|
Mouriès
Mouriès (; , ) is a commune in France, commune in the Bouches-du-Rhône Departments of France, department in southern France. Population Economy Mouriès is known for its olive oil production, calling itself "the olive oil capital of France" (a claim disputed by Nyons, further north). There are still two working olive oil mills in town, including one which allows tours. In December of every year there is a festival celebrating the end of the harvest and the new oil, with a small parade and the benediction of the oil, along with various markets. Wednesday is market day. The small tourism office in town supplies a list of all of the market days in the area. In winter the market here is much larger than in the other towns in the area (Maussane, Aureille or Eygalières). File:140604-Mouries-Markt-03.jpg, market in Mouriès, Cours Paul Revoil File:140604-Mouries-Markt-01.jpg, market in Mouriès, Cours Paul Revoil File:140604-Mouries-Markt-02.jpg, market in Mouriès, Cours P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aureille
Aureille (; ) is a Communes of France, commune in the Bouches-du-Rhône Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southern France. The commune has been awarded one flower by the ''National Council of Towns and Villages in Bloom'' in the ''Competition of cities and villages in Bloom''. Geography Location Aureille is located between the Alpilles mountain chain and the Crau plain some 8 km from Eyguières in the east and 8 km from Mouriès in the west. It is dominated by the ''Signal of Opiès'', the highest point in the commune, in the north-east. It is a member of the communes of the Baux Valley but traditionally it is closer to the city of Arles. Access Road D17 passes through the commune south of the town from Eyguières in the east to Mouries in the west. Road D25A branches off this road in the commune and goes to the village then continues north to join the D25 just north of the commune. The nearest motorway is the A54 auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Bouches-du-Rhône Department
The following is a list of the 119 communes of the Bouches-du-Rhône department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Périmètre des groupements en 2025 BANATIC. Accessed 28 May 2025. * Métropole d'Aix-Marseille-Provence
The Aix-Marseille-Provence Metropolis (, ) is the ''métropole'', an intercommunal structure, centred on the cities of Marseille and Aix-en-Provence. It is located in the Bouches-du-Rhône, Var and Vaucluse departments, in the Provence-Al ... (partly)
* [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpilles
The Alpilles ( , ) is a small range of low mountains in Provence, southern France, located about south of Avignon. Geography The range is an extension of the much larger Luberon range. Although it is not high – some 498 m (1,634 ft) at its highest point – the Alpilles range stands out impressively, as it rises abruptly from the Rhône valley and from the very flat alluvial plain of Crau. The range is about 25 km long by about 8 to 10 km wide, running in an east–west direction between the Rhône and Durance rivers. The landscape of the Alpilles is one of arid limestone peaks separated by dry valleys. Communes The Chaîne des Alpilles is part of the territory of 15 communes: Aureille, Les Baux-de-Provence, Eygalières, Eyguières, Fontvieille, Mas-Blanc-des-Alpilles, Maussane-les-Alpilles, Mouriès, Paradou, Orgon, Saint-Étienne-du-Grès, Saint-Martin-de-Crau, Saint-Rémy-de-Provence, Sénas, Tarascon. Flora and fauna The lower slopes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eygalières
Eygalières (; Provençal: ''Aigalieras'' or ''Eigaliero'' ) is a commune in the Bouches-du-Rhône department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, Southern France. In 2020, it had a population of 1,730. Demographics See also * Alpilles * Jardin de l'alchimiste * Communes of the Bouches-du-Rhône department The following is a list of the 119 communes of the Bouches-du-Rhône department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025): References External links Website about Eygalières Communes of Bouches-du-Rhône [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salon-de-Provence
Salon-de-Provence (, ; or , ), commonly known as Salon, is a commune located about northwest of Marseille in the Bouches-du-Rhône department (Metropolis of Aix-Marseille Provence), region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, Southern France. It is the home of an important French Air and Space Force (''Armée de l'Air et de l'Espace'') air base. History Salon was a Gallo-Roman oppidum well positioned on the salt trade routes between Adriatic, Atlantic and Mediterranean seas, hence its name. This region was under the Phocaean influence since the sixth century BC, and stretches of the Via Aurelia can still be recognized just outside the town, but the earliest mention of the place under its familiar name is of the ninth century, as ''Villa Salone''. The archbishops of Arles controlled the site. Its principal claim to fame today is as the place where Nostradamus spent his last years and is buried. His dwelling is maintained as a museum, and for four days every June or July, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arles
Arles ( , , ; ; Classical ) is a coastal city and Communes of France, commune in the South of France, a Subprefectures in France, subprefecture in the Bouches-du-Rhône Departments of France, department of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region, in the former Provinces of France, province of Provence. A large part of the Camargue, the largest wetlands in France, is located within the territory of the commune, which is the List of French communes by surface area, largest in Metropolitan France in terms of geographic territory. In non-metropolitan France, Maripasoula in French Guiana is the largest French commune in general. The commune's land area is roughly similar to that of Singapore. The city has a long history, and was of considerable importance in the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis. The Arles, Roman and Romanesque Monuments, Roman and Romanesque Monuments of Arles were listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1981 for their testimony to the his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligures
The Ligures or Ligurians were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day Northern Italy, north-western Italy, is named. Because of the strong Celts, Celtic influences on their language and culture, they were also known in antiquity as Celto-Ligurians. In pre-Roman times, the Ligurians occupied the present-day Italian region of Liguria, Piedmont, northern Tuscany, western Lombardy, western Emilia-Romagna, and northern Sardinia, reaching also Elba and Sicily. They inhabited also the Regions of France, French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and Corsica;Strabo, ''Geography'', book 4, chapter 6Livy, ''History of Rome'', book XLVII however, it is generally believed that around 20th century BC, 2000 BC the Ligurians occupied a much larger area, extending as far as what is today Catalonia (in the north-eastern corner of the Iberian Peninsula). The origins of the ancient Ligurians are unclear, and an autochthonous origin is increasingly probable. What little is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
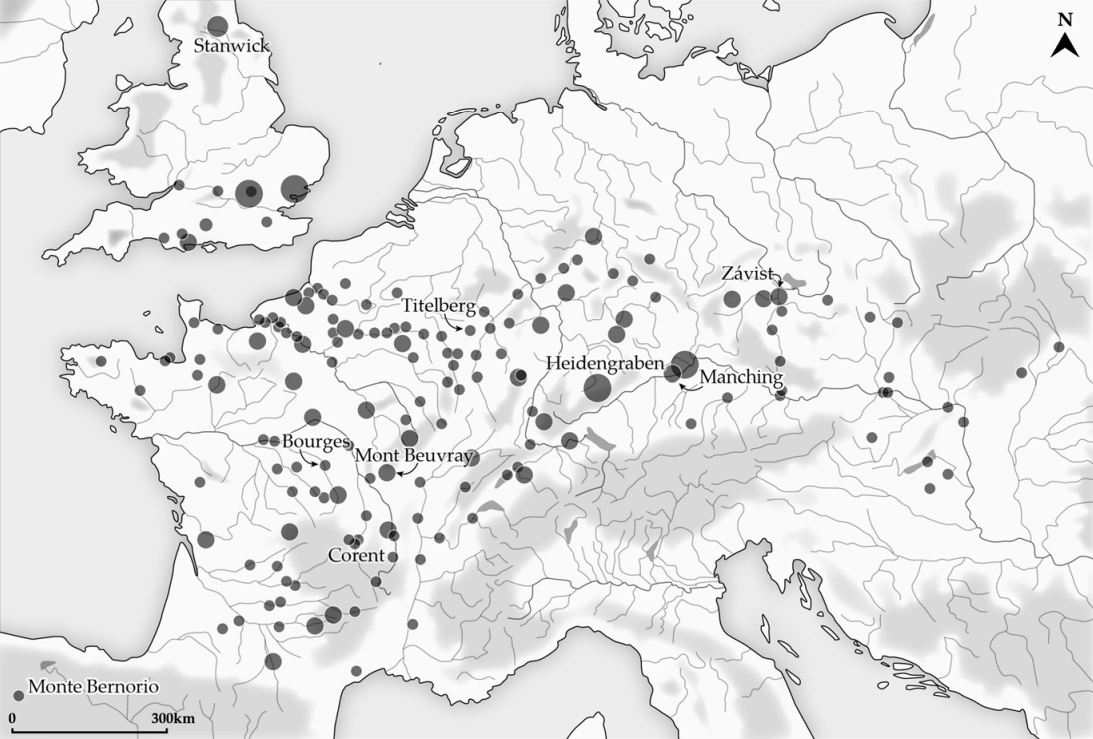
Oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from British Iron Age, Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Great Hungarian Plain, Hungarian Plain in the east. These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned. In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, ''oppida'' continued to be used into the 1st century AD. Definition is a Latin word meaning 'defended (fortified) administrative centre or town', originally used in reference to non-Roman towns as well as provincial towns under Roman control. The word is derived from the earlier Latin , 'encl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celto-Ligurian
The Ligures or Ligurians were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day north-western Italy, is named. Because of the strong Celtic influences on their language and culture, they were also known in antiquity as Celto-Ligurians. In pre-Roman times, the Ligurians occupied the present-day Italian region of Liguria, Piedmont, northern Tuscany, western Lombardy, western Emilia-Romagna, and northern Sardinia, reaching also Elba and Sicily. They inhabited also the French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and Corsica;Strabo, ''Geography'', book 4, chapter 6Livy, ''History of Rome'', book XLVII however, it is generally believed that around 2000 BC the Ligurians occupied a much larger area, extending as far as what is today Catalonia (in the north-eastern corner of the Iberian Peninsula). The origins of the ancient Ligurians are unclear, and an autochthonous origin is increasingly probable. What little is known today about the ancient Ligurian language is based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
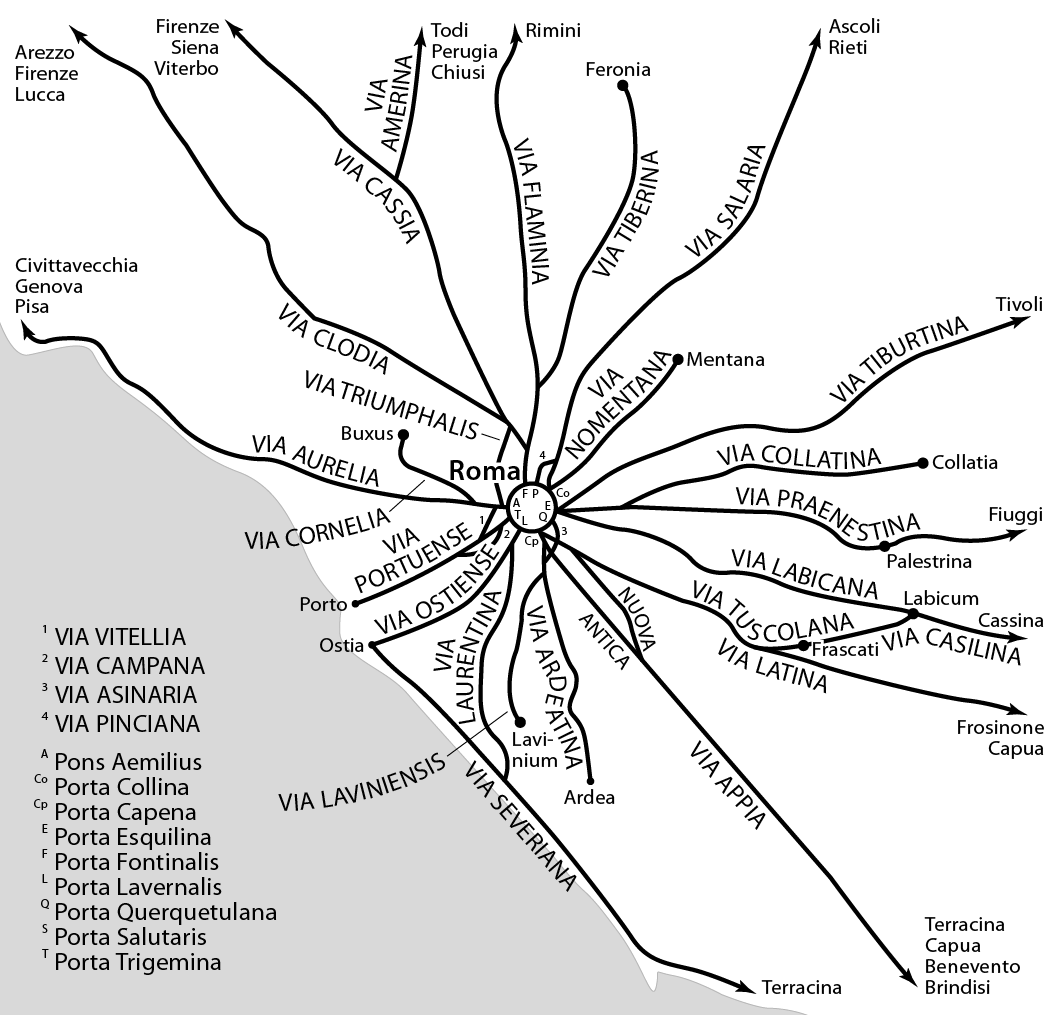
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
A () is a level of administrative divisions of France, administrative division in the France, French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipality, municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlet (place), hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the Municipal arrondissem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commune In France
A () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondissements of its largest cities, the are the lowest level of administrative d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |