|
Muhammad Khan Bangash
Nawab Ghazanfar-Jang, Bangash Khan (1665 – 1743) was the first Nawab of Farrukhabad in Uttar Pradesh, India. He was a "Bawan Hazari Sardar" (Commander of 52,000 men strong force) in the Mughal Army. He served as governor of Malwa Subah, Malwa and Allahabad provinces of the Mughal empire. He was also viceroy of Assam from 1735-1743. Although regarded as rude and illiterate he was well regarded for his loyalty, and it is believed that had fortune sided with him he would have been able to establish a kingdom rivalling those in the Deccan or Oudh State, Awadh. Life Muhammad Khan belonged to the Karlani Khaghzai clan of the Pashtuns, Pashtun Bangash tribe. In India they were referred to as ''qaum-i-bangash''. His father, Ain Khan Bangash had migrated from his native lands in the time of Aurangzeb and settled in Mau Rashidabad. Muhammad Khan gained a reputation as one of the most powerful of the Afghan mercenary warriors who inhabited that part of Hindustan, and eventually came to est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nawab
Nawab (Balochi language, Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب; bn, নবাব/নওয়াব; hi, नवाब; Punjabi language, Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ; Persian language, Persian, Punjabi language, Punjabi , Sindhi language, Sindhi, Urdu: ), also spelled Nawaab, Navaab, Navab, Nowab, Nabob, Nawaabshah, Nawabshah or Nobab, is a Royal title indicating a sovereign ruler, often of a South Asian state, in many ways comparable to the western title of Prince. The relationship of a Nawab to the Emperor of India has been compared to that of the Kingdom of Saxony, Kings of Saxony to the German Emperor. In earlier times the title was ratified and bestowed by the reigning Mughal emperor to semi-autonomous Muslim rulers of subdivisions or princely states in the Indian subcontinent loyal to the Mughal Empire, for example the Nawabs of Bengal. The title is common among Muslim rulers of South Asia as an equivalent to the title Maharaja. "Nawab" usually refers to males and literally mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling from July 1658 until his death in 1707. Under his emperorship, the Mughals reached their greatest extent with their territory spanning nearly the entirety of South Asia. Widely considered to be the last effective Mughal ruler, Aurangzeb compiled the Fatawa 'Alamgiri and was amongst the few monarchs to have fully established Sharia and Islamic economics throughout South Asia.Catherine Blanshard Asher, (1992"Architecture of Mughal India – Part 1" Cambridge university Press, Volume 1, Page 252. Belonging to the aristocratic Timurid dynasty, Aurangzeb's early life was occupied with pious pursuits. He held administrative and military posts under his father Shah Jahan () and gained recognition as an accomplished military commander. Aurang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
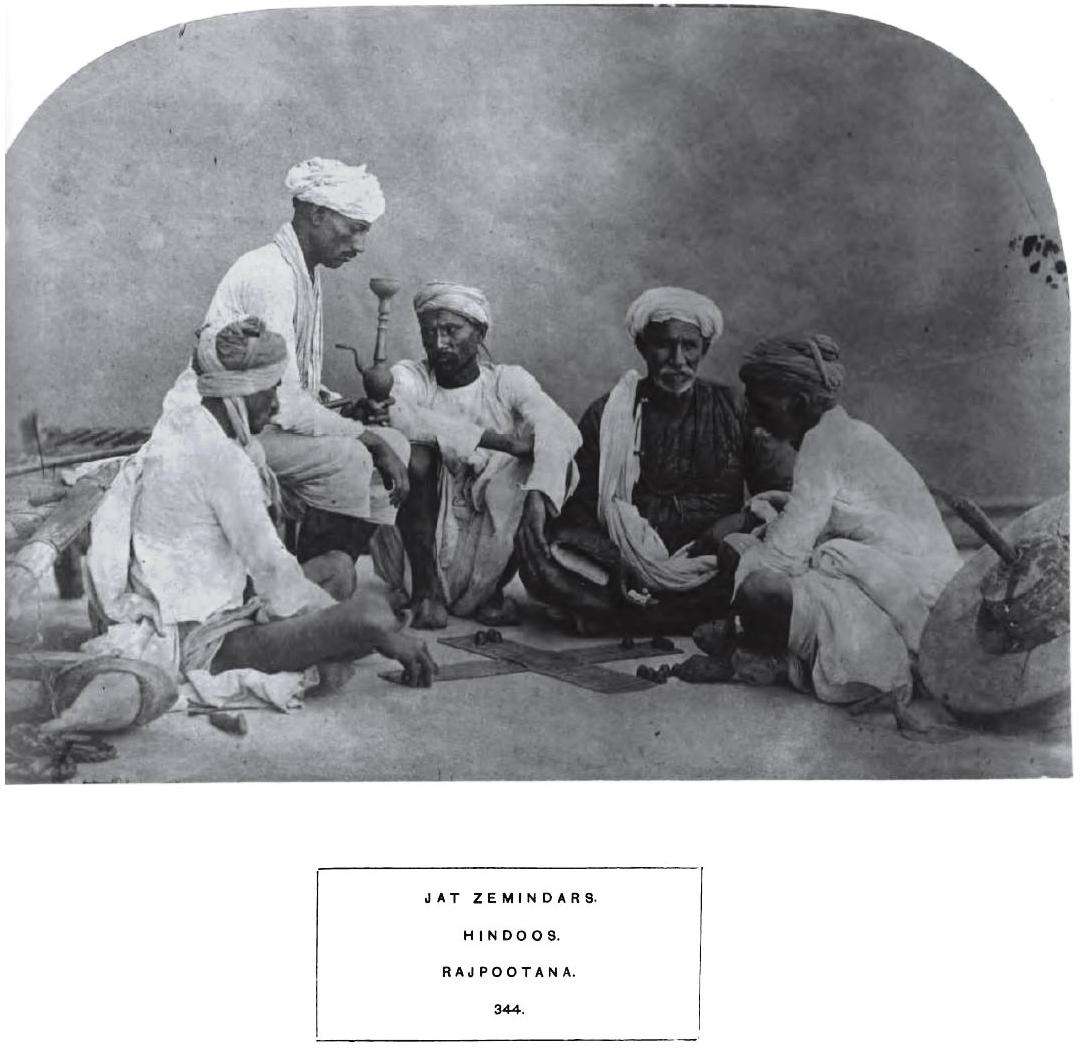
Jat People
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subsequently into the Delhi Territory, northeastern Rajputana, and the western Gangetic Plain in the 17th and 18th centuries. Quote: "Hiuen Tsang gave the following account of a numerous pastoral-nomadic population in seventh-century Sin-ti (Sind): 'By the side of the river.. f Sind along the flat marshy lowlands for some thousand li, there are several hundreds of thousands very great manyfamilies ..hichgive themselves exclusively to tending cattle and from this derive their livelihood. They have no masters, and whether men or women, have neither rich nor poor.' While they were left unnamed by the Chinese pilgrim, these same people of lower Sind were called Jats' or 'Jats of the wastes' by the Arab geographers. The Jats, as 'dromedary men.' we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhatrasal
Chhatrasal Bundela (4 May 1649 – 20 December 1731) was an Indian warrior and ruler from the Bundela Rajput clan, who fought against the Mughal Empire, and established his own kingdom in Bundelkhand during the 17th-18th centuries. Early life Chhatrasal was born at Kachar Kachnai in Tikamgarh, on 4 May 1649, to Champat Rai and Sarandha. He was a descendant of Rudra Pratap Singh of Orchha. Power Struggle against the Mughals Chhatrasal was 12 when his father Champat Rai of Mahoba was killed by the Mughals during the reign of Aurangzeb. Inspired by Chhatrapati Shivaji's ideals he travelled to Maharashtra and sought guidance from him. Chhatrasal raised the banner of revolt against the Mughals in Bundelkhand at the age of 22, with an army of 5 horsemen and 25 swordsmen, in 1671. Chhatrasal declared independence from Mughals in the 1720s and was able to resist the Mughals until he was attacked by Muhammad Khan Bangash in December 1728. Chhatrasal was 79 years old when he led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakori
Kakori is a town and a nagar panchayat in Lucknow district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, 14 km north of Lucknow. Kakori was a centre Urdu poetry, literature and the Qadiriya Qalandari Sufi order. On 9 August 1925 Indian revolutionaries robbed a train of government funds in Kakori, an incident known as Kakori train robbery or the Kakori Train Action. Kakori Train Action The town has a memorial to several revolutionaries involved in the Indian independence movement who looted a train near Kakori in August 1925 in what is known as the Kakori Train Action. Geography Kakori is located at . It has an average elevation of 121 metres (396 feet). Demographics India census, Kakori had a population of 16,731. Males constitute 53% of the population and females 47%. Kakori has an average literacy rate of 46%, lower than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 51%, and female literacy is 40%. In Kakori, 13% of the population is under 6 years of age. Popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a tribe or a royal family member in Arabian countries, in some countries it is also given to those of great knowledge in religious affairs as a surname by a prestige religious leader from a chain of Sufi scholars. It is also commonly used to refer to a Muslim religious scholar. It is also used as an honorary title by people claiming to be descended from Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali both patrilineal and matrilineal who are grandsons of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The term is literally translated to " Elder" (is also translated to "Lord/Master" in a monarchical context). The word 'sheikh' is mentioned in the 23rd verse of Surah Al-Qasas in the Quran. Etymology and meaning The word in Arabic stems from a triliteral root connected with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucknow
Lucknow (, ) is the capital and the largest city of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and it is also the second largest urban agglomeration in Uttar Pradesh. Lucknow is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous district and division. Having a population of 2.8 million as per 2011 census, it is the eleventh most populous city and the twelfth-most populous urban agglomeration of India. Lucknow has always been a multicultural city that flourished as a North Indian cultural and artistic hub, and the seat of power of Nawabs in the 18th and 19th centuries. It continues to be an important centre of governance, administration, education, commerce, aerospace, finance, pharmaceuticals, technology, design, culture, tourism, music and poetry. The city stands at an elevation of approximately above sea level. Lucknow city had an area of till December 2019, when 88 villages were added to the municipal limits and the area increased to . Bounded on the east by Barabanki, on the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaikhzada
Shaikhzadah or Shaikhzada (Urdu: شيخ زاده) is a Baloch tribe in Balochistan, Pakistan. See also * Shaikhs in South Asia ''Shaikh'', also rendered as ''Sheikh'', ''Sheik'', ''Shaik'', ''Shaykh'', ''Shaikh'', ''Shekh'', ''Cheikh'', ''Šeih'', ''Šejh'', ''Şeyh'' and other variants (Arabic: , ''shaykh''; pl. ''shuyūkh''), is a title given to many South Asian Musli ... References {{Indian Muslim Social groups of Uttar Pradesh Muslim communities of India Shaikh clans Social groups of Pakistan Muslim communities of Uttar Pradesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awadh
Awadh (), known in British historical texts as Avadh or Oudh, is a region in the modern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, which was before independence known as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh. It is synonymous with the Kośāla region of Hindu, Bauddh, and Jain scriptures. Awadh is bounded by the Ganges Doab to the southwest, Rohilkhand to the northwest, Nepal to the north, and Bhojpur-Purvanchal to the east. Its inhabitants are referred to as Awadhis. It was established as one of the twelve original subahs (top-level imperial provinces) under 16th-century Mughal emperor Akbar and became a hereditary tributary polity around 1722, with Faizabad as its initial capital and Saadat Ali Khan as its first Subadar Nawab and progenitor of a dynasty of Nawabs of Awadh (often styled Nawab Wazir al-Mamalik). The traditional capital of Awadh is Lucknow, also the station of the British Resident, which now is the capital of Uttar Pradesh. Etymology The word Awadh is supposed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadat Ali Khan I
Saadat Ali Khan Nishapuri (c. 1680 – 19 March 1739) was the Subahdar Nawab of Awadh (Oudh) from 26 January 1722 to 1739 and the son of Muhammad Nasir. At age 25 he accompanied his father on the final campaign of the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb against the Maratha in the Deccan, and the emperor awarded him the title of Khan Bahadur for his service. Early life Khan's date of birth has not been recorded. According to historian Ashirbadi Lal Srivastava, Khan was born in and his birth name was Mir Muhammad Amin. His father was Mir Muhammad Nasir, a merchant in Khorasan. Khan had one elder brother, Mir Muhammad Baqar. One of their ancestors was Mir Shamsuddin, a ''sayyid'' (descendant of Muhammad) and a ''kazi'' (Islamic judge) in Nishapur. He was a twenty-first-generation descendant of Musa al-Kadhim, the seventh imam of Shia Islam. No historian has recorded any events in Khan's early life. The Safavid dynasty began declining in the mid-seventeenth century. Sultan Husayn (the last ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaimganj
Kaimganj is a town in Farrukhabad district in the Indian State of Uttar Pradesh. Kaimganj Railway Station is a major station between Farrukhabad and Kasganj on Rajputana railway link of North Eastern Railway. Description Kaimganj is just 10 km from the ancient city of Kampil (ancient Kampilya) on the left bank of great river Ganges in Farrukhabad district. Kaimganj was founded by Nawab Mohammad Khan Bangash in 1713 and named after his son Qaim Khan, who was also the first administrator of this town. The meaning of the word ''Ganj'' is market place. This town is also associated with Dhruva, Draupadi and Charak. The famous book on Ayurveda, Charaka Samhita was also written in the same town. The town has an ancient grand jama masjid whose foundation was laid by Omar Daraaz Khan aka Munnu Khan who was a zamindar and was a well known figure in Kaimganj This town is the birthplace of Dr. Zakir Hussain, the third President of India from 13 May 1967 until his death on 3 May 1969 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammadabad, Farrukhabad
Mohammadabad is a town and a nagar panchayat in Farrukhabad district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Demographics India census, Mohammadabad had a population of 24,687. The sex ratio is 864 women per 1000 men. Mohammadabad has an average literacy rate of 78.5%, substantially higher than the national average. The male literacy is 85.63%, and female literacy is 70.12%. In Mohammadabad, 18% of the population is under 6 years of age. Shekhapur Khajuri, Nagla moti near pakhna rly station, dheerpur, Karthiya, Pancham Nagala is famous village in this nagar panchayat and block. Geography Mohammadabad has a 61 m elevation from sea level. †Includes Sikhs (0.2%), Buddhists Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ... (<0.2%). References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |