|
Mid Ulster English
Ulster English, also called Northern Hiberno-English or Northern Irish English, is the variety of English spoken mostly around the Irish province of Ulster and throughout Northern Ireland. The dialect has been influenced by the local Ulster dialect of the Scots language, brought over by Scottish settlers during the Plantation of Ulster and subsequent settlements throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. It also coexists alongside the Ulster dialect of the Irish (Gaelic) language, which also influenced the dialect. The two major divisions of Ulster English are ''Mid-Ulster English'', the most widespread variety, and ''Ulster Scots English'', spoken in much of northern County Antrim along a continuum with the Scots language. ''South Ulster English'' is a geographically transitional dialect between Mid-Ulster English and English spoken south of Ulster, in the Republic of Ireland. Phonology In general, Ulster English speakers' declarative sentences (with typical grammat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Dialects In Ulster Contrast
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Culture, language and peoples * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity * English studies, the study of English language and literature Media * ''English'' (2013 film), a Malayalam-language film * ''English'' (novel), a Chinese book by Wang Gang ** ''English'' (2018 film), a Chinese adaptation * ''The English'' (TV series), a 2022 Western-genre miniseries * ''English'' (play), a 2022 play by Sanaz Toossi People and fictional characters * English (surname), a list of people and fictional characters * English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach * English Gardner (born 1992), American track and field sprinter * English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer * Aiden English, a ring name of Matthew Rehwoldt (born 1987), American former professional wrestler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantation Of Ulster
The Plantation of Ulster (; Ulster Scots dialects, Ulster Scots: ) was the organised Settler colonialism, colonisation (''Plantation (settlement or colony), plantation'') of Ulstera Provinces of Ireland, province of Irelandby people from Great Britain during the reign of King James VI and I. Small privately funded plantations by wealthy landowners began in 1606,... while the official plantation began in 1609. Most of the land had been confiscated from the native Irish nobility, Gaelic chiefs, several of whom Flight of the Earls, had fled Ireland for mainland Europe in 1607 following the Nine Years' War (Ireland), Nine Years' War against Kingdom of Ireland, English rule. The official plantation comprised an estimated half a million Irish acre, acres (2,000 km2) of arable land in counties County Armagh, Armagh, County Cavan, Cavan, County Fermanagh, Fermanagh, County Tyrone, Tyrone, County Donegal, Donegal, and County Londonderry, Londonderry. Land in counties County Antrim, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Raising
Canadian raising (also sometimes known as English diphthong raising) is an allophonic rule of phonology in many varieties of North American English that changes the pronunciation of diphthongs with open-vowel starting points. Most commonly, the shift affects or , or both, when they are pronounced before voiceless consonants (therefore, in words like ''price'' and ''clout'', respectively, but not in ''prize'' and ''cloud''). In North American English, and usually begin in an open vowel but through raising they shift to , or . Canadian English often has raising in words with both (''height, life, psych, type'', etc.) and (''clout, house, south, scout,'' etc.), while a number of American English varieties (such as Inland North, Western New England, and increasingly more General American accents) have this feature in but not . It is thought to have originated in Canada in the late 19th century. In the U.S., ''aboot'' , an exaggerated version of the raised pronunciati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphthong
A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of the speech apparatus) moves during the pronunciation of the vowel. In most varieties of English, the phrase "no highway cowboys" ( ) has five distinct diphthongs, one in every syllable. Diphthongs contrast with monophthongs, where the tongue or other speech organs do not move and the syllable contains only a single vowel sound. For instance, in English, the word ''ah'' is spoken as a monophthong (), while the word ''ow'' is spoken as a diphthong in most varieties (). Where two adjacent vowel sounds occur in different syllables (e.g. in the English word ''re-elect'') the result is described as hiatus, not as a diphthong. Diphthongs often form when separate vowels are run together in rapid speech during a conversation. However, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophthong
A monophthong ( ) is a pure vowel sound, or one whose articulation at beginning and end is relatively fixed, with the tongue moving neither up nor down and neither forward nor backward towards a new position of articulation. A monophthong can be contrasted with a diphthong, where the vowel quality changes (glides from one quality to another) within the same syllable, and with hiatus, where two vowels are next to each other but in different syllables. A vowel sound whose quality does not change over the duration of the vowel is called a pure vowel. The word comes . ) Sound changes The conversions of monophthongs to diphthongs (diphthongization), and of diphthongs to monophthongs (monophthongization), are major elements of language change and are likely the cause of further changes. In some languages, due to monophthongization, graphemes that originally represented diphthongs now represent monophthongs. See also * Diphthong, also known as a vowel cluster * Vowel hiatus * In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation for the sounds of speech. The IPA is used by linguists, lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of lexical item, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, Intonation (linguistics), intonation and the separation of syllables. To represent additional qualities of speechsuch as tooth wikt:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made with a cleft lip and cleft palate, cleft palatean extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet, extended set of symbols may be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Question
A question is an utterance which serves as a request for information. Questions are sometimes distinguished from interrogatives, which are the grammar, grammatical forms, typically used to express them. Rhetorical questions, for instance, are interrogative in form but may not be considered wiktionary:bona fide, bona fide questions, as they are not expected to be answered. Questions come in a number of varieties. For instance; ''Polar questions'' are those such as the English language, English example "Is this a polar question?", which can be answered with yes and no, "yes" or "no". ''Alternative questions'' such as "Is this a polar question, or an alternative question?" present a list of possibilities to choose from. ''Open-ended question, Open questions'' such as "What kind of question is this?" allow many possible resolutions. Questions are widely studied in linguistics and philosophy of language. In the subfield of pragmatics, questions are regarded as illocutionary acts whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Rising Terminal
The high rising terminal (HRT), also known as rising inflection, upspeak, uptalk, or high rising intonation (HRI), is a feature of some variants of English where declarative sentences can end with a rising pitch similar to that typically found in yes–no questions. HRT has been claimed to be especially common among younger speakers and women, though its exact sociolinguistic implications are an ongoing subject of research. Intonational characteristics Empirically, one report proposes that HRT in American English and Australian English is marked by a high tone (high pitch or high fundamental frequency) beginning on the final accented syllable near the end of the statement (the terminal), and continuing to increase in frequency (up to 40%) to the end of the intonational phrase. New research suggests that the actual rise can occur one or more syllables after the last accented syllable of the phrase, and its range is much more variable than previously thought. Usage In the Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
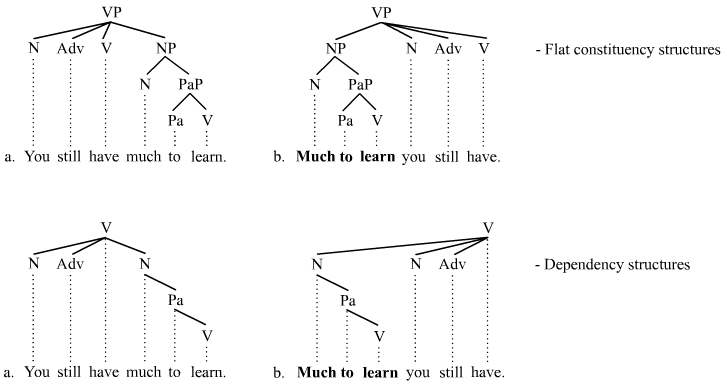
Topicalization
Topicalization is a mechanism of syntax that establishes an expression as the sentence or clause topic (linguistics), topic by having it appear at the front of the sentence or clause (as opposed to in a canonical position later in the sentence). This involves a phrasal movement of determiners, prepositions, and verbs to sentence-initial position. Topicalization often results in a discontinuity (linguistics), discontinuity and is thus one of a number of established discontinuity types, the other three being wh-movement, ''wh''-fronting, Scrambling (linguistics), scrambling, and extraposition. Topicalization is also used as a Constituent (linguistics), constituency test; an expression that can be topicalized is deemed a constituent. The topicalization of Argument (linguistics), arguments in English is rare, whereas circumstantial Adjunct (grammar), adjuncts are often topicalized. Most languages allow topicalization, and in some languages, topicalization occurs much more frequently an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declarative Sentence
Declarative may refer to: * Declarative learning, acquiring information that one can speak about * Declarative memory, one of two types of long term human memory * Declarative programming In computer science, declarative programming is a programming paradigm—a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs—that expresses the logic of a computation without describing its control flow. Many languages that ap ..., a computer programming paradigm * Declarative sentence, a type of sentence that makes a statement * Declarative mood, a grammatical verb form used in declarative sentences See also * Declaration (other) {{disamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardized varieties, such as those used in developing countries or isolated areas. The non-standard dialects of a language with a writing system will operate at different degrees of distance from the standardized written form. Standard and nonstandard dialects A ''standard dialect'', also known as a "standardized language", is supported by institutions. Such institutional support may include any or all of the following: government recognition or designation; formal presentation in schooling as the "correct" form of a language; informal monitoring of everyday Usage (language), usage; published grammars, dictionaries, and textbooks that set forth a normative spoken and written form; and an extensive formal literature (be it prose, poetry, non-ficti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |