|
Morlacco
( vec, Morlac) or Morlacco del Grappa is an Italian cow's-milk cheese from Monte Grappa, in the provinces of Italy, provinces of Province of Vicenza, Vicenza, Province of Treviso, Treviso, and Province of Belluno, Belluno) where cheesemakers once produced a Soft cheese, soft cow's milk cheese, low in fat, with an uncooked curd that was named after their native region: Morlachia. The local Burlina cows - a breed that is at risk of extinction - produced the milk used for this cheese. The Burlina cow is small and hardy and has a piebald black and white coat. Today, Morlacco del Grappa cheese is once again produced on Monte Grappa with skimmed milk from the evening's milking mixed with whole milk from that of the morning. After 20 days of Cheese ripening, aging, the cheese is ready for consumption, but it can be left to age for up to three months. References Morlachs, cheese Cheeses of Veneto Italian cheeses Cow's-milk cheeses {{Cheese-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morlachs
Morlachs ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Morlaci, Морлаци or , ; it, Morlacchi; ro, Morlaci) has been an exonym used for a rural Christian community in Herzegovina, Lika and the Dalmatian Hinterland. The term was initially used for a bilingual Vlach pastoralist community in the mountains of Croatia in the second half of the 14th until the early 16th century. Then, when the community straddled the Venetian– Ottoman border until in the 17th century, it only referred to Slavic-speaking, mainly Eastern Orthodox but also Roman Catholic people. The Vlach i.e. Morlach population of Herzegovina and Dalmatian hinterland from the Venetian and Turkish side were of either Roman Catholic or Christian Orthodox faith. Venetian sources from 17th and 18th century make no distinction between Orthodox and Catholics, they refer to both groupings as Morlachs. The exonym ceased to be used in an ethnic sense by the end of the 18th century, and came to be viewed as derogatory, but has been renewed as a social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burlina
The Burlina is a breed of cattle from the mountainous areas of the Veneto region of north-east Italy. It is distributed mainly in the provinces of Treviso, Verona and Vicenza. It is a dual-purpose breed, but is raised principally for milk production. It has been suggested that it may be related to the similar Bretonne Pie Noir breed of small pied dairy cattle in Brittany. History The origins of the Burlina are unknown. It has been suggested that it may be related to the Bretonne Pie Noir, a breed of small pied dairy cattle in Brittany, or that it may have been brought into Italy by Cimbrian migrants. The Burlina was one of the most numerous breeds present in north-eastern Italy in the early 20th century, numbering tens of thousands of head. Until the 1930s, it was the commonest dairy breed on the Altopiano di Asiago, in the Colli Berici, on Monte Grappa and in the Monti Lessini. Numbers declined significantly during the First World War, under the Fascist regime and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veneto
it, Veneto (man) it, Veneta (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-34 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €163 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €33,200 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.900 · 9th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITD , websi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monte Grappa
Monte Grappa ( vec, Mónte Grapa) (1,775 m) is a mountain of the Venetian Prealps in Veneto, Italy. It lies between the Venetian plain to the south and the central alpine areas to the North. To the west, it is parted from the Asiago upland by the Brenta river, and to the east it is separated from the Cesen-Visentin massif by the Piave river. To the north lie Corlo lake and Feltre valley. In the past, the mountain was called ''Alpe Madre'' (''Mother Alp''), and is currently divided among three provinces: Vicenza to the west, Treviso to the south and Belluno to the northeast. It is the highest peak of a small massif, which also includes many other peaks such as Col Moschin, Colle della Berretta, Monte Asolone, Monte Pertica, Prassolan, Monti Solaroli, Fontana Secca, Monte Peurna, Monte Santo, Monte Tomatico, Meatte, Monte Pallon, and Monte Tomba. In September 2021, UNESCO announced that Monte Grappa would become one of 20 new biosphere reserves as part of their Man and the Biosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheeses Of Veneto
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During production, milk is usually acidified and the enzymes of either rennet or bacterial enzymes with similar activity are added to cause the casein to coagulate. The solid curds are then separated from the liquid whey and pressed into finished cheese. Some cheeses have aromatic molds on the rind, the outer layer, or throughout. Over a thousand types of cheese exist and are produced in various countries. Their styles, textures and flavors depend on the origin of the milk (including the animal's diet), whether they have been pasteurized, the butterfat content, the bacteria and mold, the processing, and how long they have been aged. Herbs, spices, or wood smoke may be used as flavoring agents. The yellow to red color of many cheeses is produced by adding an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheese Ripening
Cheese ripening, alternatively cheese maturation or affinage, is a process in cheesemaking. It is responsible for the distinct flavour of cheese, and through the modification of "''ripening agents''", determines the features that define many different varieties of cheeses, such as taste, texture, and body. The process is "characterized by a series of complex physical, chemical and microbiological changes" that incorporates the agents of " bacteria and enzymes of the milk, lactic culture, rennet, lipases, added moulds or yeasts, and environmental contaminants". The majority of cheese is ripened, except for fresh cheese. History Cheese ripening was not always the highly industrialised process it is today; in the past, cellars and caves were used to ripen cheeses instead of the current highly regulated process involving machinery and biochemistry. Some cheeses still are made using more historical methods, such as the blue cheese Roquefort, which is required to be ripened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. Early-lactation milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibodies that strengthen the immune system, and thus reduces the risk of many diseases. Milk contains many nutrients, including protein and lactose. As an agricultural product, dairy milk is collected from farm animals. In 2011, dairy farms produced around of milk from 260 million dairy cows. India is the world's largest producer of milk and the leading exporter of skimmed milk powder, but it exports few other milk products. Because there is an ever-increasing demand for dairy products within India, it could eventually become a net importer of dairy products. New Zealand, Germany and the Netherlands are the largest exporters o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skimmed Milk
Skimmed milk (British English), or skim milk (American English), is made when all the milkfat is removed from whole milk. It tends to contain around 0.1% fat. Background Historically, skimmed milk was used for fattening pigs, and was recommended as "not only the very best supplement for growing pigs, but is of almost equal value for fattening purposes" as it "furnishes a complete protein" and makes the feed "more palatable". Terminology In the United Kingdom, milk is traditionally marketed and labelled as follows: * Whole milk (around 3.0–4% fat) – Plastic bottles marketed in blue packaging. * Semi-skimmed milk (around 1.8% fat) – Plastic bottles are marketed in green packaging. * Skimmed milk (around 0.1% fat) – Plastic bottles are marketed in red packaging. * Channel Island milk (around 5–5.5% fat) Often referred to as gold top, although this varies. Additionally, some supermarkets in the UK now market milk as: * 1% fat milk – Normally sold in purple or or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piebald
A piebald or pied animal is one that has a pattern of unpigmented spots (white) on a pigmented background of hair, feathers or scales. Thus a piebald black and white dog is a black dog with white spots. The animal's skin under the white background is not pigmented. Location of the unpigmented spots is dependent on the migration of melanoblasts (primordial pigment cells) from the neural crest to paired bilateral locations in the skin of the early embryo. The resulting pattern appears symmetrical only if melanoblasts migrate to both locations of a pair and proliferate to the same degree in both locations. The appearance of symmetry can be obliterated if the proliferation of the melanocytes (pigment cells) within the developing spots is so great that the sizes of the spots increase to the point that some of the spots merge, leaving only small areas of the white background among the spots and at the tips of the extremities. Animals with this pattern may include birds, cats, cattl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curd
Curd is obtained by coagulating milk in a sequential process called curdling. It can be a final dairy product or the first stage in cheesemaking. The coagulation can be caused by adding rennet or any edible acidic substance such as lemon juice or vinegar, and then allowing it to coagulate. The increased acidity causes the milk proteins ( casein) to tangle into solid masses, or ''curds''. Milk that has been left to sour ( raw milk alone or pasteurized milk with added lactic acid bacteria) will also naturally produce curds, and sour milk cheeses are produced this way. Producing cheese curds is one of the first steps in cheesemaking; the curds are pressed and drained to varying amounts for different styles of cheese and different secondary agents (molds for blue cheeses, etc.) are introduced before the desired aging finishes the cheese. The remaining liquid, which contains only whey proteins, is the whey. In cow's milk, 90 percent of the proteins are caseins. Curds ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
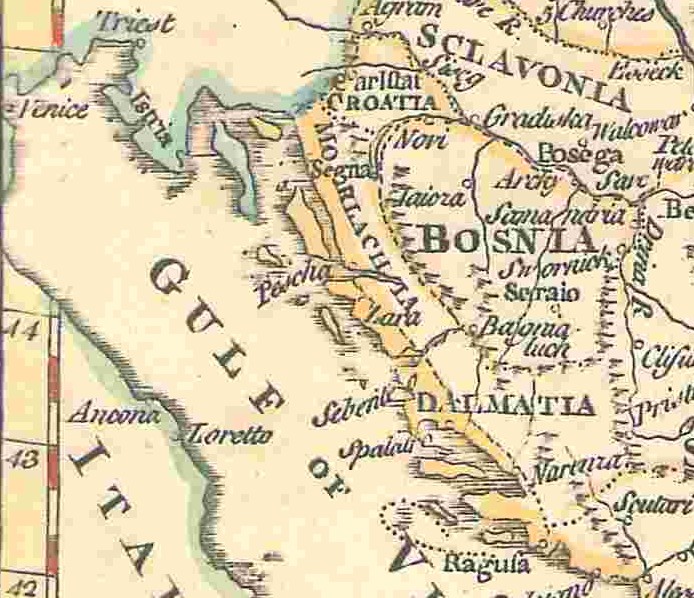
Morlachia
Morlachia ( la, Morlachia; it, Morlacchia; hr, Morlakija; ro, Morlachia) was a vaguely defined region, named after the Morlachs, used on European maps between the 16th and the 19th centuries. Morlachia was located in modern-day Croatia between Istria and Dalmatia, being opposite to the island of Krk. The Morlachs were originally a Romance people related to modern Romanians before their Slavicisation. Overview In old topography, the toponym Morlachia was given great importance on maps, sometimes being placed at the same "level" or at a superior one than regions such as Bosnia or Croatia. This can be explained by the important geographical position Morlachia had, being located between the Ottoman Empire, the Republic of Venice and the Habsburg monarchy and its realms from the 16th to the 19th century. However, following the demise of Ottoman power in the region and the fall of the Republic of Venice in the latter century, Morlachia lost relevance and the Morlachs of the region b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cow's Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. Early-lactation milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibodies that strengthen the immune system, and thus reduces the risk of many diseases. Milk contains many nutrients, including protein and lactose. As an agricultural product, dairy milk is collected from farm animals. In 2011, dairy farms produced around of milk from 260 million dairy cows. India is the world's largest producer of milk and the leading exporter of skimmed milk powder, but it exports few other milk products. Because there is an ever-increasing demand for dairy products within India, it could eventually become a net importer of dairy products. New Zealand, Germany and the Netherlands are the largest exporters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)
_(20577597926).jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)