|
Mediterranean Ridge
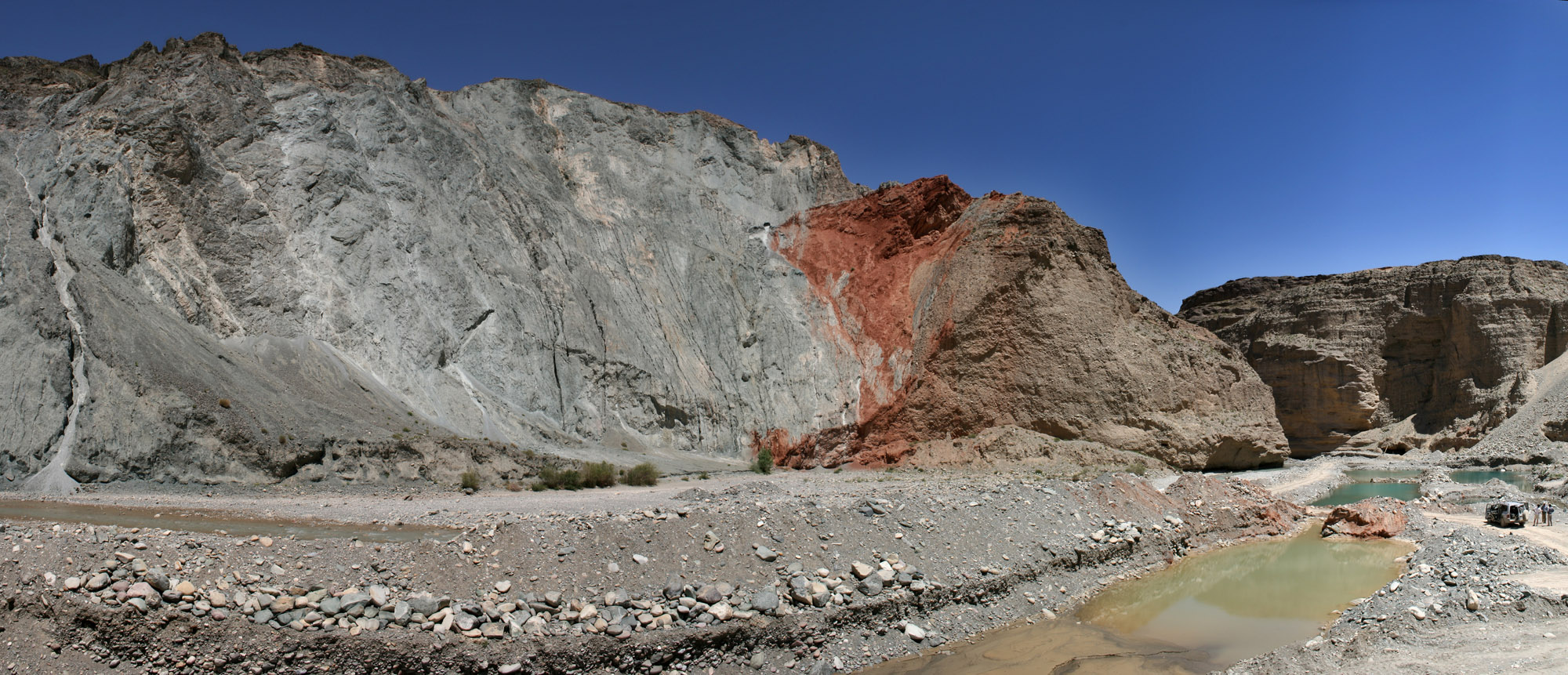
The Mediterranean Ridge is a wide ridge in the bed of the Mediterranean Sea, running along a rough quarter circle from Calabria, south of Crete, to the southwest corner of Turkey. It is an accretionary wedge caused by the African Plate subducting under the Eurasian and Anatolian plates. As the African Plate moves slowly north-northeastward, the sedimentary rocks covering the Mediterranean seafloor are being affected by active shortening, involving both thrust faulting and folding, lifting them up and forming the ridge. Along the ridge, five deep basins full of anoxic brine have been found (including the L'Atalante basin), where Messinian evaporite deposits of brine caught up in this ongoing orogeny have dissolved. In the far future, it could form part of a long high mountain range as the continued northward movement of the African Plate obliterates the eastern part of the Mediterranean Sea. Incipient collision with Africa The central section of the Mediterranean Ridge shows ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenic Arc
The Hellenic arc or Aegean arc is an arcuate mountain chain of the southern Aegean Sea located on the southern margin of the Aegean Sea Plate. Geologically it results from the subduction of the African Plate under it along the Hellenic subduction zone. The Hellenic Trench trends parallel to its southern side. The Aegean Sea Plate, a microplate, is often considered part of the Eurasian Plate from which it is in the process of diverging. The arc itself is mainly marine, the mountaintops appearing as islands in the Ionian Sea, Crete and its environs, or in the Dodecanese group. It encroaches on mainland terrain in the Peloponnesus, on Crete, on Rhodes, and on the southern coast of Anatolia, thus being encompassed by both Greece and Turkey. The direction of subduction is northward. Locations on the arc or near it on the north side are therefore called "outer" as they are at the outer margin of the plate. Locations further north are "inner." Generally the motion of subduction is from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fold (geology)
In structural geology, a fold is a stack of originally planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, that are bent or curved during permanent deformation. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to mountain-sized folds. They occur as single isolated folds or in periodic sets (known as ''fold trains''). Synsedimentary folds are those formed during sedimentary deposition. Folds form under varied conditions of stress, pore pressure, and temperature gradient, as evidenced by their presence in soft sediments, the full spectrum of metamorphic rocks, and even as primary flow structures in some igneous rocks. A set of folds distributed on a regional scale constitutes a fold belt, a common feature of orogenic zones. Folds are commonly formed by shortening of existing layers, but may also be formed as a result of displacement on a non-planar fault (''fault bend fold''), at the tip of a propagating fault (''fault propagation fold''), by differential compaction or due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
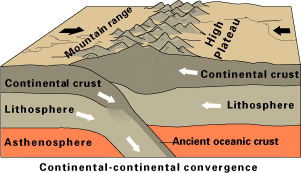
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Geology
Regional geology is the geological study of large-scale regions. Usually, it encompasses multiple geological disciplines to piece together the history of an area. It is the geologic equivalent of regional geography. The size and the borders of each region are defined by geologically significant boundaries and by the occurrence of geologic processes. Examples of geologically significant boundaries are the interfingering facies change in sedimentary deposits when discussing a sedimentary basin system, or the leading or boundary thrust of an orogen. Africa * Geology of Africa ** Geology of Chad ** Geology of Egypt ** Geology of Madagascar ** Geology of Rwanda ** Geology of Togo Antarctica * Geology of Antarctica Asia * Geology of Asia ** Geology of Armenia ** Geology of Azerbaijan ** Geology of Bangladesh ** Geology of China ***Geology of Fujian ** Geology of Georgia (country) ** Geology of Hong Kong ** Geology of India *** Geology of Sikkim ** Geology of Indonesia ** Geology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multibeam Echosounder
A multibeam echosounder (MBES) is a type of sonar that is used to map the seabed. It emits acoustic waves in a fan shape beneath its transceiver. The time it takes for the sound waves to reflect off the seabed and return to the receiver is used to calculate the water depth. Unlike other sonars and echo sounders, MBES uses beamforming to extract directional information from the returning soundwaves, producing a swath of depth soundings from a single ping. History and progression Multibeam sonar sounding systems, also known as ''swathe'' (British English) or ''swath'' (American English), originated for military applications. The Sonar Array Sounding System (SASS) was developed in the early 1960s by the US Navy, in conjunction with General Instrument to map large swaths of the ocean floor to assist the underwater navigation of its submarine force. SASS was tested aboard the USS ''Compass Island'' (AG-153). The final array system, composed of sixty-one one degree beams with a swa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between longitudes E16 and E25, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, also known as '' Pentapolis'' ("Five Cities") in antiquity, was part of the Roman province of Crete and Cyrenaica, later divided into ''Libya Pentapolis'' and ''Libya Sicca''. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as ''Barqa'', after the city of Barca. Cyrenaica became an Italian colony in 1911. After the 1934 formation of Libya, the Cyrenaica province was designated as one of the three primary provinces of the country. During World War II, it fell under British military and civil administration from 1943 until 1951, and finally in the Kingdom of Libya from 1951 until 1963. The region that used to be Cyrenaica officially until 1963 has formed seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messinian Evaporite
The Messinian evaporite deposit is a geological deposit of evaporites which was found on Sicily and named after the city of Messina. It was later found to underlie much of the bed of the Mediterranean Sea, including the L'Atalante basin. It was formed during the Messinian salinity crisis The Messinian salinity crisis (MSC), also referred to as the Messinian event, and in its latest stage as the Lago Mare event, was a geological event during which the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete desiccation (d .... References Regional geology Geologic formations of Europe Geology of Italy {{Europe-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Atalante Basin
L'Atalante basin is a hypersaline brine lake at the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea about west of the island of Crete. It is named for the French ''L'Atalante'', one of the oceanographic research vessels involved in its discovery in 1993. L'Atalante and its neighbors the Urania and Discovery deep hyper saline anoxic basins (DHABs) are at most 35,000 years old. They were formed by Messinian evaporite salt deposits dissolving out of the Mediterranean Ridge and collecting in abyssal depressions about deep. L'Atalante is the smallest of the three; its surface begins at about below sea level. Description and biology The L'Atalante basin's salinity is near saturation at 365 (about 8 times that of ordinary seawater), which prevents it from mixing with the oxygenated waters above; therefore, it is completely anoxic. The approximately halocline between the seawater above and brine below teems with bacterial and archaeal cells: they are chemoautotrophs, which feed on ammonia from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for brining foods) up to about 26% (a typical saturated solution, depending on temperature). Brine forms naturally due to evaporation of ground saline water but it is also generated in the mining of sodium chloride. Brine is used for food processing and cooking (pickling and brining), for de-icing of roads and other structures, and in a number of technological processes. It is also a by-product of many industrial processes, such as desalination, so it requires wastewater treatment for proper disposal or further utilization (fresh water recovery). In nature Brines are produced in multiple ways in nature. Modification of seawater via evaporation results in the concentration of salts in the residual fluid, a characteristic geologic deposit call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anoxic Sea Water
Anoxic waters are areas of sea water, fresh water, or groundwater that are depleted of dissolved oxygen. The US Geological Survey defines anoxic groundwater as those with dissolved oxygen concentration of less than 0.5 milligrams per litre. Anoxic waters can be contrasted with Hypoxia (environmental), hypoxic waters, which are low (but not lacking) in dissolved oxygen. This condition is generally found in areas that have restricted water exchange. In most cases, oxygen is prevented from reaching the deeper levels by a physical barrier, as well as by a pronounced density stratification, in which, for instance, heavier hypersaline waters rest at the bottom of a basin. Anoxic conditions will occur if the rate of redox, oxidation of organic matter by bacteria is greater than the supply of dissolved oxygen. Anoxic waters are a natural phenomenon, and have occurred throughout geological history. The Permian–Triassic extinction event, a mass extinction of species from the world's oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular ''klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is referred to as a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)