|
Mikulin AM-34
The Mikulin AM-34 (M-34) was a Soviet mass-produced, liquid-cooled, aircraft engine of domestic design. Its initial development was troubled, but it eventually became one of the most successful Soviet aircraft engines of the 1930s. It was utilized on numerous aircraft, including the Beriev MBR-2, Tupolev TB-3, Tupolev TB-4, Tupolev ANT-20, Petlyakov Pe-8, Kalinin K-7, Polikarpov I-17, and Bolkhovitinov DB-A, as well as the G-5 and various prototype motor torpedo boats. A version of the maritime model was adapted for use in several prototype heavy tanks in 1939, although none was placed into production. Design and development Before World War II, the Soviet aeroengine industry was mainly engaged in producing foreign designs, notably Wright, Bristol, Hispano-Suiza, and Gnome-Rhône. Several engines of so-called original design were developed, although these were probably largely based on foreign models (e.g. Mikulin M-17, Shvetsov M-25, Klimov M-103 etc.) The M-34 was thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V12 Engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine where two banks of six cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V12 engines are more common than V10 engines. However, they are less common than V8 engines. The first V12 engine was built in 1904 for use in racing boats. Due to the balanced nature of the engine and the smooth delivery of power, V12 engines were found in early luxury automobiles, boats, aircraft, and tanks. Aircraft V12 engines reached their apogee during World War II, following which they were mostly replaced by jet engines. In Formula One racing, V12 engines were common during the late 1960s and early 1990s. Applications of V12 engines in the 21st century have been as marine engines, in railway locomotives, as large stationary power as well as in some European sports and luxury cars. Design Balance and smoothness Each bank of a V12 engine essentially functions as a straight-six engine, which by itself has perfect primary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klimov M-103
The Klimov M-103 is a V12 liquid-cooled piston aircraft engine used by Soviet aircraft during World War II.Gunston 1989, p.90. Design and development The M-103 was a further development of the Klimov M-100 engine that was itself a licensed copy of the French Hispano-Suiza 12Ybrs. It differed from both engines in a number of aspects such as increased compression ratio, increased supercharger ratio, increased rpm's, strengthened cylinder blocks, a new crankshaft, a more aggressive camshaft, and flat bottomed cylinders. Developed in 1936 it was ready for testing in October 1936. The first two models failed testing due to cracked cylinder blocks and the engine was resubmitted for testing in 1937. After passing its trials it was cleared for production in 1938 and 11,681 were produced until 1942 at its factory in Rybinsk. The M-103 was followed by the M-105. Variants * M-103A - 148mm rather than 150mm bore cylinders. * M-103P - A ShVAK cannon fitted to fire through the engine v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Fuel
Various alcohols are used as fuel for internal combustion engines. The first four aliphatic alcohols (methanol, ethanol, propanol, and butanol) are of interest as fuels because they can be synthesized chemically or biologically, and they have characteristics which allow them to be used in internal combustion engines. The general chemical formula for alcohol fuel is CnH2n+1OH. Most methanol is produced from natural gas, although it can be produced from biomass using very similar chemical processes. Ethanol is commonly produced from biological material through fermentation processes. Biobutanol has the advantage in combustion engines in that its energy density is closer to gasoline than the simpler alcohols (while still retaining over 25% higher octane rating); however, biobutanol is currently more difficult to produce than ethanol or methanol. When obtained from biological materials and/or biological processes, they are known as bioalcohols (e.g. "bioethanol"). There is no chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of petroleum and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic continuous pi bonds between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is partially responsible for the aroma of gasoline. It is used primarily as a precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structure, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. Although benzene is a major industrial chemical, it finds limited use in consumer items because of its toxicity. History Discovery The word "''benzene''" derives from "''gum benzoin''" (benzoin res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henschel Hs 130
The Henschel Hs 130 was a German high-altitude reconnaissance and bomber aircraft developed in World War II. It suffered from various mechanical faults and was never used operationally, only existing as prototype airframes. Development Development of the Hs 130 began with two Hs 128 prototypes, which first flew on 11 April 1939, with the second prototype flying on 20 February 1940.Dressel and Greil 1994, p.166. Both prototypes were research aircraft, used for testing pressurized cabins, engine superchargers, and cantilever wings. Different engines powered the two prototypes; the V1 by Daimler-Benz DB 601s and the V2 by Junkers Jumo 210s. Both had fixed landing gear.Donald 1999, p.147. While trials of the two prototypes were not successful, the potential of a high altitude aircraft caught the attention of Theodor Rowehl, commander of the ''Luftwaffe''s special reconnaissance unit. Rowehl's interest in the Hs 128's potential for high-altitude reconnaissance missions led Reich A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispano-Suiza 12Y
The Hispano-Suiza 12Y was an aircraft engine produced by Hispano-Suiza for the French Air Force before the Second World War. The 12Y became the primary French 1,000 hp (750 kW) class engine and was used in a number of famous aircraft, including the Morane-Saulnier M.S.406 and Dewoitine D.520. Its design was based on the earlier, and somewhat smaller, 12X. The 12X did not see widespread use before the 12Y replaced it and became one of the most powerful French designs on the eve of the war. The 12Z was being designed but this was ended by the fall of France and the German occupation. The 12Y was produced under Hispano-Suiza licence in the Soviet Union as the Klimov M-100. This design led to the highly successful Klimov VK-105 series that powered the Yakovlev and Lavochkin fighters as well as the Petlyakov Pe-2 bomber. Licensed production of the early models was also undertaken in Czechoslovakia as the Avia HS 12Ydrs and in Switzerland as the HS-77. Design and devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and/or increase power outputs. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeppelin-Staaken R
Zeppelin-Staaken (sometimes Zeppelin Werke Staaken or Zeppelin-Werke GmbH), was a German aircraft manufacturer originally located in Gotha. The company built the largest aircraft of World War I, the "Riesenflugzeug" (giant aircraft).Mondey, 1978. p 309. Aircraft built *Zeppelin-Staaken Riesenflugzeuge ** Zeppelin-Staaken R.IV ** Zeppelin-Staaken R.V ** Zeppelin-Staaken R.VI ** Zeppelin-Staaken R.VII **Zeppelin-Staaken 8301 ** Zeppelin-Staaken R.XIV **Zeppelin-Staaken R.XV ** Zeppelin-Staaken R.XVI **Zeppelin-Staaken E-4/20 See also *Riesenflugzeug A ''Riesenflugzeug'' (plural ''Riesenflugzeuge'', German for "giant aircraft"), sometimes colloquially referred to in English as an R-plane, was any member of a class of large World War I German bombers, possessing at least three aircraft engines, ... References Citations Bibliography * External links Zeppelin-Staaken R.III German Military Aviation Service {{Idflieg R-class designations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignition Magneto
An ignition magneto, or high-tension magneto, is a magneto that provides current for the ignition system of a spark-ignition engine, such as a petrol engine. It produces pulses of high voltage for the spark plugs. The older term ''tension'' means ''voltage''. The use of ignition magnetos is now confined mainly to engines where there is no other available electrical supply, for example in lawnmowers and chainsaws. It is also widely used in aviation piston engines even though an electrical supply is usually available. In this case, the magneto's self-powered operation is considered to offer increased reliability; in theory, the magneto should continue operation as long as the engine is turning. History Firing the gap of a spark plug, particularly in the combustion chamber of a high-compression engine, requires a greater voltage (or ''higher tension'') than can be achieved by a simple magneto. The ''high-tension magneto'' combines an alternating current magneto generator a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
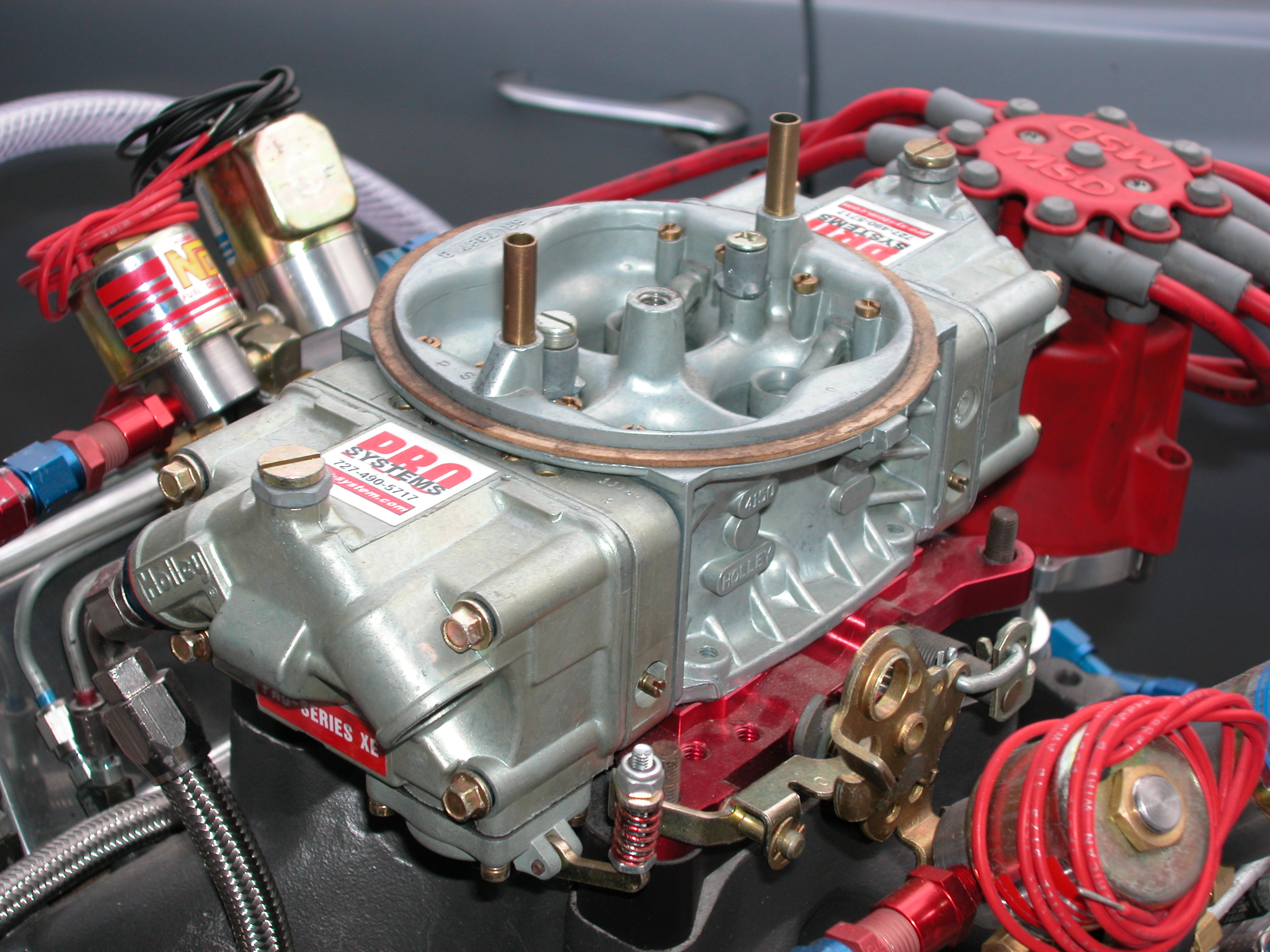
Carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baranov Central Institute Of Aviation Motors Development
The P. I. Baranov Central Institute of Aviation Motor Development (also known as the "Central Institute for Aviation Motor Development named after P. I. Baranov" or simply "Central Institute of Aviation Motors", CIAM or TsIAM, ''Tsentralniy Institut Aviatsionnogo Motorostroeniya'', russian: Центральный институт авиационного моторостроения) is the only specialized Russian research and engineering facility dealing with advanced aerospace propulsion research, aircraft engine certification and other gas dynamics-related issues. It was founded in 1930. CIAM operates the largest aerospace engine testing facility in Europe, surpassed only by the United States's Arnold Engineering Development Center and Glenn Research Center. It is based in Lefortovo (the southeast okrug of Moscow) with an address of 2 Aviamotornaya street, Moscow, Postcode 111116. CIAM also operates a scientific testing center in Lytkarino, Moscow Oblast. History The bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


2.png)



.jpg)