|
Microbial Loop
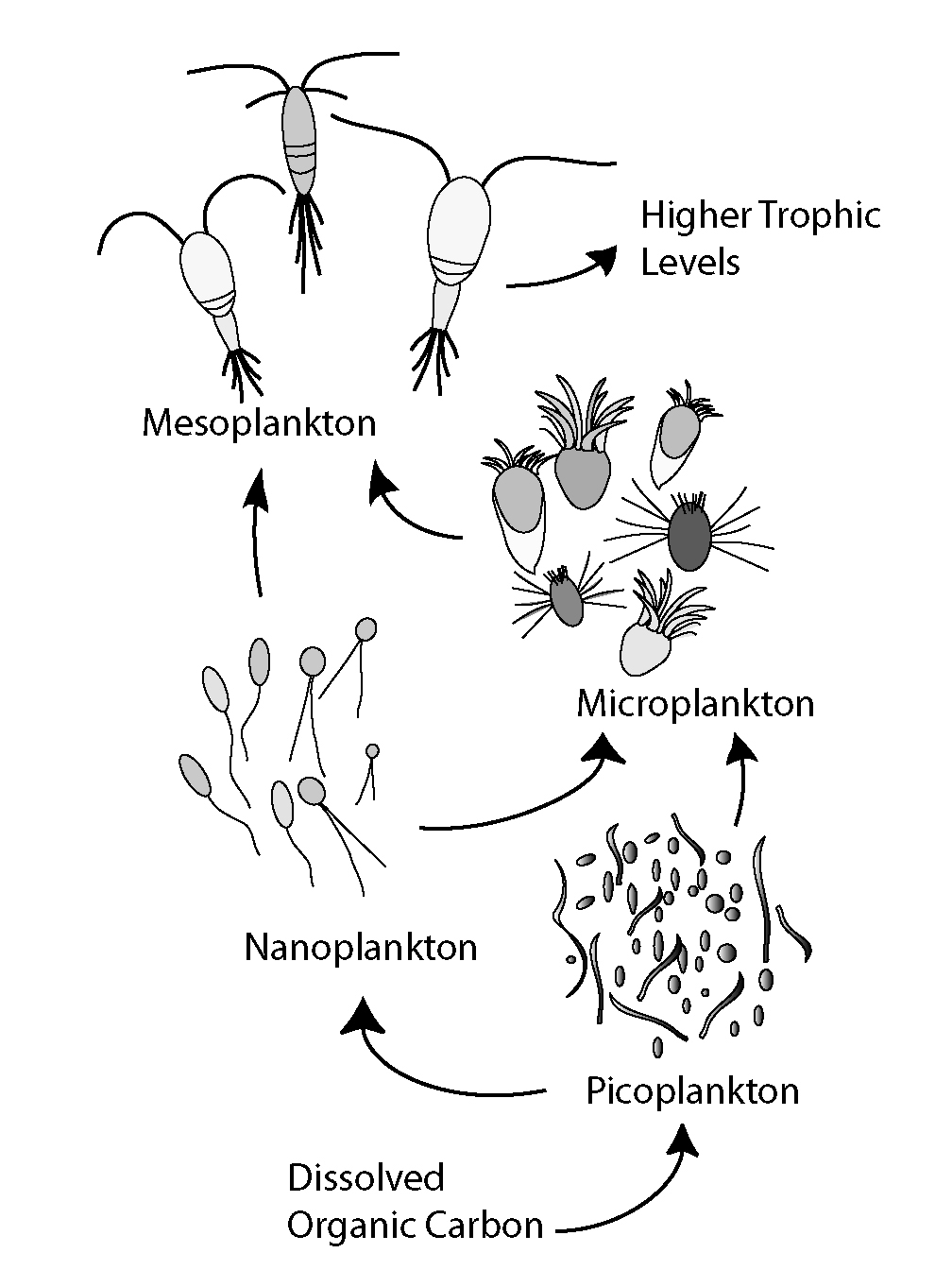
The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is returned to higher trophic levels via its incorporation into bacterial biomass, and then coupled with the classic food chain formed by phytoplankton-zooplankton- nekton. In soil systems, the microbial loop refers to soil carbon. The term microbial loop was coined by Farooq Azam, Tom Fenchel et al. in 1983 to include the role played by bacteria in the carbon and nutrient cycles of the marine environment. In general, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is introduced into the ocean environment from bacterial lysis, the leakage or exudation of fixed carbon from phytoplankton (e.g., mucilaginous exopolymer from diatoms), sudden cell senescence, sloppy feeding by zooplankton, the excretion of waste products by aquatic animals, or the breakdown or dissolution of organic particles from terrestrial plants and soils. Bacteria in the microbial loop decompose this particulate detritus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Another name for food web is consumer-resource system. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs. To maintain their bodies, grow, develop, and to reproduce, autotrophs produce organic matter from inorganic substances, including both minerals and gases such as carbon dioxide. These chemical reactions require energy, which mainly comes from the Sun and largely by photosynthesis, although a very small amount comes from bioelectrogenesis in wetlands, and mineral electron donors in hydrothermal vents and hot springs. These trophic levels are not binary, but form a gradient that includes complete autotrophs, which obtain their sole source of carbon from the atmosphere, mixotrophs (such as carnivorous plants), which are autotrophic organisms th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prochlorococcus
''Prochlorococcus'' is a genus of very small (0.6 μm) marine cyanobacteria with an unusual pigmentation ( chlorophyll ''a2'' and ''b2''). These bacteria belong to the photosynthetic picoplankton and are probably the most abundant photosynthetic organism on Earth. ''Prochlorococcus'' microbes are among the major primary producers in the ocean, responsible for a large percentage of the photosynthetic production of oxygen.Munn, C. ''Marine Microbiology: ecology and applications Second Ed.'' Garland Science, 2011. Prochlorococcus strains, called ecotypes, have physiological differences enabling them to exploit different ecological niches. Analysis of the genome sequences of ''Prochlorococcus'' strains show that 1,273 genes are common to all strains, and the average genome size is about 2,000 genes. In contrast, eukaryotic algae have over 10,000 genes. Discovery Although there had been several earlier records of very small chlorophyll-''b''-containing cyanobacteria in the oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult and then, after more molts, achieves adult development. The nauplius form is so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate
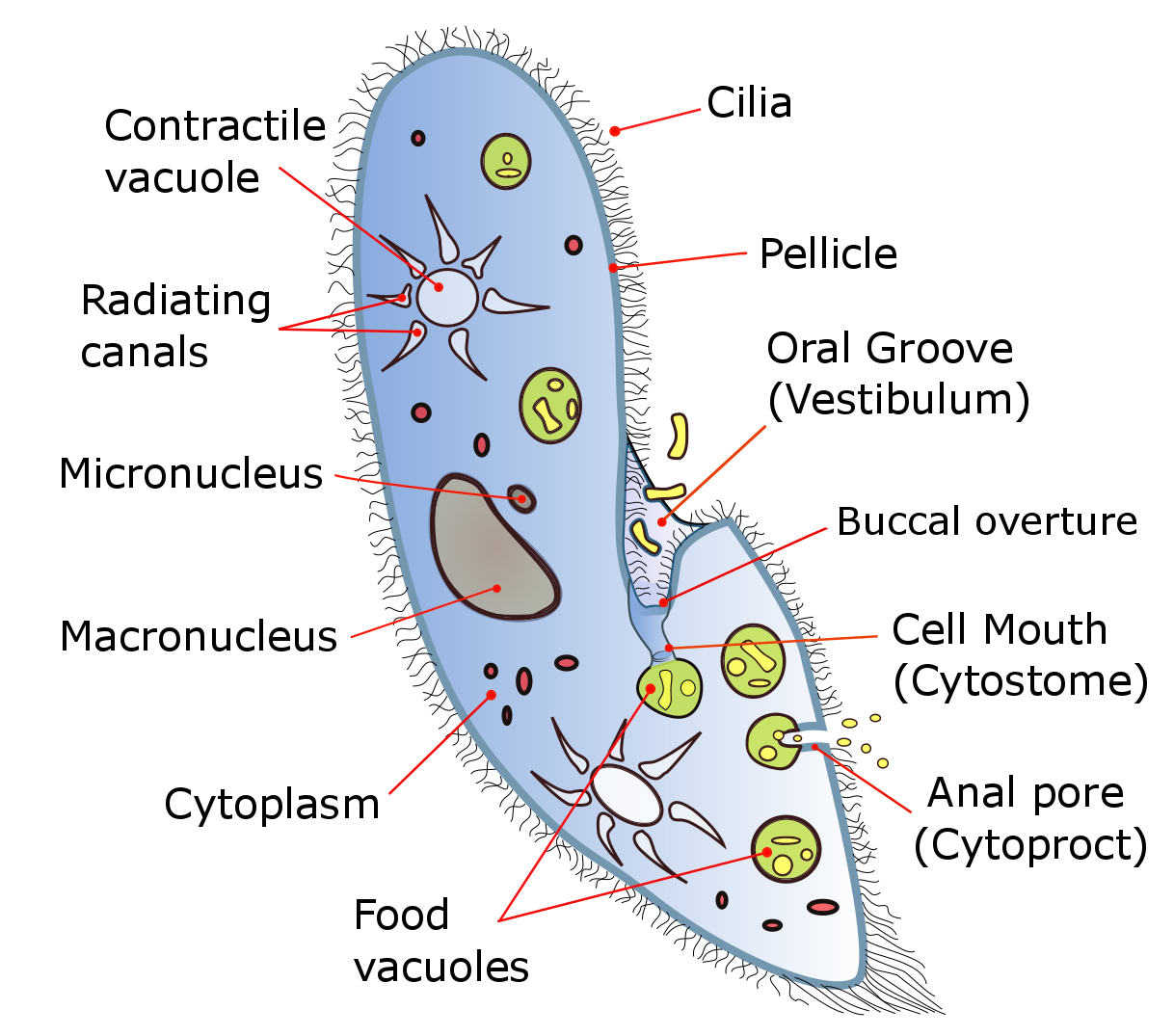
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some obligate and opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species range in size from as little as 10 µm in some colpodeans to as much as 4 mm in length in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterivore
A bacterivore is an organism which obtains energy and nutrients primarily or entirely from the consumption of bacteria. The term is most commonly used to describe free-living, heterotrophic, microscopic organisms such as nematodes as well as many species of amoeba and numerous other types of protozoans, but some macroscopic invertebrates are also bacterivores, including sponges, polychaetes, and certain molluscs and arthropods. Many bacterivorous organisms are adapted for generalist predation on any species of bacteria, but not all bacteria are easily digested; the spores of some species, such as ''Clostridium perfringens'', will never be prey because of their cellular attributes. In microbiology Bacterivores can sometimes be a problem in microbiology studies. For instance, when scientists seek to assess microorganisms in samples from the environment (such as freshwater), the samples are often contaminated with microscopic bacterivores, which interfere with the growing of bacteria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans ( Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are known as '' primary producers'' or autotrophs, and form the base of the food chain. In terrestrial ecoregions, these are mainly plants, while in aquatic ecoregions algae predominate in this role. Ecologists distinguish primary production as either ''net'' or ''gross'', the former accounting for losses to processes such as cellular respiration, the latter not. Overview Primary production is the production of chemical energy in organic compounds by living organisms. The main source of this energy is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acridine Orange
Acridine orange is an organic compound that serves as a nucleic acid-selective fluorescent dye with cationic properties useful for cell cycle determination. Acridine orange is cell-permeable, which allows the dye to interact with DNA by intercalation, or RNA via electrostatic attractions. When bound to DNA, acridine orange is very similar spectrally to an organic compound known as fluorescein. Acridine orange and fluorescein have a maximum excitation at 502 nm and 525 nm (green). When acridine orange associates with RNA, the fluorescent dye experiences a maximum excitation shift from 525 nm (green) to 460 nm (blue). The shift in maximum excitation also produces a maximum emission of 650 nm (red). Acridine orange is able to withstand low pH environments, allowing the fluorescent dye to penetrate acidic organelles such as lysosomes and phagolysosomes that are membrane-bound organelles essential for acid hydrolysis or for producing products of phagocytosis of apo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epifluorescence Microscope
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image. Principle The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength (or wavelengths) which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths (i.e., of a different color than the absorbed light). The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of a spectral emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are a light source (xenon arc lamp or mercury-vapor lamp are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterioplankton Counting Methods
Bacterioplankton counting is the estimation of the abundance of bacterioplankton in a specific body of water, which is useful information to marine microbiologists. Various counting methodologies have been developed over the years to determine the number present in the water being observed. Methods used for counting bacterioplankton include epifluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, measures of productivity through frequency of dividing cells (FDC), thymidine incorporation, and leucine incorporation. Factors such as salinity, temperature, latitude, various nutrient levels, water movement and the presence of other organisms can affect bacterioplankton enumeration. Changes in these factors affect the bacterioplankton count, causing it to vary by body of water, location, distance from shore and season. Bacterioplankton count is usually expressed in cells per ml (cells ml−1). Uses In understanding marine microbiology and the aquatic ecosystem, bacterioplankton counts can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agar Plate
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics. Individual microorganisms placed on the plate will grow into individual colonies, each a clone genetically identical to the individual ancestor organism (except for the low, unavoidable rate of mutation). Thus, the plate can be used either to estimate the concentration of organisms in a liquid culture or a suitable dilution of that culture using a colony counter, or to generate genetically pure cultures from a mixed culture of genetically different organisms. Several methods are available to plate out cells. One technique is known as " streaking". In this technique, a drop of the culture on the end of a thin, sterile loop of wire, sometimes known as an inoculator, is streaked across the surface of the agar leaving organisms behind, a higher number at the beginning of the streak and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |