|
Ministry Of Energy (Myanmar)
The Ministry of Energy ( my, , 'MOE') is a ministry in the Burmese government responsible for the country's energy sector, in particular exploration of crude oil and natural gas and manufacture and distribution of petrochemicals and petroleum products. History From 1948 to 1985, organizations for energy sector are organized under Ministry of Mines and Ministry of Industry (2). Ministry of Energy was formed on 1985 April (12) by Council of State. In 2016, newly elected president Htin Kyaw combined Ministry of Electric Power and Ministry of Energy as Ministry of Electricity and Energy. In 2022 May, SAC reconstituted the ministry as Ministry of Electric Power and Ministry of Energy. Ministers Ministers of MOE (2011 - 2016) *Than Htay (30 March 2011 - 25 July 2013) *Zayar Aung (14 August 2015 - 30 March 2016) Ministers of MOEE (2016 - 2022) *Aung San Suu Kyi (30 March 2016 - 6 April 2016) * Pe Zin Tun (7 April 2016 - 1 August 2017) * Win Khaing (2 August 2017 - 1 February 2021) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Myanmar
Myanmar ( also known as Burma) operates ''de jure'' as a unitary assembly-independent republic under its 2008 constitution. On 1 February 2021, Myanmar's military took over the government in a coup, causing ongoing anti-coup protests. Political conditions The history of Myanmar, formerly called Burma, began with the Pagan Kingdom in 849. Although each kingdom has constantly been at war with their neighbors, it was the largest South East Asian Empire during the 16th century under the Taungoo Dynasty. The thousand-year line of Burmese monarchy ended with the Third Anglo-Burmese War in 1885. The country was then administered as part of British India until 1937. British Burma began with its official recognition on the colonial map that marks its new borders containing over 100 ethnicities. It was named Burma after the dominant ethnic group Bamar, who make up 68 percent of the population. During World War II, a coalition of mostly members of the Bamar ethnic group volunteer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Electric Power
The Ministry of Electric Power ( my, လျှပ်စစ်စွမ်းအားဝန်ကြီးဌာန; abbreviated MOEP) administers Burma's electric power policies. The current minister is Thaung Han . History On 1 October 1951, Electricity Supply Board (ESB) was organized under the Ministry of Industry. On 16 March 1972, it was changed as Electric Power Corporation (EPC). On 1 April 1975, the Ministry of Industry was organized as No 1 and No 2, the EPC was composed under the Ministry of No 2 Industry. On 12 April 1985,the Ministry of No 2 Industry was changed as Ministry of Energy, so the EPC was composed under it. On 1 April 1989, the EPC was changed into Myanmar Electric Power Enterprise (MEPE). On 15 November 1997,the Ministry of Electrical Power was started organized and there were three departments under it, Department of Electrical Power, Myanmar Electric Power Enterprise and Department of Hydropower. On 15 May 2006, the ministry was divided into No 1 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Ministries Of Myanmar
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government relocated the administrative functions to the purpose-built capital city of Naypyidaw in north central Myanmar. With over 7 million people, Yangon is Myanmar's most populous city and its most important commercial centre. Yangon boasts the largest number of colonial-era buildings in Southeast Asia, and has a unique colonial-era urban core that is remarkably intact. The colonial-era commercial core is centered around the Sule Pagoda, which is reputed to be over 2,000 years old. The city is also home to the gilded Shwedagon Pagoda – Myanmar's most sacred and famous Buddhist pagoda. Yangon suffers from deeply inadequate infrastructure, especially compared to other major cities in Southeast Asia, such as Jakarta, Bangkok or Hanoi. Though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myanmar Engineering Society
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, John Wells explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a non-rhotic variety of English, in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: [ˈmjænmɑː, ˈbɜːmə]. So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as [mɑːr] or of Burma as [bɜːrmə] by some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a spelling pronunciation based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. The final ''r'' in ''Myanmar'' was not intended for pronunciation and is there to ensure that the final a is pronounced with the broad a, broad ''ah'' () in "father". If the Burmese name my, မြန်မာ, label=none were spelled "Myanma" in English, this would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aung Than Oo
Aung Than Oo is a Burmese politician who was previously Economy Minister for Yangon Region. In June 2022 Aung Than Oo was dismissed by Myanmar's State Administration Council (SAC) per Order No. 41/2022, following Constitutional Article 419. Before his ministerial tenure Aung Than Oo was the Vice-Chairman of the Myanmar Rice Federation and a Union Solidarity and Development Party The Union Solidarity and Development Party ( my, ပြည်ထောင်စုကြံ့ခိုင်ရေးနှင့် ဖွံ့ဖြိုးရေးပါတီ; abbr. USDP) is a political party in Myanmar, registered on ... member. He won the 2010 general election but lost to the NLD in 2015 and 2020 elections. References {{reflist Burmese politicians Year of birth missing (living people) Living people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Win Khaing
Win or WIN may refer to: * A victory Arts and entertainment Film * ''Win!'', a 2016 American film Literature * ''Win'' (Coben novel), a 2121 novel by Harlan Coben * WIN (pacifist magazine), published by the War Resisters League * WIN (wrestling magazine), American high school and college amateur wrestling publication Music * Win (band), a Scottish band * "Win" (song), by Jay Rock * "Win", a song by Brian McKnight from the album ''Gold'' * "Win", a song by David Bowie from the album ''Young Americans'' * "Win", a song by Stefflon Don and DJ Khaled from the mixtape ''Secure'' * Worldwide Independent Network (WIN), a coalition of independent music bodies, see Independent record label#Worldwide Independent Network (WIN)) Television and radio * DWNU or Win Radio, a Filipino radio station * Win FM, an Indian radio station * WIN Television, an Australian television network ** WIN Corporation, the owner of WIN Television ** WIN News, the news service for WIN Television ** WIN (TV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pe Zin Tun
Pe may refer to: Physical education Language * Pe language * Pe (Cyrillic), a letter (П) in the Cyrillic alphabet * Pe (Semitic letter), a letter (פ ,ف, etc.) in several Semitic alphabets ** Pe (Persian letter), a letter (پ) in the Arabic alphabet * Pe (Armenian), a letter (Պ պ) in the Armenian alphabet Mathematics, science, and technology * Weierstrass p (also called "pe"), a mathematical letter (℘) used in Weierstrass's elliptic functions and power sets * Péclet number (abbreviated "Pe."), a dimensionless number used in physics * Pe (text editor), a text editor for BeOS * Petlyakov, Russian aircraft design bureau * Pulmonary emphysema, a lung disease * Pulmonary embolism, a medical condition * Portable Executable, a Microsoft Windows executable file format * Provider edge router, an edge network router * Polyethylene, a type of plastic Places * Pe (city), Ancient Egyptian city that merged into Buto * Pe, Tibet, a town on the Yarlung Tsangpo River * .pe, the Internet c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
