|
Moritz Von Bissing
Moritz Ferdinand Freiherr von Bissing (30 January 1844 – 18 April 1917) was a German officer from Prussia. Life and pre-WWI army career Bissing was born at Ober Bellmannsdorf in the Province of Silesia. He was the son of Moritz von Bissing, a member of the landed gentry who was known to speak his mind to the Kaiser. In 1865 Bissing entered the Prussian Army as a lieutenant in the cavalry, and he soon saw active service in the Austro-Prussian War and the Franco-Prussian War. Gaining steady promotion, in 1887 the young Major was appointed as an aide-de-camp to the crown prince, who later became the Emperor Wilhelm II. He served in the guards cavalry until 1897, when he was given command of the 29th Infantry Division. From 1901 to 1907 Bissing commanded the VII Army Corps in Münster. In 1902 he was promoted to General of the Cavalry, and he retired from the army in 1908. First World War Upon the outbreak of the First World War, Bissing was recalled to active duty as deputy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radzimów
Radzimów (german: Bellmannsdorf) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Sulików, within Zgorzelec County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in southwestern Poland, close to the Czech border. It lies approximately southeast of Sulików, southeast of Zgorzelec, and west of the regional capital Wrocław. The village has a population of 784. File:Radzimow (2).jpg, Crossroads File:Radzimow (slawojka) (1).jpg, Toilet File:Radzimów (005).jpg, House Notable residents * Moritz von Bissing Moritz Ferdinand Freiherr von Bissing (30 January 1844 – 18 April 1917) was a German officer from Prussia. Life and pre-WWI army career Bissing was born at Ober Bellmannsdorf in the Province of Silesia. He was the son of Moritz von Bissing, ... (1844–1917), Prussian general References Villages in Zgorzelec County {{DEFAULTSORT:Radzimow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generaloberst
A ("colonel general") was the second-highest general officer rank in the German ''Reichswehr'' and ''Wehrmacht'', the Austro-Hungarian Common Army, the East Germany, East German National People's Army and in their respective police services. The rank was equal to a four-star full general but below a general field marshal. The rank was equivalent to a ''Generaladmiral'' in the ''Kriegsmarine'' until 1945 or to a ''Flottenadmiral'' in the ''Volksmarine'' until 1990. It was the highest ordinary military rank and the highest military rank awarded in peacetime; the higher rank of general field marshal was awarded only in wartime by the head of state. In general, a ''Generaloberst'' had the same privileges as a general field marshal. A literal translation of ''Generaloberst'' would be "uppermost general", but it is often translated as "colonel-general" by analogy to ''Oberst'', "colonel", such as in countries in which the rank was adopted like Russia (, ''general-polkovnik''). "Ober ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Crown (Prussia)
The Royal Order of the Crown (german: Königlicher Kronen-Orden) was a Prussian order of chivalry. Instituted in 1861 as an honour equal in rank to the Order of the Red Eagle, membership could only be conferred upon commissioned officers (or civilians of approximately equivalent status), but there was a medal associated with the order which could be earned by non-commissioned officers and enlisted men. Officially the Order of the Red Eagle and the Order of the Crown were equal. Most officials did however prefer to be appointed in the older Order of the Red Eagle. The Order of the Crown was often used as an award for someone who had to be rewarded while the Prussian government did not want to use the Order of the Red Eagle. Classes The Order had six classes: *Grand Cross – wore the Grand Cross badge on a sash on the right shoulder, plus the star on the left chest; *1st Class – wore the badge on a sash on the right shoulder, plus the star on the left chest; *2nd Class – wore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Red Eagle
The Order of the Red Eagle (german: Roter Adlerorden) was an order of chivalry of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was awarded to both military personnel and civilians, to recognize valor in combat, excellence in military leadership, long and faithful service to the kingdom, or other achievements. As with most German (and most other European) orders, the Order of the Red Eagle could only be awarded to commissioned officers or civilians of approximately equivalent status. However, there was a medal of the order, which could be awarded to non-commissioned officers and enlisted men, lower ranking civil servants and other civilians. History The predecessor to the Order of the Red Eagle was founded on 17 November 1705, by the Margrave Georg Wilhelm of Brandenburg-Bayreuth as the '' Ordre de la Sincerité''. This soon fell into disuse but was revived in 1712 in Brandenburg-Bayreuth and again in 1734 in Brandenburg-Ansbach, where it first received the name of "Order of the Brandenburg Red Eagle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (german: link=no, Eisernes Kreuz, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, and later in the German Empire (1871–1918) and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). King Frederick William III of Prussia established it on 17 March 1813 during the Napoleonic Wars (EK 1813). The award was backdated to the birthday (10 March) of his late wife, Queen Louise. Louise was the first person to receive this decoration (posthumously). Recommissioned Iron Cross was also awarded during the Franco-Prussian War (EK 1870), World War I (EK 1914), and World War II (EK 1939). During the 1930s and World War II, the Nazi regime superimposed a swastika on the traditional medal. The Iron Cross was usually a military decoration only, though there were instances awarded to civilians for performing military functions, including Hanna Reitsch, who received the Iron Cross, 2nd class, and Iron Cross, 1st Class, and Melitta Schenk Gräfin von Stauffenberg, who received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Rhine-Main regions. Berlin straddles the banks of the Spree, which flows into the Havel (a tributary of the Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the city's main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel and Dahme, the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee. Due to its l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invalidenfriedhof
The Invalids' Cemetery (german: Invalidenfriedhof) is one of the oldest cemeteries in Berlin. It was the traditional resting place of the Prussian Army, and is regarded as particularly important as a memorial to the German Wars of Liberation of 1813–15. History The cemetery was established in 1748 to provide burial grounds for those veterans wounded in the War of the Austrian Succession, who inhabited a nearby hostel (''Invalidenhaus'') built on the orders of King Frederick the Great. A royal decree of 1824 declared that the ''Invalidenfriedhof'' should become the burial ground for all distinguished Prussian military personnel, including Bogislav Count Tauentzien von Wittenberg. One of the most notable tombs from this period is that of Gerhard von Scharnhorst (a hero of the Napoleonic Wars), designed by Schinkel with a sculpture of a slumbering lion cast out of captured cannon by Rauch. The cemetery was also the resting place of the soldiers killed during the Revolutions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edith Cavell
Edith Louisa Cavell ( ; 4 December 1865 – 12 October 1915) was a British nurse. She is celebrated for saving the lives of soldiers from both sides without discrimination and for helping some 200 Allied soldiers escape from German-occupied Belgium during the First World War, for which she was arrested under martial law. She was accused of treason, found guilty by a court-martial and sentenced to death. Despite international pressure for mercy, she was shot by a German firing squad. Her execution received worldwide condemnation and extensive press coverage. The night before her execution, she said, "Patriotism is not enough. I must have no hatred or bitterness towards anyone." These words were later inscribed on a memorial to her near Trafalgar Square. Her strong Anglican beliefs propelled her to help all those who needed it, both German and Allied soldiers. She was quoted as saying, "I can't stop while there are lives to be saved." The Church of England commemorates her in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
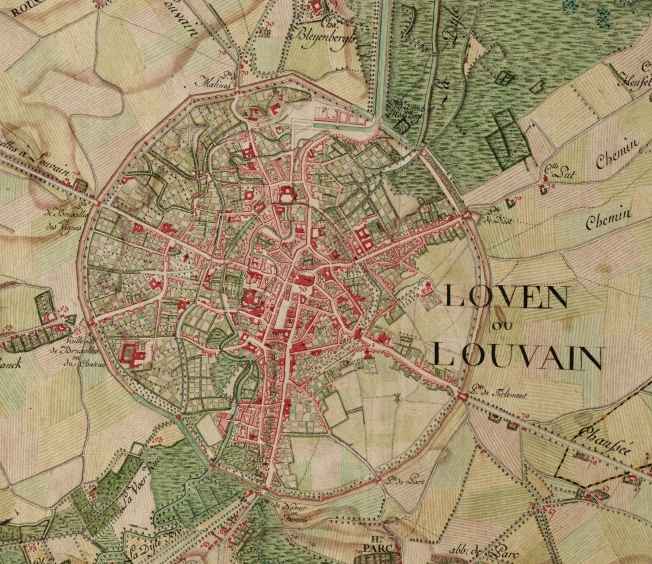
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic city and the former neighbouring municipalities of Heverlee, Kessel-Lo, a part of Korbeek-Lo, Wilsele and Wijgmaal. It is the eighth largest city in Belgium, with more than 100,244 inhabitants. KU Leuven, Belgium's largest university, has its flagship campus in Leuven, which has been a university city since 1425. This makes it the oldest university city in the Low Countries. The city is home of the headquarters of Anheuser-Busch InBev, the world's largest beer brewer and sixth-largest fast-moving consumer goods company. History Middle Ages The earliest mention of Leuven (''Loven'') dates from 891, when a Viking army was defeated by the Frankish king Arnulf of Carinthia (see: Battle of Leuven). According to a legend, the city's red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walloon Movement
The Walloon Movement (french: Mouvement wallon) is an umbrella term for all Belgium, Belgian political movements that either assert the existence of a Walloons, Walloon identity and of Wallonia and/or defend French culture and language within Belgium, either within the framework of the 1830 Deal or either defending the linguistic rights of French-speakers. The movement began as a defence of the primacy of French but later gained political and socio-economic objectives. In French, the terms ''wallingantisme'' and ''wallingants'' are also used to describe, sometimes pejoratively, the movement and its activists. To a lesser extent, the Walloon Movement is also associated with the representation of the small German-speaking Community of Belgium, German-speaking population in the East Belgium of the Walloon Region. History Historians agree that the Walloon political movement began in 1880 with the foundation of a ''Walloon and French-speaking defence movement'' following the first ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namur (city)
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration. Namur stands at the confluence of the rivers Sambre and Meuse and straddles three different regions – Hesbaye to the north, Condroz to the south-east, and Entre-Sambre-et-Meuse to the south-west. The city of Charleroi is located to the west. The language spoken is French. The municipality consists of the following districts: Beez, Belgrade, Boninne, Bouge, Champion, Cognelée, Daussoulx, Dave, Erpent, Flawinne, Gelbressée, Jambes, Lives-sur-Meuse, Loyers, Malonne, Marche-les-Dames, Naninne, Saint-Servais, Saint-Marc, Suarlée, Temploux, Vedrin, Wépion, and Wierde. History Early history The town began as an important trading settlement in Celtic times, straddling east–west and north–south trade routes across the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theobald Von Bethmann Hollweg
Theobald Theodor Friedrich Alfred von Bethmann Hollweg (29 November 1856 – 1 January 1921) was a German politician who was the chancellor of the German Empire from 1909 to 1917. He oversaw the German entry into World War I. According to biographer Konrad H. Jarausch, a primary concern for Bethmann in July 1914 was the steady growth of Russian power, and the growing closeness of the British and French military collaboration. Under these circumstances he decided to run what he considered a calculated risk to back Austria-Hungary in a local war against Serbia, while risking a major war with Russia. He calculated that France would not support Russia. This calculation proved to be mistaken when Russia decided on general mobilization. The German army saw an opportunity to use the Schlieffen Plan for a quick victory against a poorly prepared France. By rushing through Belgium, however, Germany expanded the war to include the United Kingdom. Bethmann Hollweg thus failed to keep France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)