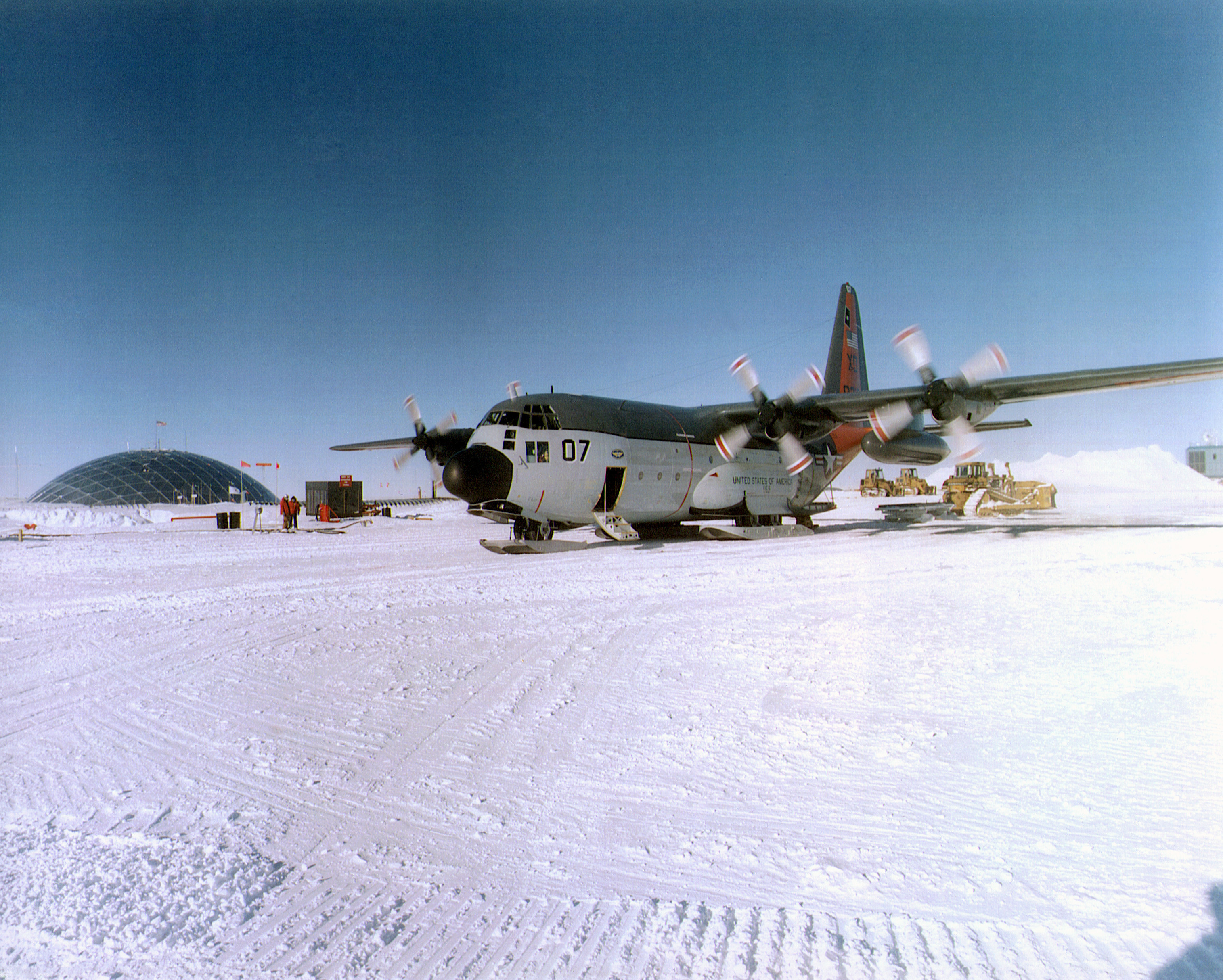
C-130 South Pole
C13 or C-13 may be: * French Defence, Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings code * C13 White Lead (Painting) Convention, 1921 * C13 grenade, the Canadian Forces designation for a M67 grenade * Autovia C-13, a highway in Catalonia in Spain * Caterpillar C13 Engine, an engine by Caterpillar Inc. * , a 1906 British C-class submarine * IEC 60320 C13, a polarised, three pole plug used in electric power cables * LNER Class C13, a 4-4-2T steam locomotive of 1907, built for suburban passenger services around London * OTO Melara C13 * Sauber C13, a 1994 racing car * Caldwell 13 (NGC 457, the Owl Cluster or ET Cluster), an open star cluster in the constellation Cassiopeia * The 13th century * in music, a chord with the structure 1 - 3 - 5 - b7 - 9 - 13 * Carbon-13, a natural stable isotope of carbon * Head and neck cancer, Malignant neoplasm of hypopharynx ICD-10 code * IEC 60320#C13/C14 coupler, C13/C14 Coupler, a class of cable connector used by most desktop computers {{Letter-Number Combination D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population, seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and List of cities in Brazil by population, its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 States of Brazil, states and the Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese language, Portuguese as an List of territorial entities where Portuguese is an official language, official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most Multiculturalism, multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass Immigration to Brazil, immigration from around the world; and the most populous Catholic Church by country, Roman Catholic-major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
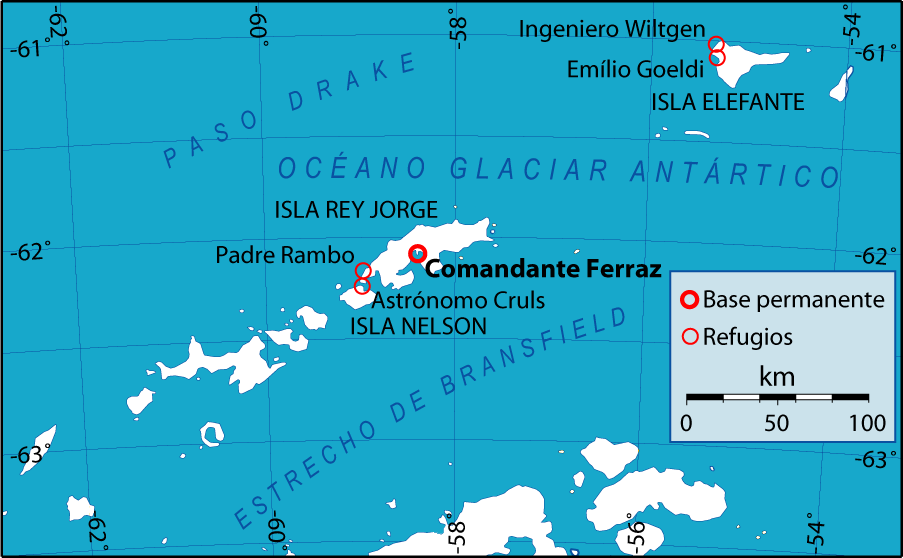
Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station
The Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station ( pt, Estação Antártica Comandante Ferraz) is a permanent Antarctic research station named after the Brazilian Navy Commander Luís Antônio de Carvalho Ferraz (1940-1982), who visited Antarctica many times with the British exploration team and managed to convince his government to create a self-guided Brazilian Antarctic Program. Located in Admiralty Bay ( pt, Baía do Almirantado), King George Island ( pt, Ilha do Rei George), near the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, 130 km north of the peninsula, the station began operating on 6 February 1984, brought to Antarctica in modules by the oceanographic ship ''Barão de Teffé'' and several other Brazilian naval ships. It now houses about 64 people, including researchers, technicians and staff, military and civilians. History The station was named after Navy Commander Luís Antônio de Carvalho Ferraz, a hydrographer and oceanographer who visited Antarctica twice on British vessels. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operación 90
Operación 90 (''Operation NINETY'') was the first Argentine ground expedition to the South Pole, conducted in 1965, by ten soldiers of the Argentine Army under then-Colonel Jorge Edgard Leal. It was performed to attempt to cement Argentina's claims to a portion of Antarctica, as well as for scientific reasons and to perfect polar exploration techniques. The operation was named after the target: 90 degree South latitude point (the geographic South Pole). It remains the only documented breach of the provisions of the 1959 Antarctic Treaty, which prohibits any military activity on the continent. Leal's team departed on six snowcat vehicles (believed to be Tucker Sno Cat based on the spelling used) from General Belgrano Army Base on October 26, 1965. The main group was preceded by a scouting four-men patrol on a sled drawn by 18 dogs. While the scouts remained at 83° 2″ S, Leal and his men reached the geographic South Pole on December 10. They then returned to Base Belgrano, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Deep Freeze
Operation Deep Freeze (OpDFrz or ODF) is codename for a series of United States missions to Antarctica, beginning with "Operation Deep Freeze I" in 1955–56, followed by "Operation Deep Freeze II", "Operation Deep Freeze III", and so on. (There was an initial operation before Admiral Richard Byrd proposed 'Deep Freeze'). Given the continuing and constant US presence in Antarctica since that date, "Operation Deep Freeze" has come to be used as a general term for US operations in that continent, and in particular for the regular missions to resupply US Antarctic bases, coordinated by the United States military. Task Force 199 was involved. Prior to International Geophysical Year The U.S. Navy already had a record of earlier exploration in Antarctica. As early as 1839, Captain Charles Wilkes led the first U.S. Naval expedition into Antarctic waters. In 1929, Admiral Richard E. Byrd established a naval base at Little America I, led an expedition to explore further inland, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
González Videla Antarctic Base
González Videla Base is an inactive research station on the Antarctic mainland at Waterboat Point in Paradise Bay. It is named after Chilean President Gabriel González Videla, who in the 1940s became the first chief of state of any nation to visit Antarctica. The station was active from 1951–58, and was reopened briefly in the early 1980s. Occasional summer visits are made by Chilean parties and tourists. On the north edge of the station there is a sign identifying Waterboat Point as an official historic site under the Antarctic Treaty. This was the place where the smallest ever wintering-over party (two men) spent a year and a day in 1921-1922. The two men, Thomas Bagshawe and M.C. Lester, had been part of the British Imperial Expedition, but their particular project, which involved flying a number of aircraft to the South Pole, was aborted. Nevertheless, they decided to stay over for the winter and made their shelter in an old whaling boat they found on this site. Their t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMAS Wyatt Earp
HMAS ''Wyatt Earp'' (formerly known as FV ''Fanefjord'', MV ''Wyatt Earp'', and HMAS ''Wongala'') was a motor vessel commissioned into the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) from 1939 to 1945 and again from 1947 to 1948. Early years The ship was constructed as a single-deck motor vessel named FV ''Fanejord'', built from pine and oak for the Norwegian herring fishing trade. While being a motorised vessel, her masts and booms normally used for cargo handling were capable of being rigged for sailing in an emergency. She was purchased by the American explorer and aviator, Lincoln Ellsworth, for his 1933 Antarctic expedition, refitted and sheathed with oak and armour plate, and renamed ''Wyatt Earp'' after the marshal of Dodge City and Tombstone, Arizona. ''Wyatt Earp'' was used on four of Ellsworth's Antarctic expeditions between 1933 and 1939, primarily as a base ship for his aircraft. Mount Wyatt Earp, discovered on Ellesworth's trans-Antarctic flight of Nov. 23, 1935 in the northern p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |