|
Muley Zidán
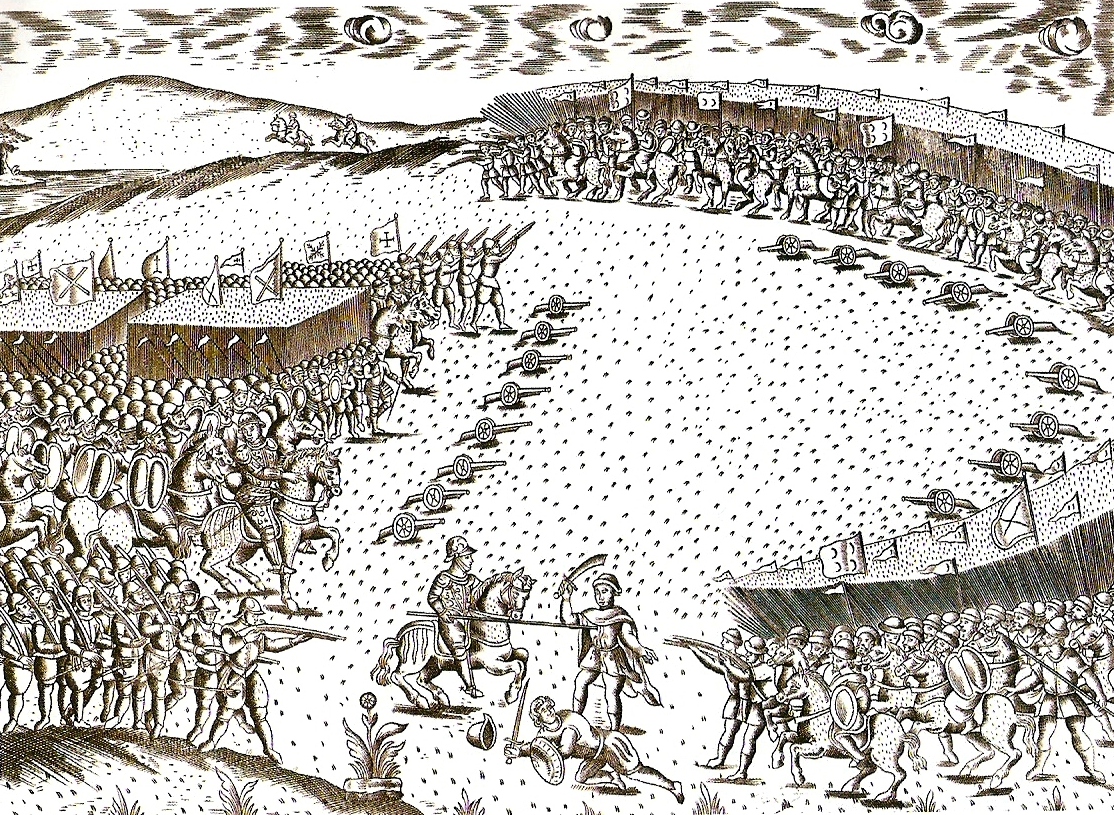
Zidan Abu Maali ( ar, زيدان أبو معالي) (? – September 1627; or Muley Zidan) was the embattled Saadi Sultan of Morocco from 1603 to 1627. He was the son and heir of Ahmad al-Mansur by his wife Lalla Aisha bint Abu Bakkar, a lady of the Chebanate tribe. He ruled only over the southern half of the country after his brother Mohammed esh Sheikh el Mamun took the northern half and a rebel from Tafilalt, Ahmed ibn Abi Mahalli, marched on Marrakesh claiming to be the Mahdi. This led Muley Zidan to be encircled in Safi amid other failed military campaigns against the rebellious north. These events were exacerbated by a context of chaos that ensued amid a plague pandemic which left a third of the country dead. His reign saw the end of the Anglo-Spanish war (with the 1604 Treaty of London)—which broke the Anglo-Dutch axis that Morocco was relying upon as a means of protection from Spain, and so caused the Spanish navy to resume devastating raids on the Moroccan coast— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadi Dynasty
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, السعديون, translit=as-saʿdiyyūn) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arabs, Arab Moroccan Sharifism, Sharifian dynasty. The dynasty's rise to power started in 1510 when Abu Abdallah al-Qaim, Muhammad al-Qa'im was declared leader of the tribes of the Sous valley in their resistance against the Portugal, Portuguese who occupied Agadir and other coastal cities. Al-Qai'm's son, Ahmad al-Araj, secured control of Marrakesh by 1525 and, after a period of rivalry, his brother Mohammed ash-Sheikh, Muhammad al-Shaykh captured Agadir from the Portuguese and eventually captured Fez, Morocco, Fez from the Wattasid dynasty, Wattasids, securing control over nearly all of Morocco. After Muhammad al-Shaykh's assassination by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in 1557 his son Abdallah al-Ghalib enjoyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahdi
The Mahdi ( ar, ٱلْمَهْدِيّ, al-Mahdī, lit=the Guided) is a Messianism, messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the Eschatology, end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad who will appear shortly before the Prophets in Islam, prophet Jesus in Islam, ʿĪsā (Jesus) and lead Muslims to rule the world. Though the Mahdi is not referenced in the Quran, and is absent from several List of hadith Books, canonical compilations of hadith – including the two most-revered Sunni hadith collections: ''Sahih al-Bukhari'' and ''Sahih Muslim'' – he is mentioned in other Hadith, hadith literature. The doctrine of the mahdi seems to have gained traction during the confusion and unrest of the religious and political upheavals of the first and second centuries of Islam. Among the first references to the Mahdi appear in the late 7th century, when the revolutionary Mukhtar al-Thaqafi, Mukhtar ibn Abi Uba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish language, Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Spain, Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larache
Larache ( ar, العرايش, al-'Araysh) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast, where the Loukkos River meets the Atlantic Ocean. Larache is one of the most important cities of the Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima region. Many civilisations and cultures have influenced the history of Larache, starting in the ancient city of Lixus during the 12th centuryBCE. Between the period of being a strategic Berber town and then a Phoenician trading centre to Morocco's independence era around the 1950s, Larache was a nexus for many cultures. History In 1471, the Portuguese settlers from Asilah and Tangier drove the inhabitants out of Larache, and again it remained uninhabited until the Saadi Sultan Mohammed ash-Sheikh decided to repopulate it and build a stronghold on the plateau above river Loukos. He constructed a fortress at the entrance to the port as a means of controlling access to the river. For a long time, attempts by the Portuguese, Spanish and French to take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidi Al-Ayachi
Sidi M'Hamed al-Ayachi (; ), also el-Ayachi or al-Ayashi ( – 1641), was a Moroccan marabout, warlord, and jihadist. The Sultan of Morocco, Mulay Zidan al-Nasir, had made him governor (''qā′id'') of Azmūr, but in 1627 he decided to secede and created his own state. Since the death of Ahmad al-Mansur in 1603, Morocco had progressively fallen into a state of anarchy due to his sons fighting for the thrones, it caused a loss of central authority beheld by the Sultan. With Morocco in a state of civil war, in 1610 to reinforce his power, Mohammed esh Sheikh el Mamun conceded to the Spanish the city of Larache and pledged of their alliance. However, they also seized the opportunity to capture al-Ma'mura in 1614. The Sultan's seeming inability to defend the country, infuriated Sidi al-Ayachi, and he began a counter-offensive against Spain, privateering against its shipping, and obtaining the help of the Moriscos and the English. He managed to re-capture al-Mamura, albeit temporarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies. James Fearon"Iraq's Civil War" in ''Foreign Affairs'', March/April 2007. For further discussion on civil war classification, see the section "Formal classification". The term is a calque of Latin '' bellum civile'' which was used to refer to the various civil wars of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. Most modern civil wars involve intervention by outside powers. According to Patrick M. Regan in his book ''Civil Wars and Foreign Powers'' (2000) about two thirds of the 138 intrastate conflicts between the end of World War II and 2000 saw international intervention, with the United States intervening in 35 of these conflicts. A civil war is a high-intensity conflict, often involving regular armed forces, that is sustained, org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchy
Anarchy is a society without a government. It may also refer to a society or group of people that entirely rejects a set hierarchy. ''Anarchy'' was first used in English in 1539, meaning "an absence of government". Pierre-Joseph Proudhon adopted ''anarchy'' and ''anarchist'' in his 1840 treatise ''What Is Property?'' to refer to anarchism, a new political philosophy and social movement that advocates stateless societies based on Free association (Marxism and anarchism), free and voluntary associations. Anarchists seek a system based on the abolition of all coercive hierarchy, in particular the state, and many advocate for the creation of a system of direct democracy, worker cooperatives or privatization. In practical terms, ''anarchy'' can refer to the curtailment or abolition of traditional forms of government and institutions. It can also designate a nation or any inhabited place that has no system of government or central rule. Anarchy is primarily advocated by individual anar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulay Al-Mansur
Ahmad al-Mansur ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد المنصور, Ahmad Abu al-Abbas al-Mansur, also al-Mansur al-Dahabbi (the Golden), ar, أحمد المنصور الذهبي; and Ahmed al-Mansour; 1549 in Fes – 25 August 1603, Fes) was the Saadi Sultan of Morocco from 1578 to his death in 1603, the sixth and most famous of all rulers of the Saadis. Ahmad al-Mansur was an important figure in both Europe and Africa in the sixteenth century. His powerful army and strategic location made him an important power player in the late Renaissance period. He has been described as "a man of profound Islamic learning, a lover of books, calligraphy and mathematics, as well as a connoisseur of mystical texts and a lover of scholarly discussions." Early life Ahmad was the fifth son of Mohammed ash-Sheikh who was the first Saadi sultan of Morocco. His mother was Lalla Masuda. After the murder of their father, Mohammed in 1557 and the following struggle for power, the two brothers Ahmad a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salé
Salé ( ar, سلا, salā, ; ber, ⵙⵍⴰ, sla) is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the right bank of the Bou Regreg river, opposite the national capital Rabat, for which it serves as a commuter town. Founded in about 1030 by the Banu Ifran, it later became a haven for pirates in the 17th century as an independent republic before being incorporated into Alaouite Morocco. The city's name is sometimes transliterated as Salli or Sallee. The National Route 6 connects it to Fez and Meknes in the east and the N1 to Kénitra in the north-east. It recorded a population of 890,403 in the 2014 Moroccan census. History The Phoenicians established a settlement called Sala, later the site of a Roman colony, Sala Colonia, on the south side of the Bou Regreg estuary. It is sometimes confused with Salé, on the opposite north bank. Salé was founded in about 1030 by Arabic-speaking Berbers who apparently cultivated the legend that the name was derived from that of Salah, son of Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azemmour
Azemmour or Azammur ( ar, أزمور, azammūr; ber, ⴰⵣⵎⵎⵓⵔ, azemmur, lit=wild olive tree) is a Moroccan city, lying at the Atlantic ocean coast, on the left bank of the Oum Er-Rbia River, 75 km southwest of Casablanca. Etymology The word Azemmour comes from the Berber word ''Azemmur'' ("wild olive tree"). History Azemmour is generally identified as the Punic Azama, latinized as Asama. Before 1486, it was a dependency of the King of Fez. In 1486 its inhabitants became vassals and tributaries of João II of Portugal. In 1513 Azemmour's governor Moulay Zayam refused to pay the tribute and mustered a powerful, well-equipped army. Manuel responded to this challenge by sending a massive fleet of 500 ships and 15 thousand soldiers (Bergreen, 19). James, Duke of Braganza led this army and on September 1st he conquered the city with no resistance from its inhabitants. Ferdinand Magellan, the man famed for leading the first-ever circumnavigation of the earth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Salé
The Republic of Salé was a city state at Salé (modern Morocco), during the 17th century. Located at the mouth of the Bou Regreg river, it was founded by Moriscos from the town of Hornachos, in Western Spain. Moriscos were the descendants of Muslims who were nominally converted to Christianity, and were subject to mass deportation during the Spanish Inquisition. The Republic's main commercial activities were the Barbary slave trade and piracy during its brief existence in the 17th century. The city is now part of Morocco. History Arrival of the Moriscos The republic traces its origins back to the beginning of the 17th century, with the arrival of approximately 3,000 wealthy Moriscos from Hornachos in western Spain, who anticipated the 1609 expulsion edicts ordered by Philip III of Spain.Coindreau 2006, p.42 After 1609, approximately 10,000 down-and-out expelled Moriscos arrived from Spain.Coindreau 2006, p.43 Cultural and language differences between the native Saletin peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of London (1604)
The Treaty of London, signed on 18 August O.S. (28 August N.S.) 1604, concluded the nineteen-year Anglo-Spanish War. The treaty restored the ''status quo'' between the two nations. The negotiations probably took place at Somerset House in Westminster and are sometimes known as the Somerset House Conference. Background The Anglo-Spanish War had been a complex and fluctuating conflict that also had connections with the Dutch Revolt, the French Wars of Religion, and the Nine Years' War in Ireland. The war by 1600 had been going on for nearly fifteen years with neither side gaining an overall benefit or a decisive advantage. The exhaustion of Spain, the rebellious opposition to the King's request for money, the mutinies of the troops in the Netherlands, and the fear of a renewal of a new war with France over the Duchy of Saluzzo all combined to emphasise the hopelessness of inflicting a vital blow on England. Early peace proposals In April 1600, Archduke Albert, the governor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)