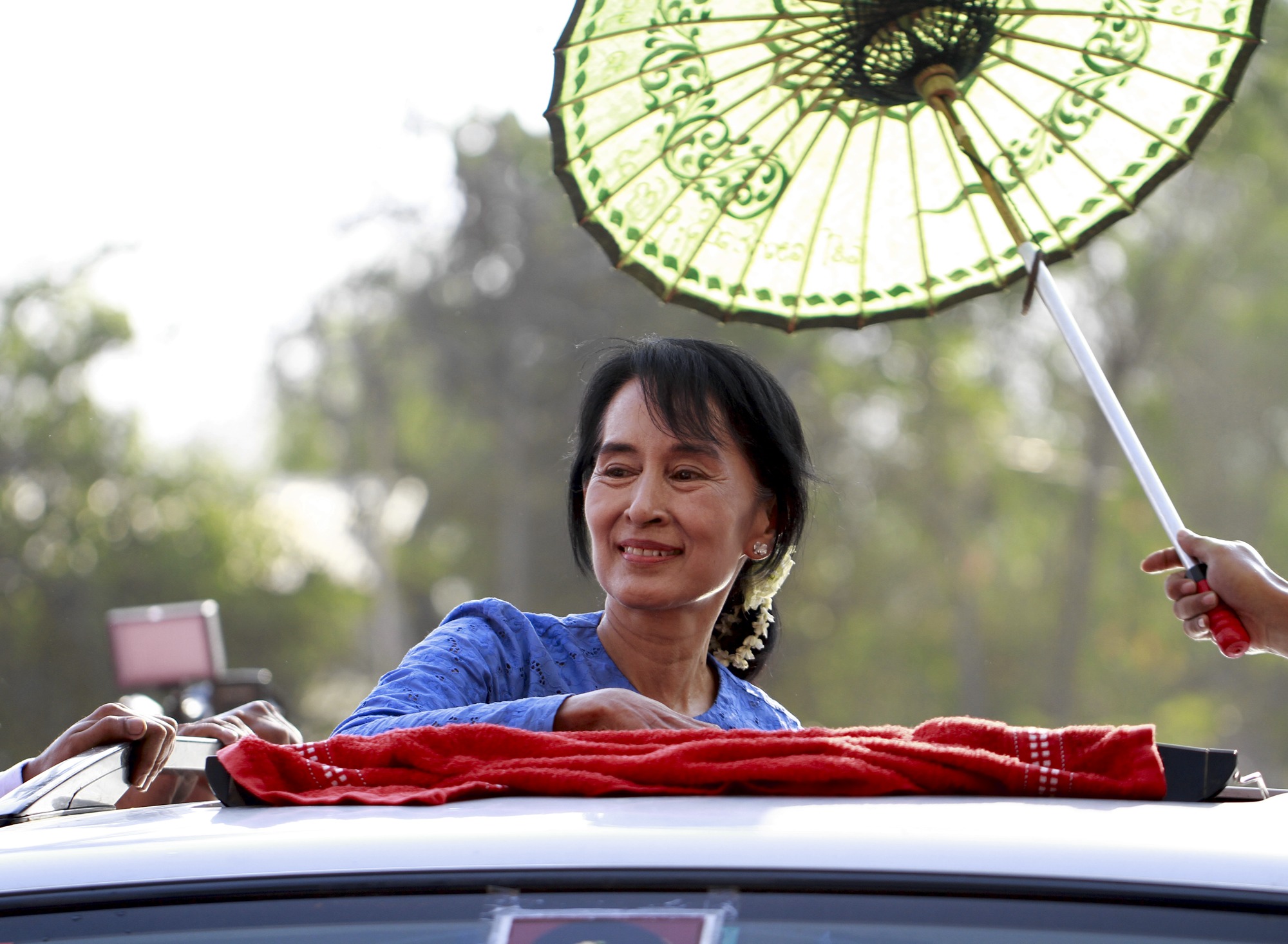
Aung San Suu Kyi
Aung San Suu Kyi (; ; born 19 June 1945) is a Burmese politician, diplomat, author, and a 1991 Nobel Peace Prize laureate who served as State Counsellor of Myanmar (equivalent to a prime minister) and Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2016 to 2021. She has served as the chairperson of the National League for Democracy (NLD) since 2011, having been the general secretary from 1988 to 2011. She played a vital role in Myanmar's transition from military junta to partial democracy in the 2010s. The youngest daughter of Aung San, Father of the Nation of modern-day Myanmar, and Khin Kyi, Aung San Suu Kyi was born in Rangoon, British Burma. After graduating from the University of Delhi in 1964 and St Hugh's College, Oxford in 1968, she worked at the United Nations for three years. She married Michael Aris in 1972, with whom she had two children. Aung San Suu Kyi rose to prominence in the 8888 Uprising of 8 August 1988 and became the General Secretary of the NLD, which she h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zayar Aung
Zeya Aung ( my, ဇေယျာအောင်; also spelt Zeyar Aung) is the incumbent Minister of Construction. He was appointed by President Thein Sein in August 2013, following the transfer of his predecessor, Than Htay Than Htay ( my, သန်းဌေး; born 12 November 1954) is a Burmese politician who served as Chairman of the Union Solidarity and Development Party from August 2016 to September 2022 due to medical treatment. He previously served as the Mi ..., by presidential order, on 25 July 2013. He previously served as Minister of Rail Transportation from September 2012 to July 2013. A military officer, Zeya Aung was Tatmadaw Northern Command Commander from August 2010 to September 2012, as well as a former Commander of the Light Infantry Division (LID) 88. Zeya Aung is the brother-in-law of Ye Htut. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Zeya Aung Transport ministers of Myanmar Energy ministers of Myanmar Communication ministers of Myanmar Information ministers of Myan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Than Htay
Than Htay ( my, သန်းဌေး; born 12 November 1954) is a Burmese politician who served as Chairman of the Union Solidarity and Development Party from August 2016 to September 2022 due to medical treatment. He previously served as the Minister for Rail Transportation, and Minister for Energy. He is a retired brigadier general in the Myanmar Army. Early life Than Htay was born on 12 November 1954 in Ayeyarwady Region. When he was 17, he was accepted into the Defence Services Academy and earned a bachelor of arts and a master’s degree in defense. Military and political career Serving in the military until 2010, he peaked as a brigadier general. He left the army at the rank of brigadier general in 2003 to become deputy minister of energy, before being promoted to minister in 2011. He joined the Union Solidarity and Development Party at its founding in the lead-up to the 2010 election. He won election to the Pyithu Hluttaw, representing Myanaung township, in the 2012 by- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |