|
Mohamed Thakurufaanu
As-Sulṭaan al-Ghaazee Muhammad Thakurufaanu al-A'uẓam () (death 26 August 1585) or As-Sultan Ghazi Muhammad Bodu Thakurufaanu ruled over the Maldive Islands from 1573 to 1585. He is known for fighting the Portuguese who ruled over the Maldives from 1558–1573 after killing Sultan Ali VI in Malé. His victory is commemorated in the Maldives as '' Qaumee Dhuvas'' or National Day. He was also the first Maldivian King to form the (a unified military body). Early years Muhammad Thakurufaanu was the son of Katheebu Hussain of Utheemu in Thiladhummathi Atoll and Lady Aiminaa Dhiyoa of Ihavandhoo. Muhammad Thakurufan learned (Martial Arts). Defeat of the Portuguese After killing Sultan Ali IV, the Maldives was ruled by and the Portuguese. was a regent of the (Sultan Hassan IX) who was the first Maldivian and the only member of its royalty to renounce Islam and convert to Christianity, later upon his deposition he took refuge in Goa, India. After the invasion, the Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sultans Of The Maldives
Maldives was turned into a Sultanate in 1153 when the Buddhist King Dhovemi converted to Islam. Prior to that the Maldives was a Buddhist Kingdom, a Hindu Kingdom and before that a matriarchal society with each atoll ruled by a chief queen according to some accounts or by others, several theocratic societies ruled by priests known as ''Sawamias'' of heliolatric, selenolatric and astrolatric religions. All the rulers before King Koimala only ruled over parts of the Maldives or Deeva Maari (and Dheeva Mahal) as it was known then. Koimala was the first king to rule over all the islands of the Maldives as we know today and the island of Maliku. The formal title of the Sultan up to 1965 was, ''Sultan of Land and Sea, Lord of the twelve-thousand islands and Sultan of the Maldives'' which came with the style ''Highness''. After independence in 1965 the Sultan assumed the title King with the style Majesty. This style was used until 1968, when the Maldives became a republic for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
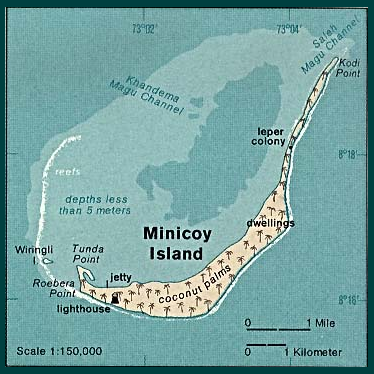
Minicoy
Minicoy, locally known as Maliku (), is an island in Lakshadweep, India. Along with Viringili, it is on ''Maliku atoll'', the southernmost atoll of Lakshadweep archipelago. Administratively, it is a census town in the Indian union territory of Lakshadweep. The island is situated 425 km west of Trivandrum, the capital city of Kerala. Etymology Minicoy is known as ''Maliku'' in the local language, Dhivehi, which is also the national and official language of the Republic of Maldives. The language is a descendant of Elu Prakrit and is closely related to the Sinhala language, but not mutually intelligible with it. However, the Lakhshadweep Administration refers to Dhivehi as Mahl. This is due to a misunderstanding on the part of a British civil servant who came to Minicoy in the 1900s during the time of the British Raj. The official asked a local what his language was and he replied "Dhivehi-bas". The official looked confused as he had never heard of this language. Noticing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type of tomb, or the tomb may be considered to be within the mausoleum. Overview The word ''mausoleum'' (from Greek μαυσωλείον) derives from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus (near modern-day Bodrum in Turkey), the grave of King Mausolus, the Persian satrap of Caria, whose large tomb was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Historically, mausolea were, and still may be, large and impressive constructions for a deceased leader or other person of importance. However, smaller mausolea soon became popular with the gentry and nobility in many countries. In the Roman Empire, these were often in necropoles or along roadsides: the via Appia Antica retains the ruins of many private mausolea for kilometres outside Rome. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramadan
, type = islam , longtype = Religious , image = Ramadan montage.jpg , caption=From top, left to right: A crescent moon over Sarıçam, Turkey, marking the beginning of the Islamic month of Ramadan. Ramadan Quran reading in Bandar Torkaman, Iran. Community Iftar meal in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, Tarawah prayers in a mosque in West Sumatra, Indonesia. Foods served at a traditional Iftar meal. Ramadan decorations in Jerusalem. Zakat donation boxes in Taipei, Taiwan. , official_name = , observedby = Muslims , begins = At the last night of the month of Sha'ban , ends = At the last night of the month of Ramadan , date = Variable (follows the Islamic lunar calendar) , date2022 = 2 April – 2 May , celebrations = Community iftars and Community prayers , observances = * Sawm (fasting) * Zakat and sadaqah (alms giving) * Commemorating Qadr Night * Reading the Quran * Abstaining from all bad deeds and staying humble * Taraweeh prayer (Sunni Muslims) , relatedto = Eid al-F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Mohamed Thakurufaan Male
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called ''immurement'', and is a method of final disposition, as an alternative to cremation or burial. Overview The word is used in a broad sense to encompass a number of such types of places of interment or, occasionally, burial, including: * Architectural shrines – in Christianity, an architectural shrine above a saint's first place of burial, as opposed to a similar shrine on which stands a reliquary or feretory into which the saint's remains have been transferred * Burial vault – a stone or brick-lined underground space for multiple burials, originally vaulted, often privately owned for specific family groups; usually beneath a religious building such as a church ** Cemetery ** Churchyard * Catacombs * Chamber tomb * Charnel house * Church monum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states a ..., individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minicoy Island
