|
Myanmar Architecture
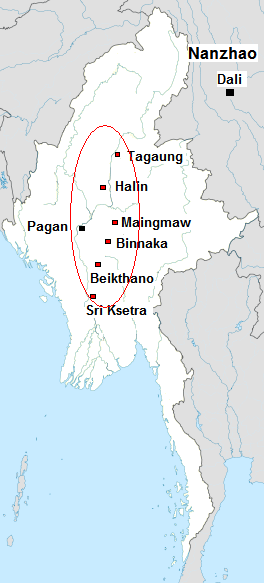
The architecture of Myanmar (formerly known as Burma), in Southeast Asia, includes architectural styles which reflect the influence of neighboring and Western nations and modernization. The country's most prominent buildings include Buddhist pagodas, stupas and temples, British colonial buildings, and modern renovations and structures. Myanmar's traditional architecture is primarily used for worship, pilgrimage, storage of Buddhist relics, political activism and tourism. History and influences Early Indian influence Much of Myanmar's architecture is tied to ancient Indian culture, and can be traced to the country's earliest known inhabitants. During the Pyu period, cylindrical stupas with four archways—often with a '' hti'' (umbrella) on top—were built. The Mon and Pyu people were the first two influential groups to migrated to Myanmar, and the first Indo-Chinese adherents of Theravada Buddhism. Beikthano, one of the first Pyu centers, contains urbanesque foundations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, John Wells explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a non-rhotic variety of English, in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: [ˈmjænmɑː, ˈbɜːmə]. So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as [mɑːr] or of Burma as [bɜːrmə] by some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a spelling pronunciation based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. The final ''r'' in ''Myanmar'' was not intended for pronunciation and is there to ensure that the final a is pronounced with the broad a, broad ''ah'' () in "father". If the Burmese name my, မြန်မာ, label=none were spelled "Myanma" in English, this would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It includes the countries of Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam, with peninsular Malaysia sometimes also being included. The term Indochina (originally Indo-China) was coined in the early nineteenth century, emphasizing the historical cultural influence of culture of India, Indian and Chinese culture, Chinese civilizations on the area. The term was later adopted as the name of the colony of French Indochina (today's Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam). Today, the term, Mainland Southeast Asia, in contrast to Maritime Southeast Asia, is more commonly referenced. Terminology The origins of the name Indo-China are usually attributed jointly to the Danish-French geographer Conrad Malte-Brun, who referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture. Stucco can be applied on construction materials such as metal, expanded metal lath, concrete, cinder block, or clay brick and adobe for decorative and structural purposes. In English, "stucco" sometimes refers to a coating for the outside of a building and " plaster" to a coating for interiors; as described below, however, the materials themselves often have little to no differences. Other European languages, notably Italian, do not have the same distinction; ''stucco'' means ''plaster'' in Italian and serves for both. Composition The basic composition of stucco is cement, water, and sand. The difference in nomenclature between stucco, plaster, and mortar is based more on use than composition. Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
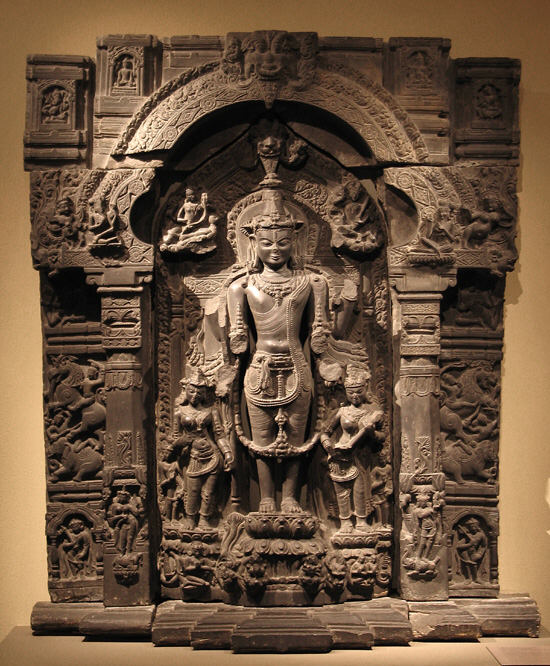
Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire (r. 750-1161 CE) was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix ''Pāla'' ("protector" in Prakrit). The empire was founded with the election of Gopāla as the emperor of Gauda in late eighth century AD. The Pala stronghold was located in Bengal and eastern Bihar, which included the major cities of Gauḍa, Vikramapura, Pāṭaliputra, Monghyr, Somapura, Ramavati ( Varendra), Tāmralipta and Jaggadala. The Pālas were astute diplomats and military conquerors. Their army was noted for its vast war elephant corps. Their navy performed both mercantile and defensive roles in the Bay of Bengal. At its zenith under emperors Dharmapala and Devapala in the early ninth century, the Pala empire extended their dominance into the northern Indian region, with its territory stretching across the Gangetic pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brick
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured construction blocks. Bricks can be joined using mortar, adhesives or by interlocking them. Bricks are usually produced at brickworks in numerous classes, types, materials, and sizes which vary with region and time period, and are produced in bulk quantities. ''Block'' is a similar term referring to a rectangular building unit composed of similar materials, but is usually larger than a brick. Lightweight bricks (also called lightweight blocks) are made from expanded clay aggregate. Fired bricks are one of the longest-lasting and strongest building materials, sometimes referred to as artificial stone, and have been used since circa 4000 BC. Air-dried bricks, also known as mud-bricks, have a history older than fired bricks, and have an add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them. A dome can rest directly upon a rotunda wall, a drum, or a system of squinches or pendentives used to accommodate the transition in shape from a rectangular or square space to the round or polygonal base of the dome. The dome's apex may be closed or may be open in the form of an oculus, which may itself be covered with a roof lantern and cupola. Domes have a long architectural lineage that extends back into prehistory. Domes were built in ancient Mesopotamia, and they have been found in Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, and Chinese architecture in the ancient world, as well as among a number of indigenous building traditions throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
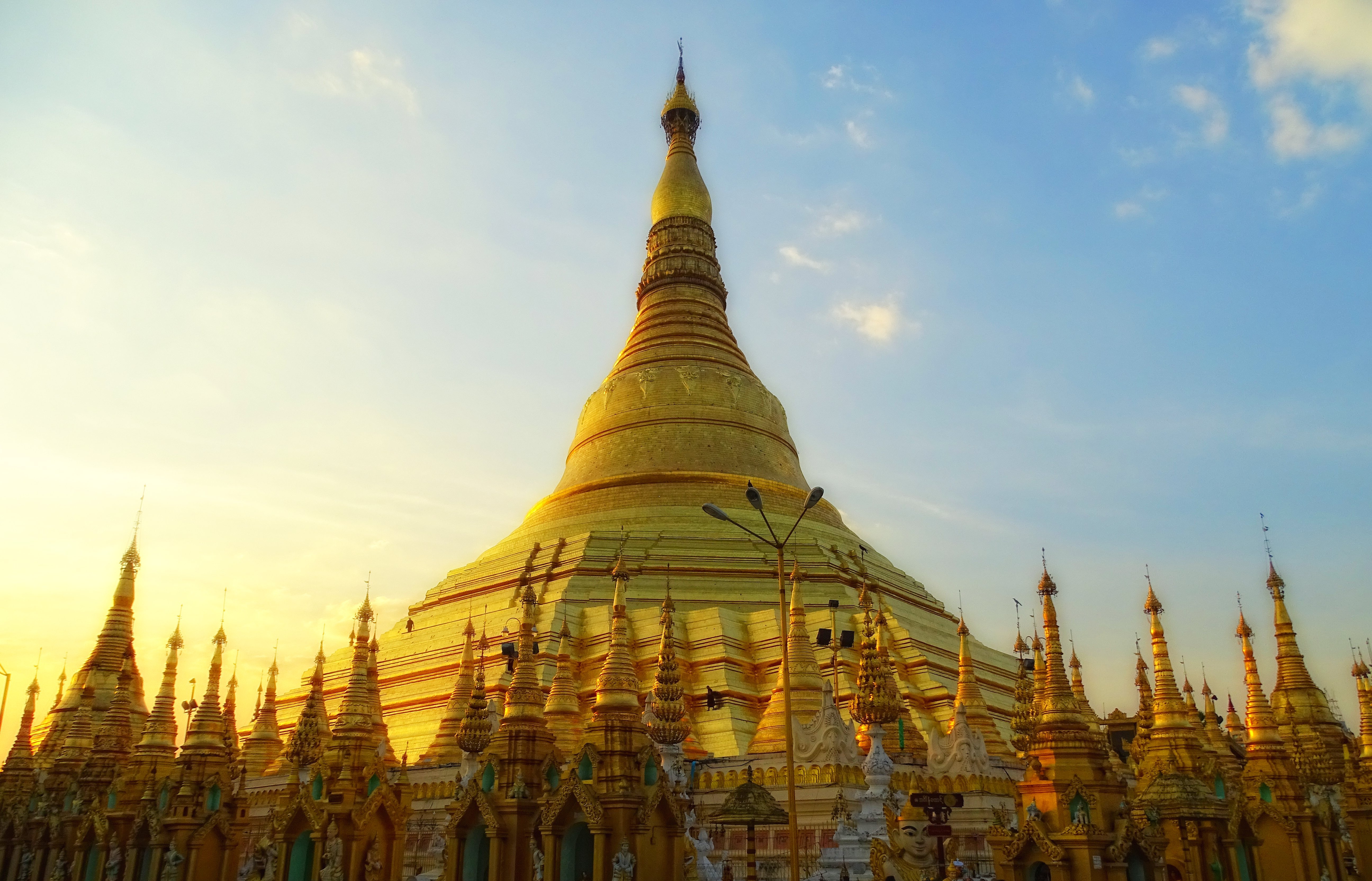
Buddhist Architecture
Buddhist religious architecture developed in the Indian subcontinent. Three types of structures are associated with the religious architecture of early Buddhism: monasteries ( viharas), places to venerate relics ( stupas), and shrines or prayer halls (chaityas, also called ''chaitya grihas''), which later came to be called temples in some places. The initial function of a stupa was the veneration and safe-guarding of the relics of Gautama Buddha. The earliest archaeologically known example of a stupa is the relic stupa located in Vaishali, Bihar in India. In accordance with changes in religious practice, stupas were gradually incorporated into chaitya-grihas (prayer halls). These are exemplified by the complexes of the Ajanta Caves and the Ellora Caves ( Maharashtra). The Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar is another well-known example. The pagoda is an evolution of the Indian stupas. Early development in India A characteristic new development at Buddhist relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
