|
Military History Of The Five Dynasties And Ten Kingdoms
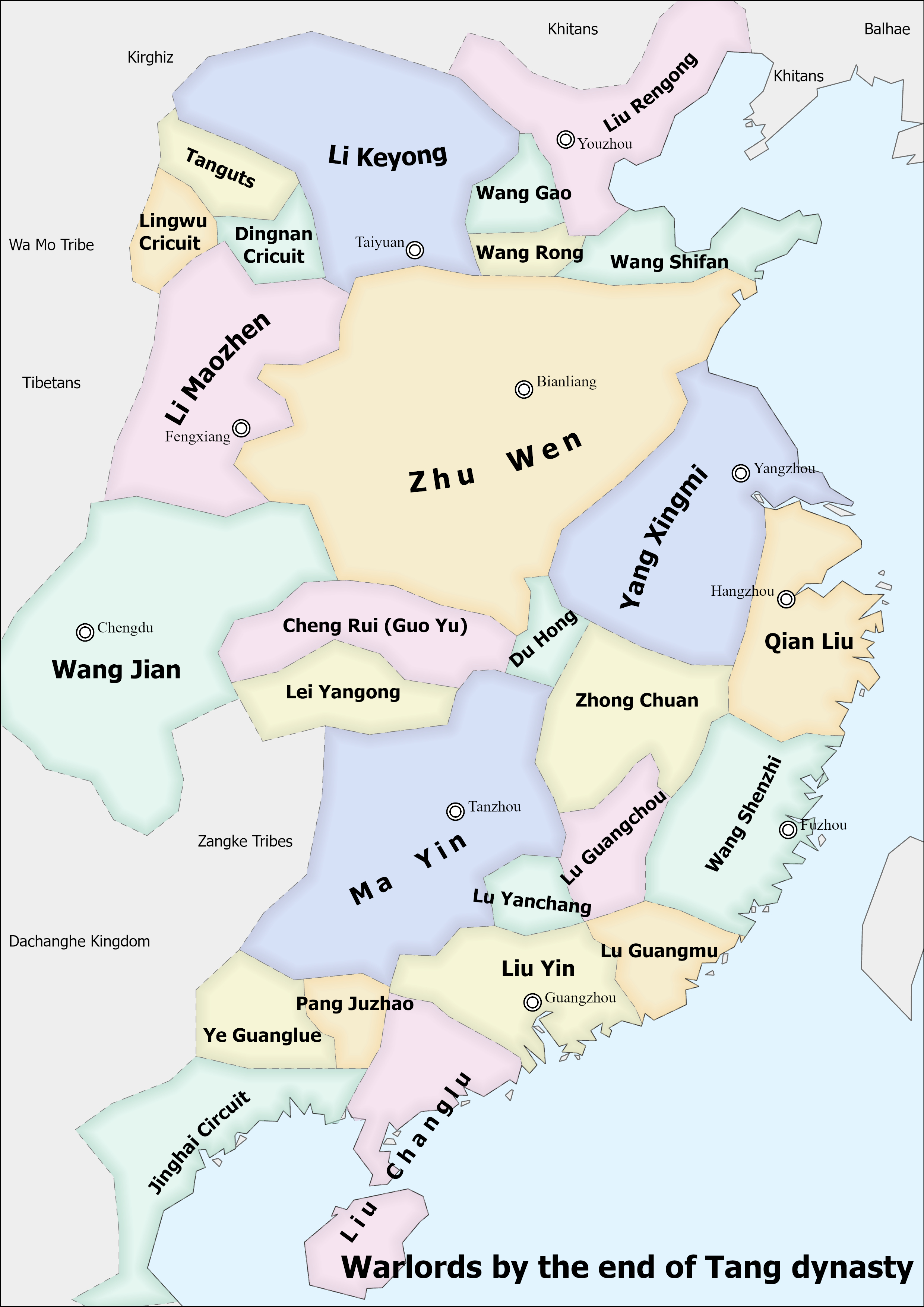
The military history of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms covers the period of Chinese history from the collapse of the Tang dynasty in 907 to the demise of Northern Han in 979. This period of Chinese history is noteworthy for the introduction of gunpowder weapons and as a transitional phase from the aristocratic imperial system to the Confucian bureaucracy which characterized the Song, Ming, and Qing dynasties. Five Dynasties Later Liang (907–923) The Later Liang dynasty was founded by Zhu Wen. Zhu Wen was originally a rebel during the Huang Chao rebellion but later surrendered to the Tang dynasty and served under the military commander Li Keyong. In 904, Zhu Wen kidnapped Emperor Zhaozong of Tang, took him to Luoyang, and killed him. Three years later he also disposed of Emperor Ai of Tang, ending the Tang dynasty, and proclaimed his own dynasty of Liang. Zhu Wen undertook several military campaigns and failed in all of them. Despite lowering taxes to win support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Dynasties And Ten Kingdoms
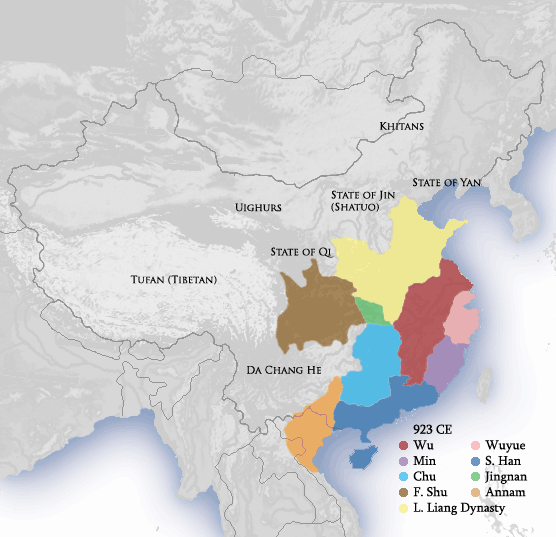
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent dynastic states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was a prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history. Traditionally, the era is seen as beginning with the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 and reaching its climax with the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. In the following 19 years, Song gradually subdued the remaining states in South China, but the Liao dynasty still remained in China's north (eventually succeeded by the Jin dynasty), and the Western Xia was eventually established in China's northwest. Many states had been ''de facto'' independent long before 907 as the Tang dynasty's control over its officials waned, but the key event was their recognition as sovereign by foreig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River (Henan), Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang, Henan, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of December 31, 2018, Luoyang had a population of 6,888,500 inhabitants with 2,751,400 people living in the built-up (or metro) area made of the city's five out of six urban districts (except the Jili District not continuously urbanized) and Yanshi District, now being conurbated. Situated on the Central Plain (China), central plain of China, Luoyang is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities#East Asia, oldest cities in China and one of the History of China#Ancient China, cradles of Chinese civilization. It is the earliest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. Name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Jin (Five Dynasties)
Jin, known as the Later Jìn (, 936–947) or the Shi Jin (石晉) in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was founded by Shi Jingtang (Emperor Gaozu) with aid from the Liao dynasty, which assumed suzerainty over the Later Jin. After Later Jin's second ruler, Shi Chonggui (Emperor Chu), fell out with the Liao dynasty, the Liao invaded in 946 and in 947, annihilated the Later Jin and annexed its former territories. Founding the Later Jin The first sinicized Shatuo state, Later Tang, was founded in 923 by Li Cunxu, son of the Shatuo chieftain Li Keyong. It extended Shatuo domains from their base in Shanxi to most of North China, and into Sichuan. After Li Cunxu’s death, his adopted son, Li Siyuan became emperor. However, the Shatuo relationship with the Khitans, which was vital to their rise to power, had soured. Shi Jingtang, the son-in-law of Li Cunxu, rebelled against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khitan People
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East. As a people descended from the proto-Mongols through the Xianbei, Khitans spoke the Khitan language, a Para-Mongolic language related to the Mongolic languages. During the Liao dynasty, they dominated a vast area of Siberia and Northern China. After the fall of the Liao dynasty in 1125 following the Jurchen invasion, many Khitans followed Yelü Dashi's group westward to establish the Qara Khitai or Western Liao dynasty, in Central Asia, which lasted nearly a century before falling to the Mongol Empire in 1218. Other regimes founded by the Khitans included the Northern Liao, Eastern Liao and Later Liao in China, as well as the Qutlugh-Khanid dynasty in Persia. Etymology There is no consensus on the etymology of the name of Khitan. There are basica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Jingtang
Shi Jingtang ( zh, 石敬瑭; 30 March 892 – 28 July 942''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 283.), also known by his temple name Gaozu (), was the founding emperor of imperial China's short-lived Later Jin during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, reigning from 936 until his death. Shi had Shatuo origins and was an important military general for the Later Tang before rebelling in 936. He overthrew Li Cunxu of the Later Tang and enlisted the help of the Khitan-ruled Liao state. For this he was called Emperor Taizong of Liao's adopted son (even though he was 10 years older). After Shi's rise to power, the Liao would later annex the strategically crucial Sixteen Prefectures and eventually annex the entire Later Jin. The rise of the Liao in northern China and Mongolia would shape Chinese politics for the centuries leading up to the Mongol Empire. Background and early life The official history ''Old History of the Five Dynasties'' stated that his family was originally descende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Siyuan
Li Siyuan (李嗣源, later changed to Li Dan (李亶)) (10 October 867 – 15 December 933), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Mingzong of Later Tang (後唐明宗), was the second emperor of the Later Tang dynasty of China, reigning from 926 until his death. He was an ethnic Shatuo originally named, in the Shatuo language, Miaojilie (邈佶烈). Adopted by the ethnic Shatuo ruler Li Keyong of the Former Jin dynasty, Li Siyuan became a trusted general under both Li Keyong and Li Keyong's successor Li Cunxu (Emperor Zhuangzong), the Later Tang founder. In 926 he seized power by a coup d'état when a mutiny called the Xingjiao Gate Incident killed Li Cunxu, and ruled with both discipline and compassion for the next seven years. Despite an abundance of natural disasters, his reign was markedly more peaceful than the half-century preceding it. Background Li Siyuan was born with the Shatuo name of Miaojilie in 867 in Yingzhou (應州; present-day Ying County, Shanxi), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Shu
Great Shu (Chinese: 大蜀, Pinyin: Dàshǔ) called in retrospect Former Shu (Chinese: 前蜀, Pinyin: Qiánshǔ) or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was one of the Ten Kingdoms formed during the chaotic period between the rules of the Tang dynasty and the Song dynasty. It existed in 907–925 CE. It was the third state named "Shu" on the same territory, the second one having been Shu Han. The country's name changed from "Shu" to "Han" (Chinese: 漢, Pinyin: Hàn) in 917–918, which is not to be confused with another contemporaneous Chinese kingdom during the same Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, the Southern Han (), 917–971 CE. Founding of the Former Shu Wang Jian was named military governor of western Sichuan by the Tang court in 891. As the Tang Dynasty weakened and eventually fell in 907, Wang was able to expand his holdings into eastern Sichuan and took the title of emperor as the Tang fell in 907. Geographical extent of the Former Shu The Shu was based in it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qi (Li Maozhen's State)
Qi () was a kingdom during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in Chinese history. The kingdom, at its prime, covered parts of modern-day Gansu, Shaanxi, and Sichuan provinces, but eventually shrank to only the immediate area around its capital Fengxiang in Shaanxi. Its only ruler was Li Maozhen, who later submitted to Later Tang. (After Li Maozhen's death in 924, his son Li Congyan would continue to govern Fengxiang until 926, when he was removed by the Later Tang's emperor Li Cunxu,''Zizhi Tongjian ''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynast ...'', vol. 274. although he would serve three later stints as governor of Fengxiang.''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 275.''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 279.) References Former countries in Chinese history {{China-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yan (Five Dynasties Period)
Yan (), sometimes known in historiography as Jie Yan (), was a short-lived monarchical state in the vicinity of present-day Beijing at the beginning of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Yan, established by Liu Shouguang in 911, only lasted for two years before its destruction by Li Cunxu of the Former Jin dynasty. As the only ruler of Yan, Liu Shouguang was noted for his cruelty. The state of Yan was therefore sometimes referred to as ''Jie Yan'', in reference to the tyrannical ruler Jie of the Xia dynasty The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In tradi .... References * {{5d10k Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Former countries in Chinese history 911 establishments 910s disestablishments States and territories established in the 910s States and territories d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shatuo
The Shatuo, or the Shatuo Turks (; also transcribed as Sha-t'o, Sanskrit SartZuev Yu.A., ''"Horse Tamgas from Vassal Princedoms (Translation of Chinese composition "Tanghuyao" of 8-10th centuries)"'', Kazakh SSR Academy of Sciences, Alma-Ata, I960, p. 127 (In Russian)) were a Turkic tribe that heavily influenced northern Chinese politics from the late ninth century through the tenth century. They are noted for founding three, Later Tang, Later Jin, and Later Han, of the five dynasties and one, Northern Han, of the ten kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Northern Han would later be conquered by the Song dynasty. After which, they mostly disappeared as an ethnic group and assimilated into the Han Chinese ethnicity. Origins Chuyue The Shatuo tribe were descended mainly from the Western Turkic Chuyue tribe, who in turn belonged to a group of four Chuy tribes, collectively known as Yueban. The Yueban state survived to the end of the 480s when its indep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin (Later Tang Precursor)
Jin (晉; 883 (or 896 or 907)–923), also known as Hedong (河東) and Former Jin (前晉) in Chinese historiography, was a dynastic state of China and the predecessor of the Later Tang dynasty. Its princely rulers were the ethnic Shatuo warlords Li Keyong and Li Cunxu (Li Keyong's son). Although the Five Dynasties period began only in 907, Li Keyong's territory which centered around modern Shanxi can be referred to as Jin as early as 896, when he was officially created the Prince of Jin by the failing and powerless Tang dynasty court, or even (by extension, anachronistically) as early as 883, when he was created the ''jiedushi'' military governor of Hedong Circuit, which controlled more or less the same territory. History The Jin rulers Li Keyong and Li Keyong's son Li Cunxu, of Shatuo extraction, claimed to be the rightful subjects of the defunct Tang dynasty (618–907), in a struggle against the usurper state of the Later Liang dynasty. At the time of the Tang dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the Northern Song dynasty. As of 31 December 2018, around 4,465,000 people lived in Kaifeng's Prefecture, of whom 1,652,000 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Xiangfu, Longting, Shunhe Hui, Gulou and Yuwantai Districts. Located along the Yellow River's southern bank, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the west, Xinxiang to the northwest, Shangqiu to the east, Zhoukou to the southeast, Xuchang to the southwest, and Heze of Shandong to the northeast. Kaifeng is also a major city in the world by scientific research outputs as tracked by the Nature Index. The city is home to a campus of Henan University, one of the national key universities in the Double First Class University Plan. Names The postal romanization for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |