|
Mycoplasma Genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (''MG'', commonly known as Mgen) is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in humans. Medical reports published in 2007 and 2015 state that Mgen is becoming increasingly common. Resistance to multiple antibiotics is becoming prevalent, including to azithromycin, which until recently was the most reliable treatment. The bacteria was first isolated from the urogenital tract of humans in 1981, and was eventually identified as a new species of ''Mycoplasma'' in 1983. It can cause negative health effects in men and women. It also increases the risk factor for HIV spread with higher occurrences in those previously treated with the azithromycin antibiotics. Specifically, it causes urethritis in both men and women, and also cervicitis and pelvic inflammation in women. It presents clinically similar symptoms to that of ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' infection and has shown hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Map
Gene maps help describe the spatial arrangement of genes on a chromosome. Genes are designated to a specific location on a chromosome known as the locus and can be used as molecular markers to find the distance between other genes on a chromosome. Maps provide researchers with the opportunity to predict the inheritance patterns of specific traits, which can eventually lead to a better understanding of disease-linked traits. The genetic basis to gene maps is to provide an outline that can potentially help researchers carry out DNA sequencing. A gene map helps point out the relative positions of genes and allows researchers to locate regions of interest in the genome. Genes can then be identified quickly and sequenced quickly. Two approaches to generating gene maps include physical mapping and genetic mapping. Physical mapping utilizes molecular biology techniques to inspect chromosomes. These techniques consequently allow researchers to observe chromosomes directly so that a map ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', also known as ''gonococcus'' (singular), or ''gonococci'' (plural), is a species of Gram-negative diplococci bacteria isolated by Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser, Albert Neisser in 1879. It causes the sexually transmitted infection, sexually transmitted genitourinary infection gonorrhea as well as other forms of gonococcal disease including disseminated gonococcemia, septic arthritis, and gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum. It is oxidase test, oxidase positive and aerobic, and it survives phagocyte, phagocytosis and grows inside neutrophils. Microbiological culture, Culturing it requires carbon dioxide supplementation and enriched agar (chocolate agar) with various antibiotics (Thayer–Martin agar, Thayer–Martin). It exhibits antigenic variation through genetic recombination of its pilus, pili and surface proteins that interact with the immune system. Sexual transmission is through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Sexual transmission may be prevented throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
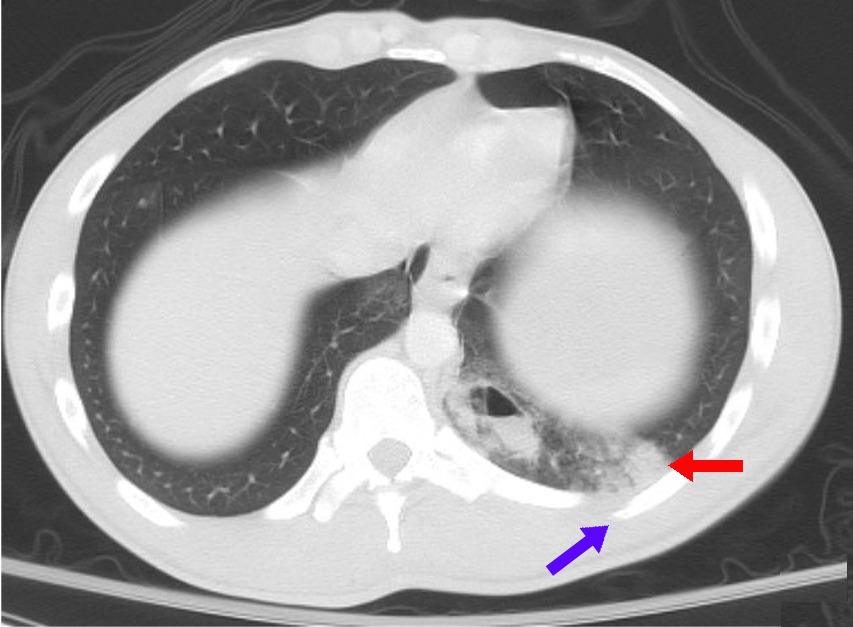
Mucopurulent Discharge
Mucopurulent discharge is the emission or secretion of fluid containing mucus and pus (''muco-'' pertaining to ''mucus'' and ''purulent'' pertaining to ''pus'') from the eye, nose, cervix, vagina or other part of the body due to infection and inflammation. Types include: *In ophthalmology, mucopurulent discharge from the eyes, and caught in the eyelashes, is a hallmark sign of bacterial conjunctivitis. The normal buildup of tears, mucus, and dirt (compare rheum) that appears at the edge of the eyelids after sleep is not mucopurulent discharge, as it does not contain pus. *Vaginal discharge Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, amou ... References "Conjunctivitis: A Systematic Review of Diagnosis and Treatment" – NCBI Symptoms {{symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asymptomatic. Infections of this kind are usually called subclinical infections. Diseases such as mental illnesses or psychosomatic conditions are considered subclinical if they present some individual symptoms but not all those normally required for a clinical diagnosis. The term clinically silent is also found. Producing only a few, mild symptoms, disease is paucisymptomatic. Symptoms appearing later, after an asymptomatic incubation period, mean a pre-symptomatic period has existed. Importance Knowing that a condition is asymptomatic is important because: * It may develop symptoms later and only then require treatment. * It may resolve itself or become benign. * It may be contagious, and the contribution of asymptomatic and pre-symptomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Genome
Artificial gene synthesis, or simply gene synthesis, refers to a group of methods that are used in synthetic biology to construct and assemble genes from nucleotides '' de novo''. Unlike DNA synthesis in living cells, artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, allowing virtually any DNA sequence to be synthesized in the laboratory. It comprises two main steps, the first of which is solid-phase DNA synthesis, sometimes known as DNA printing. This produces oligonucleotide fragments that are generally under 200 base pairs. The second step then involves connecting these oligonucleotide fragments using various DNA assembly methods. Because artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, it is theoretically possible to make a completely synthetic DNA molecule with no limits on the nucleotide sequence or size. Synthesis of the first complete gene, a yeast tRNA, was demonstrated by Har Gobind Khorana and coworkers in 1972. Synthesis of the first peptide- and protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimal Genome
{{disambiguation ...
Minimal may refer to: * Minimal (music genre), art music that employs limited or minimal musical materials * "Minimal" (song), 2006 song by Pet Shop Boys * Minimal (supermarket) or miniMAL, a former supermarket chain in Germany and Poland * Minimal (''Dungeons & Dragons''), a creature of magically reduced size in the game ''Dungeons & Dragons'' * Minimal (chocolate), a bean to bar chocolate store in Japan, featured in '' Kantaro: The Sweet Tooth Salaryman'' * Minimal (clothing), an Indonesia clothing-retail company that worked with fashion model Ayu Gani See also * *Minimalism (other) *Maximal (other) *Minimisation (other) *Minimal prime (other) In mathematics, the term minimal prime may refer to *Minimal prime ideal In mathematics, especially in commutative algebra, certain prime ideals called minimal prime ideals play an important role in understanding rings and modules. The notion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-replication
Self-replication is any behavior of a dynamical system that yields construction of an identical or similar copy of itself. Biological cells, given suitable environments, reproduce by cell division. During cell division, DNA is replicated and can be transmitted to offspring during reproduction. Biological viruses can replicate, but only by commandeering the reproductive machinery of cells through a process of infection. Harmful prion proteins can replicate by converting normal proteins into rogue forms. Computer viruses reproduce using the hardware and software already present on computers. Self-replication in robotics has been an area of research and a subject of interest in science fiction. Any self-replicating mechanism which does not make a perfect copy (mutation) will experience genetic variation and will create variants of itself. These variants will be subject to natural selection, since some will be better at surviving in their current environment than others and will ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoarchaeum Equitans
''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains of this microbe were also found on the Sub-polar Mid Oceanic Ridge, and in the Obsidian Pool in Yellowstone National Park. Since it grows in temperatures approaching boiling, at about 80 degrees Celsius, it is considered to be a thermophile. It grows best in environments with a pH of 6, and a salinity concentration of 2%. ''Nanoarchaeum'' appears to be an obligate symbiont on the archaeon ''Ignicoccus''; it must be in contact with the host organism to survive. ''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' cannot synthesize lipids but obtains them from its host. Its cells are only 400 nm in diameter, making it the smallest known living organism, and the smallest known archaeon. ''N. equitans'' genome consists of a single circular chromosome, and has an average G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Size
Genome size is the total amount of DNA contained within one copy of a single complete genome. It is typically measured in terms of mass in picograms (trillionths (10−12) of a gram, abbreviated pg) or less frequently in daltons, or as the total number of nucleotide base pairs, usually in megabases (millions of base pairs, abbreviated Mb or Mbp). One picogram is equal to 978 megabases. In diploid organisms, genome size is often used interchangeably with the term C-value. An organism's complexity is not directly proportional to its genome size; total DNA content is widely variable between biological taxa. Some single-celled organisms have much more DNA than humans, for reasons that remain unclear (see non-coding DNA and C-value enigma). Origin of the term The term "genome size" is often erroneously attributed to a 1976 paper by Ralph Hinegardner, even in discussions dealing specifically with terminology in this area of research (e.g., Greilhuber 2005). Notably, Hinegardner u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
