Microbial loop on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
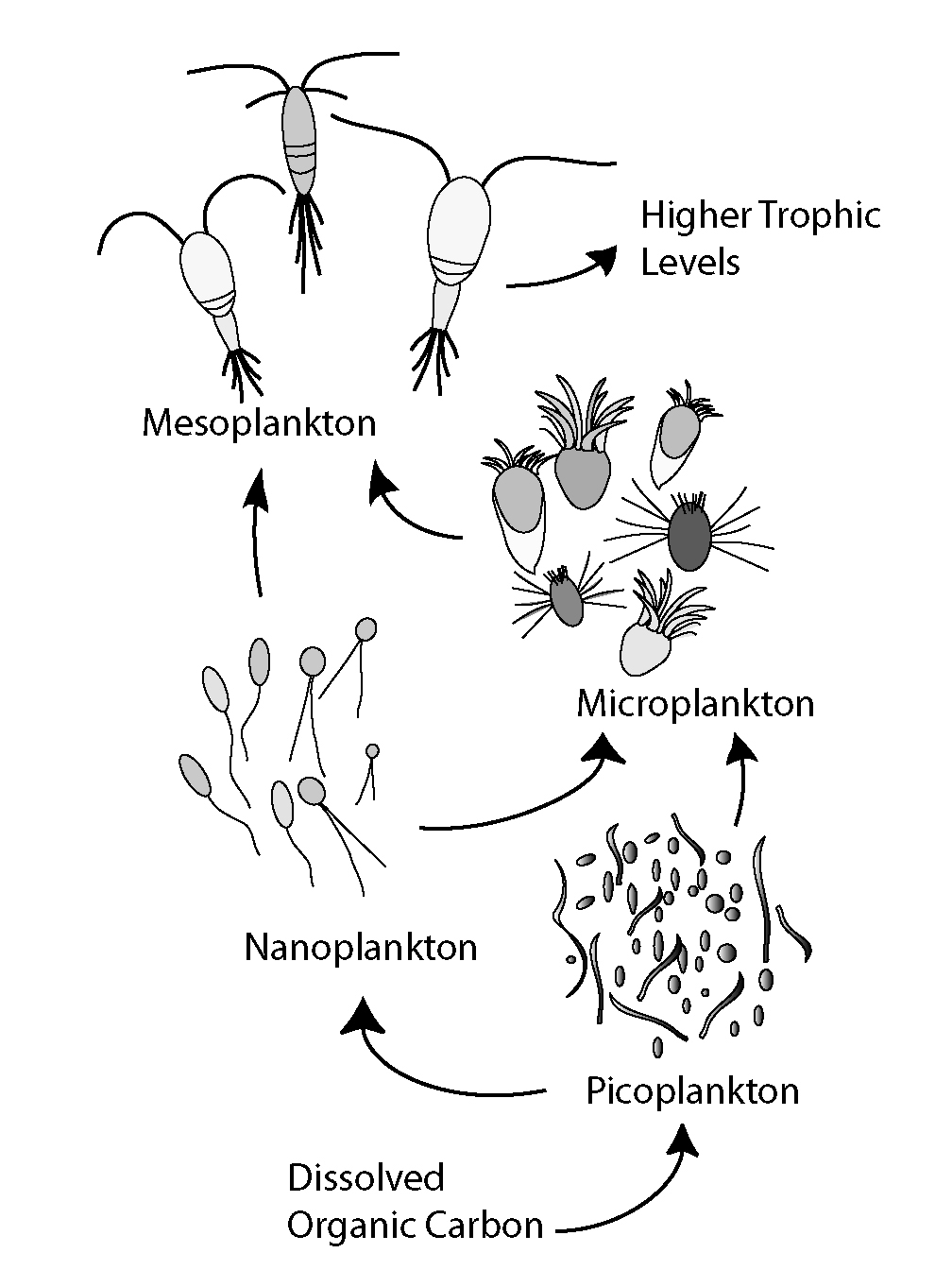 The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems,
The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems,
 Soil ecosystems are highly complex and subject to different landscape-scale perturbations that govern whether soil carbon is retained or released to the atmosphere. The ultimate fate of soil organic carbon is a function of the combined activities of plants and below ground organisms, including soil microbes. Although soil microorganisms are known to support a plethora of biogeochemical functions related to carbon cycling, the vast majority of the soil microbiome remains uncultivated and has largely cryptic functions. Only a mere fraction of soil microbial life has been catalogued to date, although new soil microbes and viruses are increasingly being discovered. This lack of knowledge results in uncertainty of the contribution of soil microorganisms to soil organic
Soil ecosystems are highly complex and subject to different landscape-scale perturbations that govern whether soil carbon is retained or released to the atmosphere. The ultimate fate of soil organic carbon is a function of the combined activities of plants and below ground organisms, including soil microbes. Although soil microorganisms are known to support a plethora of biogeochemical functions related to carbon cycling, the vast majority of the soil microbiome remains uncultivated and has largely cryptic functions. Only a mere fraction of soil microbial life has been catalogued to date, although new soil microbes and viruses are increasingly being discovered. This lack of knowledge results in uncertainty of the contribution of soil microorganisms to soil organic
 The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems,
The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems, dissolved organic carbon
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOC) is returned to higher trophic levels via its incorporation into bacterial biomass, and then coupled with the classic food chain formed by phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
-zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
-nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) is any aquatic organism that can actively and persistently propel itself through a water column (i.e. swimming) without touching the bottom. Nektons generally have powerful tails and appendages (e.g. fins, pleopods, ...
. In soil systems, the microbial loop refers to soil carbon
Soil carbon is the solid carbon stored in global Soil, soils. This includes both soil organic matter and Inorganic compound, inorganic carbon as carbonate minerals. It is vital to the soil capacity in our ecosystem. Soil carbon is a carbon sink in ...
. The term microbial loop was coined by Farooq Azam, Tom Fenchel et al. in 1983 to include the role played by bacteria in the carbon and nutrient cycle
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyc ...
s of the marine environment.
In general, dissolved organic carbon
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOC) is introduced into the ocean environment from bacterial lysis, the leakage or exudation of fixed carbon from phytoplankton (e.g., mucilaginous exopolymer from diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's B ...
s), sudden cell senescence
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of Function (biology), functional characteristics in living organisms. Whole organism senescence involves an increase in mortality rate, death rates or a decrease in fecundity with ...
, sloppy feeding by zooplankton, the excretion of waste products by aquatic animals, or the breakdown or dissolution of organic particles from terrestrial plants and soils. Bacteria in the microbial loop decompose this particulate detritus to utilize this energy-rich matter for growth. Since more than 95% of organic matter in marine ecosystems consists of polymeric, high molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
(HMW) compounds (e.g., protein, polysaccharides, lipids), only a small portion of total dissolved organic matter
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOM) is readily utilizable to most marine organisms at higher trophic levels. This means that dissolved organic carbon is not available directly to most marine organisms; marine bacteria introduce this organic carbon into the food web, resulting in additional energy becoming available to higher trophic levels. Recently the term "microbial food web
The microbial food web refers to the combined trophic interactions among microbes in aquatic environments. These microbes include viruses, bacteria, algae, heterotrophic protists (such as ciliates and flagellates). In aquatic ecosystems, microbi ...
" has been substituted for the term "microbial loop".
History
Prior to the discovery of the microbial loop, the classic view of marinefood web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Position in the food web, or trophic level, is used in ecology to broadly classify organisms as autotrophs or he ...
s was one of a linear chain from phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
to nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) is any aquatic organism that can actively and persistently propel itself through a water column (i.e. swimming) without touching the bottom. Nektons generally have powerful tails and appendages (e.g. fins, pleopods, ...
. Generally, marine bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
were not thought to be significant consumers of organic matter (including carbon), although they were known to exist. However, the view of a marine pelagic food web was challenged during the 1970s and 1980s by Pomeroy and Azam, who suggested the alternative pathway of carbon flow from bacteria to protozoan
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
s to metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a ho ...
s.
Early work in marine ecology that investigated the role of bacteria in oceanic environments concluded their role to be very minimal. Traditional methods of counting bacteria (e.g., culturing on agar plate
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to Microbiological culture, culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.
Individual microorganism ...
s) only yielded small numbers of bacteria that were much smaller than their true ambient abundance in seawater. Developments in technology for counting bacteria have led to an understanding of the significant importance of marine bacteria in oceanic environments.
In the 1970s, the alternative technique of direct microscopic counting was developed by Francisco ''et al.'' (1973) and Hobbie ''et al.'' (1977). Bacterial cells were counted with an epifluorescence microscope, producing what is called an " acridine orange direct count" (AODC). This led to a reassessment of the large concentration of bacteria in seawater, which was found to be more than was expected (typically on the order of 1 million per milliliter). Also, development of the "bacterial productivity assay" showed that a large fraction (i.e. 50%) of net primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
(NPP) was processed by marine bacteria.
In 1974, Larry Pomeroy published a paper in BioScience entitled "The Ocean's Food Web: A Changing Paradigm", where the key role of microbes in ocean productivity was highlighted. In the early 1980s, Azam and a panel of top ocean scientists published the synthesis of their discussion in the journal ''Marine Ecology Progress Series'' entitled "The Ecological Role of Water Column Microbes in the Sea". The term 'microbial loop' was introduced in this paper, which noted that the bacteria-consuming protists were in the same size class as phytoplankton and likely an important component of the diet of planktonic crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s.
Evidence accumulated since this time has indicated that some of these bacterivorous protists (such as ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
s) are actually selectively preyed upon by these copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s. In 1986, ''Prochlorococcus
''Prochlorococcus'' is a genus of very small (0.6 μm) marine cyanobacteria with an unusual pigmentation ( chlorophyll ''a2'' and ''b2''). These bacteria belong to the photosynthetic picoplankton and are probably the most abundant photosyn ...
'', which is found in high abundance in oligotrophic areas of the ocean, was discovered by Sallie W. Chisholm, Robert J. Olson, and other collaborators (although there had been several earlier records of very small cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
containing chlorophyll b
}
Chlorophyll ''b'' is a form of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll ''b'' helps in photosynthesis by absorbing light energy. It is more soluble than chlorophyll ''a'' in polar solvents because of its carbonyl group. Its color is green, and it primarily ...
in the ocean ''Prochlorococcus'' was discovered in 1986). Stemming from this discovery, researchers observed the changing role of marine bacteria along a nutrient gradient from eutrophic to oligotrophic areas in the ocean.
Factors controlling the microbial loop
The efficiency of the microbial loop is determined by the density of marine bacteria within it. It has become clear that bacterial density is mainly controlled by the grazing activity of small protozoans such as various taxonomic groups of flagellates. Also, viral infection causes bacterial lysis, which release cell contents back into thedissolved organic matter
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOM) pool, lowering the overall efficiency of the microbial loop. Mortality from viral infection has almost the same magnitude as that from protozoan grazing. However, compared to protozoan grazing, the effect of viral lysis can be very different because lysis is highly host-specific to each marine bacteria. Both protozoan grazing and viral infection balance the major fraction of bacterial growth. In addition, the microbial loop dominates in oligotrophic waters, rather than in eutrophic areas - there the classical plankton food chain predominates, due to the frequent fresh supply of mineral nutrients (e.g. spring bloom in temperate waters, upwelling
Upwelling is an physical oceanography, oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted sur ...
areas). The magnitude of the efficiency of the microbial loop can be determined by measuring bacterial incorporation of radiolabeled substrates (such as tritiated thymidine or leucine).
In marine ecosystems
The microbial loop is of particular importance in increasing the efficiency of the marine food web via the utilization of dissolved organic matter (DOM), which is typically unavailable to most marine organisms. In this sense, the process aids in recycling of organic matter and nutrients and mediates the transfer of energy above thethermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is
a distinct layer based on temperature within a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) with a high gradient of distinct te ...
. More than 30% of dissolved organic carbon
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOC) incorporated into bacteria is respired and released as carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
. The other main effect of the microbial loop in the water column is that it accelerates mineralization through regenerating production in nutrient-limited environments (e.g. oligotrophic waters). In general, the entire microbial loop is to some extent typically five to ten times the mass of all multicellular marine organisms in the marine ecosystem. Marine bacteria are the base of the food web in most oceanic environments, and they improve the trophic efficiency of both marine food webs and important aquatic processes (such as the productivity of fisheries and the amount of carbon exported to the ocean floor). Therefore, the microbial loop, together with primary production, controls the productivity of marine systems in the ocean.
Many planktonic bacteria are motile, using a flagellum to propagate, and chemotax to locate, move toward, and attach to a point source of dissolved organic matter
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOM) where fast growing cells digest all or part of the particle. Accumulation within just a few minutes at such patches is directly observable. Therefore, the water column can be considered to some extent as a spatially organized place on a small scale rather than a completely mixed system. This patch formation affects the biologically-mediated transfer of matter and energy in the microbial loop.
More currently, the microbial loop is considered to be more extended. Chemical compounds in typical bacteria (such as DNA, lipids, sugars, etc.) and similar values of C:N ratios per particle are found in the microparticles formed abiotically. Microparticles are a potentially attractive food source to bacterivorous plankton. If this is the case, the microbial loop can be extended by the pathway of direct transfer of dissolved organic matter
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remain ...
(DOM) via abiotic microparticle formation to higher trophic levels. This has ecological importance in two ways. First, it occurs without carbon loss, and makes organic matter more efficiently available to phagotrophic organisms, rather than only heterotrophic bacteria. Furthermore, abiotic transformation in the extended microbial loop depends only on temperature and the capacity of DOM to aggregate, while biotic transformation is dependent on its biological availability.
In land ecosystems
 Soil ecosystems are highly complex and subject to different landscape-scale perturbations that govern whether soil carbon is retained or released to the atmosphere. The ultimate fate of soil organic carbon is a function of the combined activities of plants and below ground organisms, including soil microbes. Although soil microorganisms are known to support a plethora of biogeochemical functions related to carbon cycling, the vast majority of the soil microbiome remains uncultivated and has largely cryptic functions. Only a mere fraction of soil microbial life has been catalogued to date, although new soil microbes and viruses are increasingly being discovered. This lack of knowledge results in uncertainty of the contribution of soil microorganisms to soil organic
Soil ecosystems are highly complex and subject to different landscape-scale perturbations that govern whether soil carbon is retained or released to the atmosphere. The ultimate fate of soil organic carbon is a function of the combined activities of plants and below ground organisms, including soil microbes. Although soil microorganisms are known to support a plethora of biogeochemical functions related to carbon cycling, the vast majority of the soil microbiome remains uncultivated and has largely cryptic functions. Only a mere fraction of soil microbial life has been catalogued to date, although new soil microbes and viruses are increasingly being discovered. This lack of knowledge results in uncertainty of the contribution of soil microorganisms to soil organic carbon cycling
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycl ...
and hinders construction of accurate predictive models for global carbon flux under climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.
The lack of information concerning the soil microbiome metabolic potential makes it particularly challenging to accurately account for the shifts in microbial activities that occur in response to environmental change. For example, plant-derived carbon inputs can prime microbial activity to decompose existing soil organic carbon at rates higher than model expectations, resulting in error within predictive models of carbon fluxes.
To account for this, a conceptual model known as the microbial carbon pump, illustrated in the diagram on the right, has been developed to define how soil microorganisms transform and stabilise soil organic matter. As shown in the diagram, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is fixed by plants (or autotrophic microorganisms) and added to soil through processes such as (1) root exudation of low-molecular weight simple carbon compounds, or deposition of leaf and root litter leading to accumulation of complex plant polysaccharides. (2) Through these processes, carbon is made bioavailable to the microbial metabolic "factory" and subsequently is either (3) respired to the atmosphere or (4) enters the stable carbon pool as microbial necromass. The exact balance of carbon efflux versus persistence is a function of several factors, including aboveground plant community composition and root exudate profiles, environmental variables, and collective microbial phenotypes (i.e., the metaphenome).
In this model, microbial metabolic activities for carbon turnover are segregated into two categories: ex vivo modification, referring to transformation of plant-derived carbon by extracellular enzymes, and in vivo turnover, for intracellular carbon used in microbial biomass turnover or deposited as dead microbial biomass, referred to as necromass. The contrasting impacts of catabolic activities that release soil organic carbon as carbon dioxide (), versus anabolic pathways that produce stable carbon compounds, control net carbon retention rates. In particular, microbial carbon sequestration represents an underrepresented aspect of soil carbon flux that the microbial carbon pump model attempts to address. A related area of uncertainty is how the type of plant-derived carbon enhances microbial soil organic carbon storage or alternatively accelerates soil organic carbon decomposition. For example, leaf litter and needle litter serve as sources of carbon for microbial growth in forest soils, but litter chemistry and pH varies by vegetation type .g., between root and foliar litter or between deciduous and coniferous forest litter (14) In turn, these biochemical differences influence soil organic carbon levels through changing decomposition dynamics. Also, increased diversity of plant communities increases rates of rhizodeposition, stimulating microbial activity and soil organic carbon storage, although soils eventually reach a saturation point beyond which they cannot store additional carbon.
See also
*Biological pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven Carbon sequestration, sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sedim ...
* f-ratio F-ratio or f-ratio may refer to:
* The F-ratio used in statistics, which relates the variances of independent samples; see F-distribution
* f-ratio (oceanography), which relates recycled and total primary production in the surface ocean
* f-number ...
* Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
* Marine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow (also known as "ocean dandruff") is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to ...
* Phycosphere
References
Bibliography
* Fenchel, T. (1988) Marine Planktonic Food Chains. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics * Fenchel, T. (2008) The microbial loop – 25 years later. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology * Fuhrman, J.A., Azam, F. (1982) Thymidine incorporation as a measure of heterotrophic bacterioplankton production in marine surface waters. Marine Biology * Kerner, M, Hohenberg, H., Ertl, S., Reckermannk, M., Spitzy, A. (2003) Self-organization of dissolved organic matter to micelle-like microparticles in river water. Nature * Kirchman, D., Sigda, J., Kapuscinski, R., Mitchell, R. (1982) Statistical analysis of the direct count method for enumerating bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology * Meinhard, S., Azam F. (1989) Protein content and protein synthesis rates of planktonic marine bacteria. Marine Ecology Progress Series * Muenster, V.U. (1985) Investigations about structure, distribution and dynamics of different organic substrates in the DOM of Lake Plusssee. Hydrobiologie * Pomeroy, L.R., Williams, P.J.leB., Azam, F. and Hobbie, J.E. (2007) "The microbial loop". ''Oceanography'', 20(2): 28–33. . * Stoderegger, K., Herndl, G.J. (1998) Production and Release of Bacterial Capsular Material and its Subsequent Utilization by Marine Bacterioplankton. Limnology & Oceanography {{modelling ecosystems Microbiology terms Environmental microbiology