Minicoy, locally known as Maliku (), is an island in Lakshadweep, India. Along with Viringili, it is on ''Maliku atoll'', the southernmost atoll of Lakshadweep archipelago. Administratively, it is a census town in the Indian union territory of Lakshadweep. The island is situated 425 km west of Trivandrum, the capital city of Kerala. Etymology Minicoy is known as ''Maliku'' in the local language, Dhivehi, which is also the national and official language of the Republic of Maldives. The language is a descendant of Elu Prakrit and is closely related to the Sinhala language, but not mutually intelligible with it. However, the Lakhshadweep Administration refers to Dhivehi as Mahl. This is due to a misunderstanding on the part of a British civil servant who came to Minicoy in the 1900s during the time of the British Raj. The official asked a local what his language was and he replied "Dhivehi-bas". The official looked confused as he had never heard of this language. Noticing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannanore
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hub Kochi and south of the major port city and a commercial hub, Mangalore. During the period of British colonial rule in India, when Kannur was a part of the Malabar District (Madras Presidency), the city was known as Cannanore. Kannur is the sixth largest urban agglomeration in Kerala. As of 2011 census, Kannur Municipal Corporation, the local body which administers mainland area of city, had a population of 232,486. Kannur was the headquarters of Kolathunadu, one of the four most important dynasties on the Malabar Coast, along with the Zamorin of Calicut, Kingdom of Cochin and Kingdom of Quilon. The Arakkal kingdom had right over the city of Kannur and Laccadive Islands in the late medieval period. Kannur municipality was formed on 1 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Raja
The Sultan Ali Raja or Ali Raja or Adi Raja was the title of the Muslim king of Arakkal kingdom from the sixteenth to early nineteenth century. Arakkal dynasty Reigning rajas and beebis * Ali Raja Ali I (1545–1591) * Ali Raja Abubakar I (1591–1607) * Ali Raja Abubakar II (1607–1610) * Ali Raja Muhammad Ali I (1610–1647) * Ali Raja Muhammad Ali II (1647–1655) * Ali Raja Kamal (1655–1656) * Ali Raja Muhammad Ali III (1656–1691) * Ali Raja Ali II (1691–1704) * Ali Raja Kunhi Amsa I (1704–1720) * Ali Raja Muhammad Ali IV (1720–1728) * Ali Raja Beevi Harrabichi Kadavube Sultana (1728–1732) * Ali Raja Beevi Junumabe Sultana I (1732–1745) * Ali Raja Kunhi Amsa II (1745–1777) * Ali Raja Beevi Junumabe Sultana II (1777–1819) Heads of the Arakkal dynasty since 1819 * Arakkal Beevi Mariambe Sultana (1819–1838) * Arakkal Beevi Hayashabe Sultana (1838–1852) * Sultan Abdul Rahman I Ali Raja (1852–1870) * Sultan Musa Ali Raja (1870–1899) * Sultan Muhammad Ali R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viber Image 2021-11-24 23-44-27-359
Viber, or Rakuten Viber, is a cross-platform voice over IP (VoIP) and instant messaging (IM) software application owned by Japanese multinational company Rakuten, provided as freeware for the Google Android, iOS, Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS and Linux platforms. Users are registered and identified through a cellular telephone number, although the service is accessible on desktop platforms without needing mobile connectivity. In addition to instant messaging it allows users to exchange media such as images and video records, and also provides a paid international landline and mobile calling service called Viber Out. As of 2018, there are over a billion registered users on the network. The software was developed in 2010 by Cyprus-based Viber Media, which was bought by Rakuten in 2014. Since 2017, its corporate name has been Rakuten Viber. It is based in Cyprus with offices in London, Manila, Moscow, Paris, San Francisco, Singapore, and Tokyo. History Founding (2010) Vib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolhufushi (Meemu Atoll)
Kolhufushi (Dhivehi: ކޮޅުފުށި) is one of the inhabited islands of Meemu Atoll. History 2004 tsunami and aftermath The island was greatly affected by the 2004 tsunami, although coral reefs took some of the impact. The island's chief, Mr. Sigee, described the water as reaching his chin. Two weeks after the disaster, the island's population was found to have lost at least sixteen people, and the island's mango and banana trees had been poisoned by the saltwater. Some homes and a century-old mosque had also been destroyed. Most of the other houses were unsuitable for habitation, leaving only a handful of functional homes. By mid-January 2005, 8% of the 13,000-strong displaced Maldivian population was housed in temporary shelters on Kolhufushi. The construction of 55 replacement houses was started in October 2008, and a further 168 houses were started in 2010. Tsunami drills were introduced on the island in 2018. A tsunami warning in 2016 had uncovered a lack of preparedness, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpeg/1200px-Taj_Mahal_(Edited).jpeg)