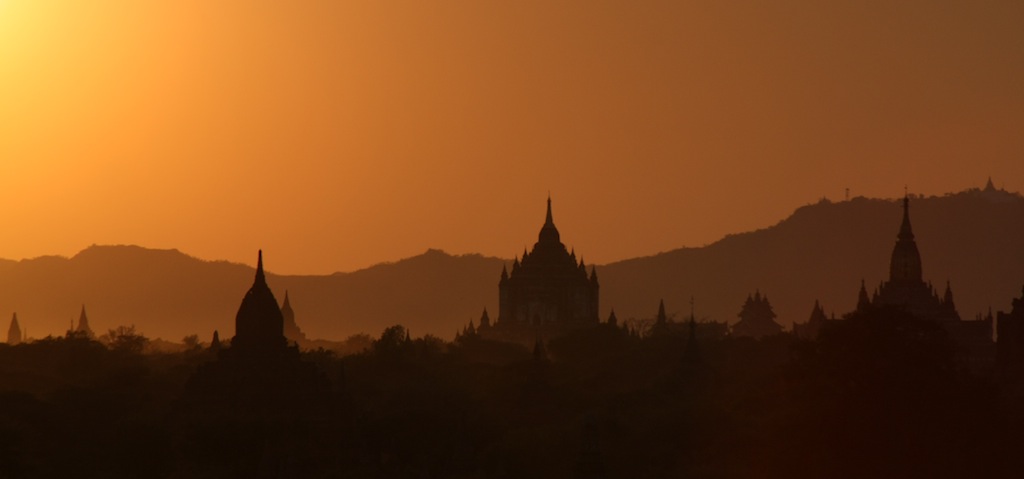
Pagan Kingdom
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. By t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrawaddy River
The Irrawaddy River ( Ayeyarwady River; , , from Indo-Aryan languages, Indic ''revatī'', meaning "abounding in riches") is a river that flows from north to south through Myanmar (Burma). It is the country's largest river and most important commercial waterway. Originating from the confluence of the N'Mai River, N'mai and Mali River, Mali rivers, it flows relatively straight North-South before emptying through the Irrawaddy Delta in the Ayeyarwady Region into the Andaman Sea. Its drainage basin of about covers a large part of Burma. After Rudyard Kipling's poem, it is sometimes referred to as 'Mandalay (poem), The Road to Mandalay'. As early as the sixth century, the river was used for trade and transport. Having developed an extensive network of irrigation, irrigation canals, the river became important to the British Empire after it had colonized Burma. The river is still as vital today, as a considerable amount of (export) goods and traffic moves by river. Rice is produced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anawrahta
Anawrahta Minsaw ( my, အနော်ရထာ မင်းစော, ; 11 May 1014 – 11 April 1077) was the founder of the Pagan Empire. Considered the father of the Burmese nation, Anawrahta turned a small principality in the dry zone of Upper Burma into the first Burmese Empire that formed the basis of modern-day Burma (Myanmar).Harvey 1925: 34Htin Aung 1967: 38 Historically verifiable Burmese history begins with his accession to the Pagan throne in 1044.Coedès 1968: 133, 148–149, 155 Anawrahta unified the entire Irrawaddy valley for the first time in history, and placed peripheral regions such as the Shan States and Arakan (Rakhine) under Pagan's suzerainty. He successfully stopped the advance of Khmer Empire into Tenasserim coastline and into Upper Menam valley, making Pagan one of two main kingdoms in mainland Southeast Asia. A strict disciplinarian, Anawrahta implemented a series of key social, religious and economic reforms that would have a lasting impa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagan
Bagan (, ; formerly Pagan) is an ancient city and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Mandalay Region of Myanmar. From the 9th to 13th centuries, the city was the capital of the Bagan Kingdom, the first kingdom that unified the regions that would later constitute Myanmar. During the kingdom's height between the 11th and 13th centuries, more than 10,000 Buddhist temples, pagodas and monasteries were constructed in the Bagan plains alone, of which the remains of over 2200 temples and pagodas survive. The Bagan Archaeological Zone is a main attraction for the country's nascent tourism industry. Etymology Bagan is the present-day standard Burmese pronunciation of the Burmese word ''Pugan'' ( my-Mymr, ပုဂံ), derived from Old Burmese ''Pukam'' ( my-Mymr, ပုကမ်). Its classical Pali name is '' Arimaddanapura'' ( my-Mymr, အရိမဒ္ဒနာပူရ, lit. "the City that Tramples on Enemies"). Its other names in Pali are in reference to its extreme dry zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
