|
Microascus Manginii
''Microascus manginii'' is a filamentous fungal species in the genus ''Microascus.'' It produces both sexual (teleomorph) and asexual (anamorph) reproductive stages known as ''M. manginii'' and ''Scopulariopsis candida'', respectively. Several synonyms appear in the literature because of taxonomic revisions and re-isolation of the species by different researchers. ''M. manginii'' is saprotrophic and commonly inhabits soil, indoor environments and decaying plant material. It is distinguishable from closely related species by its light colored and heart-shaped ascospores used for sexual reproduction. ''Scopulariopsis candida'' has been identified as the cause of some invasive infections, often in immunocompromised hosts, but is not considered a common human pathogen. There is concern about amphotericin B resistance in ''S. candida''. History and taxonomy The anamorph was first documented, unintentionally, by Professor Fernand-Pierre-Joseph Guéguen in 1899 who mistook it for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascocarp
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the size of flecks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 States of Brazil, states and the Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese language, Portuguese as an List of territorial entities where Portuguese is an official language, official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most Multiculturalism, multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass Immigration to Brazil, immigration from around the world; and the most populous Catholic Church by country, Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, and its Iberian portion is bordered to the west and south by the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and east by Spain, the sole country to have a land border with Portugal. Its two archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population. Portugal is the oldest continuously existing nation state on the Iberian Peninsula and one of the oldest in Europe, its territory having been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. It was inhabited by pre-Celtic and Celtic peoples who had contact with Phoenicians and Ancient Greek traders, it was ruled by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miconazole
Miconazole, sold under the brand name Monistat among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat ring worm, pityriasis versicolor, and yeast infections of the skin or vagina. It is used for ring worm of the body, groin (jock itch), and feet (athlete's foot). It is applied to the skin or vagina as a cream or ointment. Common side effects include itchiness or irritation of the area in which it was applied. Use in pregnancy is believed to be safe for the baby. Miconazole is in the imidazole family of medications. It works by decreasing the ability of fungi to make ergosterol, an important part of their cell membrane. Miconazole was patented in 1968 and approved for medical use in 1971. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Miconazole is mainly used externally for the treatment of ringworm including jock itch and athlete's foot. Internal application is used for oral or vaginal thrush (yeast infection). This oral gel may also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-keratin
Alpha-keratin, or α-keratin, is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. This protein is the primary component in hairs, horns, mammalian claws, nails and the epidermis layer of the skin. α-keratin is a fibrous structural protein, meaning it is made up of amino acids that form a repeating secondary structure. The secondary structure of α-keratin is very similar to that of a traditional protein α-helix and forms a coiled coil. Due to its tightly wound structure, it can function as one of the strongest biological materials and has various functions in mammals, from predatory claws to hair for warmth. α-keratin is synthesized through protein biosynthesis, utilizing transcription and translation, but as the cell matures and is full of α-keratin, it dies, creating a strong non-vascular unit of keratinized tissue. Structure α-keratin is a polypeptide chain, typically high in alanine, leucine, arginine, and cysteine, that forms a right-handed α-helix. Two of these polypeptide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scopula
''Scopula'' is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae described by Franz von Paula Schrank in 1802. Species It has 705 species which are listed here alphabetically. A *'' Scopula ablativa'' (Dognin, 1911) *''Scopula abolita'' Herbulot, 956/small> *''Scopula abornata'' (Guenée, 858 *''Scopula accentuata'' (Guenée, 858 *'' Scopula acentra'' (Warren, 1897) *'' Scopula acharis'' Prout, 1938 *'' Scopula achroa'' (Lower, 1902) *'' Scopula achrosta'' Prout, 1935 *''Scopula acidalia'' (Holland, 1894) *''Scopula acinosa'' (Prout, 1932) *''Scopula actuaria'' (Walker, 1861) *''Scopula acutanellus'' Herbulot, 1992 *''Scopula acyma'' Prout, 1932 *''Scopula addictaria'' (Walker, 1861) *''Scopula adelpharia'' (Püngeler, 1894) *''Scopula adenensis'' (Wiltshire, 1986) *''Scopula adeptaria'' (Walker, 1861) *''Scopula aegrefasciata'' Sihvonen, 2001 *''Scopula aemulata'' (Hulst, 1896) – angled wave *''Scopula aequidistans'' (Warren, 1896) *''Scopula aequifasciata'' (Christoph, 1881) *''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
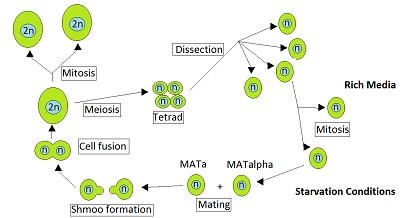
Heterothallism
Heterothallic species have sexes that reside in different individuals. The term is applied particularly to distinguish heterothallic fungi, which require two compatible partners to produce sexual spores, from homothallic ones, which are capable of sexual reproduction from a single organism. In heterothallic fungi, two different individuals contribute nuclei to form a zygote. Examples of heterothallism are included for ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus'', ''Penicillium marneffei'' and ''Neurospora crassa''. The heterothallic life cycle of ''N. crassa'' is given in some detail, since similar life cycles are present in other heterothallic fungi. Life cycle of ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' The yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' is heterothallic. This means that each yeast cell is of a certain mating type and can only mate with a cell of the other mating type. During vegetative growth that ordinarily occurs when nutrients are abundant, ''S. cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ferns, bacteria, and the growth of the pollen tube from the pollen grain of a seed plant. Seed plants Germination is usually the growth of a plant contained within a seed; it results in the formation of the seedling. It is also the process of reactivation of metabolic machinery of the seed resulting in the emergence of radicle and plumule. The seed of a vascular plant is a small package produced in a fruit or cone after the union of male and female reproductive cells. All fully developed seeds contain an embryo and, in most plant species some store of food reserves, wrapped in a seed coat. Some plants produce varying numbers of seeds that lack embryos; these are empty seeds which never germinate. Dormant seeds are viable seeds that do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Tube
A germ tube is an outgrowth produced by spores of spore-releasing fungi during germination. The germ tube differentiates, grows, and develops by mitosis to create somatic hyphae.C.J. Alexopolous, Charles W. Mims, M. Blackwell, ''Introductory Mycology, 4th ed.'' (John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken NJ, 2004) A germ tube test is a diagnostic test in which a sample of fungal spores are suspended in animal serum and examined by microscopy for the detection of any germ tubes.Chapter IV. Germ Tube Test iYEAST IDENTIFICATION document at doctorfungus.org. Retrieved July 2011 It is particularly indicated for colonies of white or cream color on fungal culture, where a positive germ tube test is strongly indicative of ''Candida albicans''. See also * Oomycota Oomycota forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms, called oomycetes (). They are filamentous and heterotrophic, and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |