|
Marcus Claudius Fronto
Marcus Claudius Fronto (killed in battle AD 170) was a Roman senator and Consul, and a general in the Imperial Roman army during the reigns of emperors Antoninus Pius (r. 138–61), Marcus Aurelius (r. 161–80), and Lucius Verus (r. 161–69). Sources Despite his important military role under Marcus Aurelius, Fronto's existence is only known from two inscriptions, both of which contain a summary of his career: # CIL III 01457, a dedication to Fronto (possibly on the base of a statue), when he was governor of Dacia in 168–170, by the citizens of Colonia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, a Roman colony, in which he is praised as "patron, bravest of men, most generous of governors" (''patrono fortissimo viro amplissimo praeside'') # CIL VI 41142, an epitaph engraved on the plinth of his statue, erected in his honour in the Forum of Trajan in Rome. The lack of mention of Fronto in surviving literary sources for this period is unsurprising, as they are extremely sparse and fragmentary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senator
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the Roman monarchy in 509 BC; the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC; the division of the Roman Empire in AD 395; and the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476; Justinian's attempted reconquest of the west in the 6th century, and lasted well into the Eastern Roman Empire's history. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, most of the time the Senate was little more than an advisory council to the king, but it also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive magistrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetor
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected '' magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge various duties. The functions of the magistracy, the ''praetura'' (praetorship), are described by the adjective: the ''praetoria potestas'' (praetorian power), the ''praetorium imperium'' (praetorian authority), and the ''praetorium ius'' (praetorian law), the legal precedents established by the ''praetores'' (praetors). ''Praetorium'', as a substantive, denoted the location from which the praetor exercised his authority, either the headquarters of his '' castra'', the courthouse (tribunal) of his judiciary, or the city hall of his provincial governorship. History of the title The status of the ''praetor'' in the early republic is unclear. The traditional account from Livy claims that the praetorship was created by the Sextian-Licinian Rogat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland , source1_coordinates= , source1_elevation = , source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein , source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland , source2_coordinates= , source2_elevation = , source_confluence = Reichenau , source_confluence_location = Tamins, Graubünden, Switzerland , source_confluence_coordinates= , source_confluence_elevation = , mouth = North Sea , mouth_location = Netherlands , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = , basin_size = , tributaries_left = , tributaries_right = , custom_label = , custom_data = , extra = The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label= Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label= Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label= Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonna
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region, Germany's largest metropolitan area, with over 11 million inhabitants. It is a university city and the birthplace of Ludwig van Beethoven. Founded in the 1st century BC as a Roman settlement in the province Germania Inferior, Bonn is one of Germany's oldest cities. It was the capital city of the Electorate of Cologne from 1597 to 1794, and residence of the Archbishops and Prince-electors of Cologne. From 1949 to 1990, Bonn was the capital of West Germany, and Germany's present constitution, the Basic Law, was declared in the city in 1949. The era when Bonn served as the capital of West Germany is referred to by historians as the Bonn Republic. From 1990 to 1999, Bonn served as the seat of government – but no longer capital – of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio I Minervia
Legio I Minervia ( First Legion "Minervan", i.e., "devoted to the goddess Minerva") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in AD 82 by emperor Domitian (r. 81–96), for his campaign against the Germanic tribe of the Chatti. Its cognomen refers to the goddess Minerva, the legion's protector. There are still records of the I ''Minervia'' in the Rhine border region in the middle of the 4th century. The legion's emblem is an image of goddess Minerva. Legio I ''Minervia'' first, and main, camp was in the city of ''Bonna'' (modern Bonn), in the province of Germania Inferior. In 89, they suppressed a revolt of the governor of Germania Superior. Due to this, Domitian gave them the cognomen ''Pia Fidelis Domitiana'' (loyal and faithful to Domitian) to acknowledge their support. History Between 101 and 106, the legion fought the Dacian Wars of emperor Trajan, commanded by Hadrian, the future emperor. The emblem with Minerva figure appears on the column of Traj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman–Parthian War Of 161–166
The Roman–Parthian War of 161–166 (also called the Parthian War of Lucius Verus) was fought between the Roman and Parthian Empires over Armenia and Upper Mesopotamia. It concluded in 166 after the Romans made successful campaigns into Lower Mesopotamia and Media and sacked Ctesiphon, the Parthian capital. Origins to Lucius' dispatch, 161–162 On his deathbed in the spring of 161, Emperor Antoninus Pius had spoken of nothing but the state and the foreign kings who had wronged him. One of those kings, Vologases IV of Parthia, made his move in late summer or early autumn 161. Vologases entered the Kingdom of Armenia (then a Roman client state), expelled its king and installed his own— Pacorus, an Arsacid like himself. At the time of the invasion, the governor of Syria was Lucius Attidius Cornelianus. Attidius had been retained as governor even though his term had ended in 161, presumably to avoid giving the Parthians the chance to wrong-foot his replacem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube River
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. Its drainage basin extends into nine more countries. The largest cities on the river are Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade and Bratislava, all of which are the capitals of their respective countries; the Danube passes through four capital cities, more than any other river in the world. Five more capital cities lie in the Danube's basin: Bucharest, Sofia, Zagreb, Ljubljana and Sarajevo. The fourth-largest city in its basin is Munich, the capital of Bavaria, standing on the Isar River. The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through much of Central and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
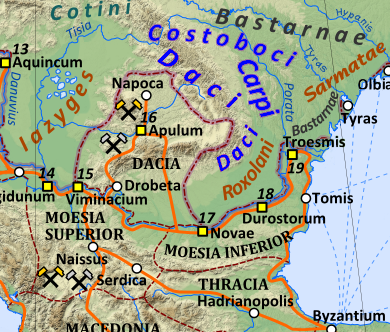
Moesia Inferior
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia (Moesia Superior), Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine (Moesia Inferior). Geography In ancient geographical sources, Moesia was bounded to the south by the Haemus ( Balkan Mountains) and Scardus (Šar) mountains, to the west by the Drinus (Drina) river, on the north by the Donaris (Danube) and on the east by the Euxine (Black Sea). History The region was inhabited chiefly by Thracians, Dacians ( Thraco-Dacian), Illyrian and Thraco-Illyrian peoples. The name of the region comes from Moesi, Thraco-Dacian peoples who lived there before the Roman conquest. Parts of Moesia belonged to the polity of Burebista, a Getae king who established his rule over a large p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio XI Claudia
Legio XI Claudia ("Claudius' Eleventh Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. The legion was levied by Julius Caesar for his campaign against the Nervii. XI ''Claudia'' dates back to the two legions (the other was the XIIth) recruited by Julius Caesar to invade Gallia in 58 BC, and it existed at least until the early 5th century, guarding lower Danube in Durostorum (modern Silistra, Bulgaria). History Founding and Service in the Late Republic Legio XI Claudia, along with Legio XII Fulminata, was a Roman Legion levied by Julius Caesar in 58 BC in Cisalpine Gaul, for his war against the Nervii. They likely were present at the Siege of Alesia. After his campaigns in Gaul, civil war broke out between Julius Caesar and Pompey, both of whom were triumvirs, and in January, 49 BC, Caesar invaded Italy with Legio XI serving in his army. They fought in 48 BC at Dyrrhachium and Pharsalus, but were disbanded in 45 BC and settled in Central Italy around the area of Bov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire (27 BC – AD 476). Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 equites (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republican period of Rome (the infantry were split into 10 cohorts each of four maniples of 120 legionaries), to 4,800 legionaries (in 10 cohorts of 6 centuries of 80 legionaries) during Caesar's age, to 5,280 men plus 120 auxiliaries in the Imperial period (split into 10 cohorts, nine of 480 men each, with the first cohort being double-strength at 960 men). It should be noted the above numbers are typical field strengths while "paper strength" was sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Tribune
A military tribune (Latin ''tribunus militum'', "tribune of the soldiers") was an officer of the Roman army who ranked below the legate and above the centurion. Young men of Equestrian rank often served as military tribune as a stepping stone to the Senate. The ''tribunus militum'' should not be confused with the elected political office of tribune of the people ''(tribunus plebis)'' nor with that of '' tribunus militum consulari potestate''. Early Rome The word ''tribunus'' derives from '' tribus'', "tribe". In Rome's earliest history, each of the three tribes (Ramnes, Luceres, and Tities) sent one commander when an army was mustered, since there was no standing army. The tribunes were commanders of the original legion of 3,000. By the time of the Greek historian Polybius (d. 118 BC), the tribunes numbered six, and they were appointed by the consuls. However, the process by which tribunes were chosen and assigned is complex and varies at different times. Republican peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |