|
Motonori Matsuyama
was a Japanese geophysicist who was (in the late 1920s) the first to provide systematic evidence that the Earth's magnetic field had been reversed in the early Pleistocene and to suggest that long periods existed in the past in which the polarity was reversed. He remarked that the Earth's field had later changed to the present polarity. The era of reversed polarity preceding the current ''Brunhes Chron'' of normal polarity is now called the ''Matuyama Reversed Chron''; and the transition between them is called the ''Brunhes–Matuyama'' or ''Matuyama-Brunhes'' reversal. Life Matuyama Motonori was born at Uyeda (now Usa) in Oita prefecture Japan on October 25, 1884, a son of a Zen abbot, Sumie (Sumiye) Tengai. His name was at first registered as Suehara Motonori after his mother’s family name, Suehara Kou, and was later changed to Sumie Motonori when his father became the chief priest at an eminent Zen Buddhist temple in Yamaguchi. In 1910 he was adopted by the Matsuyama (松 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Type L Submarine
The submarines were medium-sized submarines of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during the 1920s and World War II. The ''Type L'' submarines were built with Vickers naval technical guidance. All boats were built in the Mitsubishi Heavy Industries-Kobe Shipyard by the contract with Vickers. Class variants The ''Type L'' submarines were divided into four classes: * * * * ''Type L1 (Ro-51-class)'' In 1916, the Mitsubishi Shipbuilding Corporation got the Vickers ''L'' class submarine informations. Mitsubishi which lost competition to the Kawasaki's ''Type F'' submarines (Fiat-Laurenti design, ''Ro-1'' class and ''Ro-3'' class), bought the license for the ''L'' class submarine from Vickers. The IJN hoped an improvement of submarine technologies will be achieved and ordered this submarine from Mitsubishi. Mitsubishi bought six submarine kits, and built two boats by semi-knock down. The submarine crews were satisfied with the Vickers diesels because they proved t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the best universities in the world and it is among the most selective in the United States. The university is composed of an undergraduate college and five graduate research divisions, which contain all of the university's graduate programs and interdisciplinary committees. Chicago has eight professional schools: the Law School, the Booth School of Business, the Pritzker School of Medicine, the Crown Family School of Social Work, Policy, and Practice, the Harris School of Public Policy, the Divinity School, the Graham School of Continuing Liberal and Professional Studies, and the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering. The university has additional campuses and centers in London, Paris, Beijing, Delhi, and Hong Kong, as well as in downtown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamaguchi University
is a national university in Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan. It has campuses at the cities of Yamaguchi and Ube. History The root of the university was , a private school founded by Ueda Hōyō (, 1769–1853) in 1815. In 1863 the school became a han school of Chōshū Domain and was renamed Yamaguchi Meirinkan. After the Meiji Restoration it became a prefectural secondary school, and in 1894 it developed into , a national institute of higher education. It served as a preparatory course for the Imperial University. In February 1905 the school was reorganized into , the third national commercial college in Japan, after Tokyo (1887) and Kobe (1902). In 1944 the school was renamed Yamaguchi College of Economics. In 1949 Yamaguchi University was established by integrating six public (national and prefectural) schools in Yamaguchi Prefecture, namely, (Revived) Yamaguchi Higher School, Yamaguchi College of Economics, Ube Technical College, Yamaguchi Normal School, Yamaguchi Youth No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Hammond Hess
Harry Hammond Hess (May 24, 1906 – August 25, 1969) was an American geologist and a United States Navy officer in World War II who is considered one of the "founding fathers" of the unifying theory of plate tectonics. He is best known for his theories on sea floor spreading, specifically work on relationships between island arcs, seafloor gravity anomalies, and serpentinized peridotite, suggesting that the convection of the Earth's mantle was the driving force behind this process. Early life and education Harry Hammond Hess was born on May 24, 1906, in New York City to Julian S. Hess, a member of the New York Stock Exchange, and Elizabeth Engel Hess. He attended Asbury Park High School in Asbury Park, New Jersey. In 1923, he entered Yale University, where he intended to study electrical engineering but ended up graduating with a Bachelor of Science degree in geology. He spent two years as an exploration geologist in Northern Rhodesia. In 1934 he married Annette Burns. Teach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
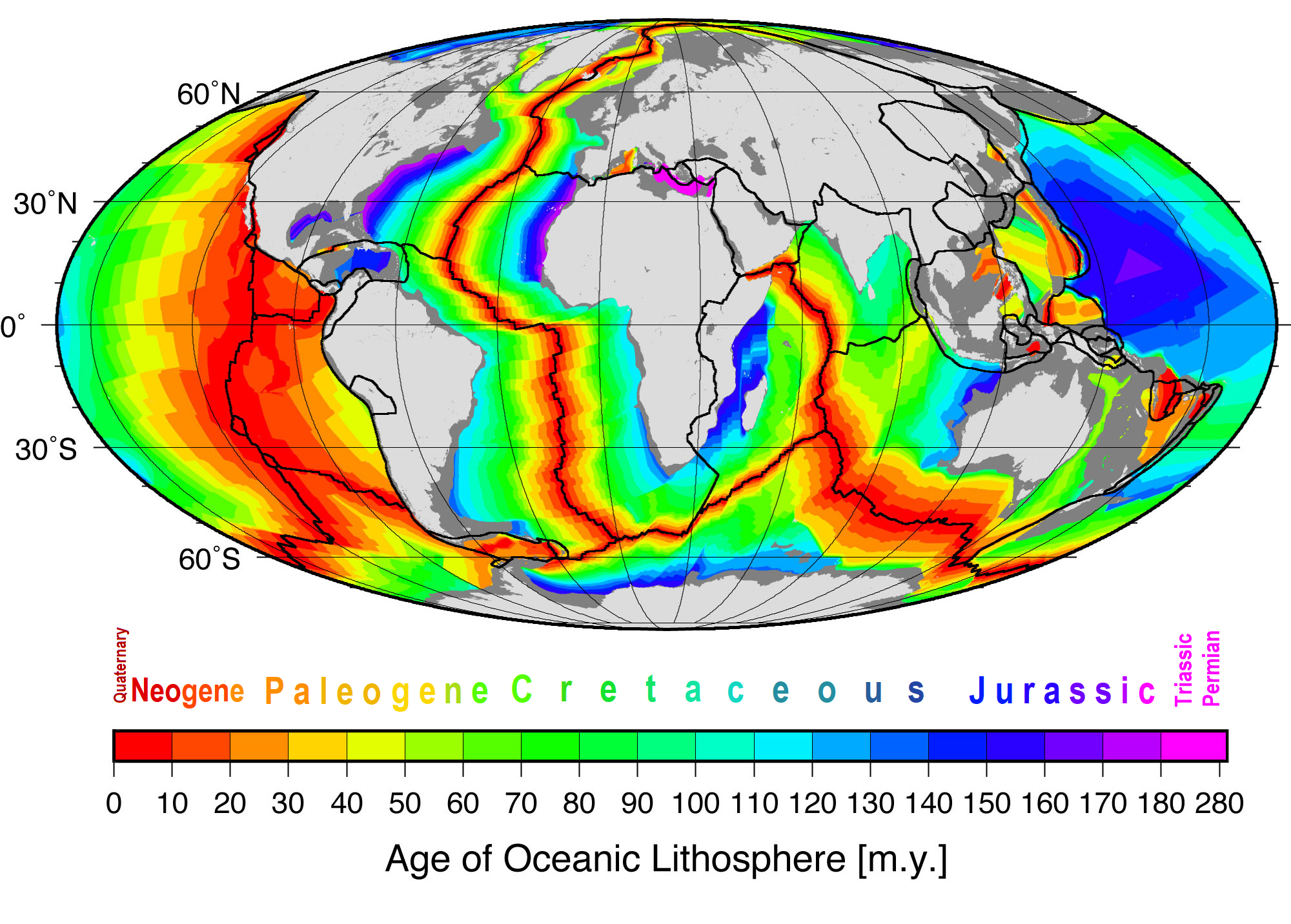
Seafloor Spreading
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. History of study Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener and Alexander du Toit of continental drift postulated that continents in motion "plowed" through the fixed and immovable seafloor. The idea that the seafloor itself moves and also carries the continents with it as it spreads from a central rift axis was proposed by Harold Hammond Hess from Princeton University and Robert Dietz of the U.S. Naval Electronics Laboratory in San Diego in the 1960s. The phenomenon is known today as plate tectonics. In locations where two plates move apart, at mid-ocean ridges, new seafloor is continually formed during seafloor spreading. Significance Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When oceanic plates diverge, tensional stress causes fractures to occur in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'. The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of the ocean is very deep, where the seabed is known as the abyssal plain. Seafloor spreading creates mid-ocean ridges along the center line of major ocean basins, where the seabed is slightly shallower than the surrounding abyssal plain. From the abyssal plain, the seabed slopes upward toward the continents and becomes, in order from deep to shallow, the continental rise, slope, and shelf. The depth within the seabed itself, such as the depth down through a sediment core, is known as the “depth below seafloor.” The ecological environment of the seabed and the deepest waters are collectively known, as a habitat for creatures, as the “benthos.” Most of the seabed throughout the world's oceans is covered in layers of marine sediments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University Press
Stanford University Press (SUP) is the publishing house of Stanford University. It is one of the oldest academic presses in the United States and the first university press to be established on the West Coast. It was among the presses officially admitted to the Association of American University Presses (now the Association of University Presses) at the organization's founding, in 1937, and is one of twenty-two current member presses from that original group. The press publishes 130 books per year across the humanities, social sciences, and business, and has more than 3,500 titles in print. History David Starr Jordan, the first president of Stanford University, posited four propositions to Leland and Jane Stanford when accepting the post, the last of which stipulated, “That provision be made for the publication of the results of any important research on the part of professors, or advanced students. Such papers may be issued from time to time as ‘Memoirs of the Leland Stanf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock (geology), rock layers (Stratum, strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary rock, sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith (geologist), William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of Stratum, strata or rock layering and the importance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and Autonomous underwater vehicle, robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navy, navies, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, Blockade runner, blockade running, Ballistic missile submarine, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance, conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Exploration Geophysicists
The Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) is a learned society dedicated to promoting the science and education of exploration geophysics in particular and geophysics in general. The Society fosters the expert and ethical practice of geophysics in the exploration and development of natural resources, in characterizing the near-surface, and in mitigating earth hazards. SEG has more than 14,000 members working in more than 114 countries. SEG was founded in 1930 in Houston, Texas but its business office has been headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma since the mid-1940s. While most SEG members are involved in exploration for petroleum, SEG members also are involved in application of geophysics methods to mineral exploration as well as environmental and engineering problems, archaeology, and other scientific endeavors. SEG publishes ''The Leading Edge'' (''TLE''), a monthly professional magazine, ''Geophysics'', a peer-reviewed archival publication, and ''Interpretation'', a peer-review ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Andries Vening Meinesz
Felix Andries Vening Meinesz (30 July 1887 – 10 August 1966) was a Dutch geophysicist and geodesist. He is known for his invention of a precise method for measuring gravity (gravimetry). Thanks to his invention, it became possible to measure gravity at sea, which led him to the discovery of gravity anomalies above the ocean floor. He later attributed these anomalies to continental drift. He was a Fellow of the Royal Society. Biography Vening Meinesz's father, Sjoerd Anne Vening Meinesz, was mayor, first of Rotterdam, then of Amsterdam. Felix was born in The Hague grew up in a protected environment. In 1910 he graduated in civil engineering in Delft. The same year he started working for the Dutch gravity survey. In 1915 he wrote his dissertation on the defects of the gravimeters used at that time. Vening Meinesz then designed a new gravimeter, which the KNMI (Royal Dutch Meteorological Institute) built. The apparatus has two pendula of the same size hanging in a frame but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer Manchuria). Its meaning may vary depending on the context: * Historical polities and geographical regions usually referred to as Manchuria: ** The Later Jin (1616–1636), the Manchu-led dynasty which renamed itself from "Jin" to "Qing", and the ethnicity from "Jurchen" to "Manchu" in 1636 ** the subsequent duration of the Qing dynasty prior to its conquest of China proper (1644) ** the northeastern region of Qing dynasty China, the homeland of Manchus, known as "Guandong" or "Guanwai" during the Qing dynasty ** The region of Northeast Asia that served as the historical homeland of the Jurchens and later their descendants Manchus ***Qing control of Dauria (the region north of the Amur River, but in its watershed) was contested in 1643 when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |