|
Microaerophile
A microaerophile is a microorganism that requires environments containing lower levels of dioxygen than that are present in the atmosphere (i.e. < 21% O2; typically 2–10% O2) for optimal growth. A more restrictive interpretation requires the microorganism to be obligate in this requirement. Many microaerophiles are also capnophiles, requiring an elevated concentration of (e.g. 10% CO2 in the case of '' Campylobacter'' ). The original definitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capnophiles
Capnophiles are microorganisms that thrive in the presence of high concentrations of carbon dioxide (). Some capnophiles may have a metabolic requirement for carbon dioxide, while others merely compete more successfully for resources under these conditions. The term is a generally descriptive one and has less relevance as a means of establishing a taxonomic or evolutionary relationship among organisms with this characteristic. For example, the ability of capnophiles to tolerate (or utilize) the amount of oxygen that is also in their environment may vary widely and may be far more critical to their survival. Species of ''Campylobacter'' are bacterial capnophiles that are more easily identified because they are also microaerophiles, organisms that can grow in high carbon dioxide as long as a small amount of free oxygen is present, but at a dramatically reduced concentration. (In the earth's atmosphere carbon dioxide levels are approximately five hundred times lower than that of oxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. ''H. pylori'' has been associated with cancer of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye (termed extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the cited organ), and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach (termed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). ''H. pylori'' infection usually has no symptoms but sometimes causes gastritis (stomach inflammation) or ulcers of the stomach or first part of the small intestine. The infection is also associated with the development of cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to: * Anaerobic adhesive, a bonding agent that does not cure in the presence of air *Anaerobic respiration, respiration in the absence of oxygen, using some other molecule as the final electron acceptor **Anaerobic organism, any organism whose redox metabolism does not depend on free oxygen **Anammox, anaerobic ammonium oxidation, a globally important microbial process of the nitrogen cycle **Anaerobic filter, an anaerobic digester with a tank containing a filter medium where anaerobic microbes can establish themselves **Anaerobic digestion, the use of anaerobic bacteria to break down waste, with biogas as a byproduct ***Anaerobic clarigester, an anaerobic digester that treats dilute biodegradable feedstocks and allows different retention times for solids and liquids ***Anaer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
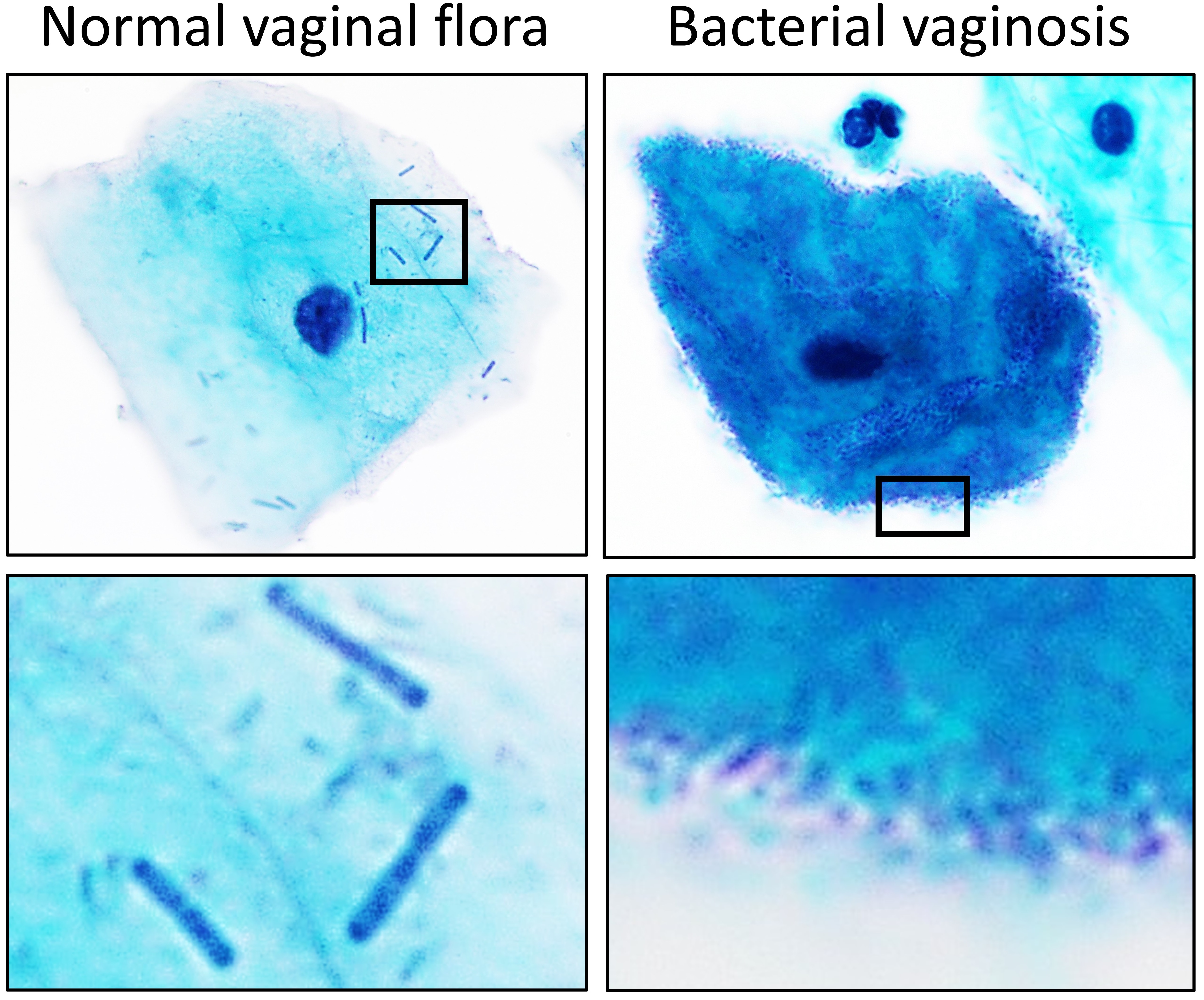
Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obligate Anaerobe
Obligate anaerobes are microorganisms killed by normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (20.95% O2). Oxygen tolerance varies between species, with some species capable of surviving in up to 8% oxygen, while others lose viability in environments with an oxygen concentration greater than 0.5%. Oxygen sensitivity The oxygen sensitivity of obligate anaerobes has been attributed to a combination of factors including oxidative stress and enzyme production. Oxygen can also damage obligate anaerobes in ways not involving oxidative stress. Because molecular oxygen contains two unpaired electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital, it is readily reduced to superoxide () and hydrogen peroxide () within cells. A reaction between these two products results in the formation of a free hydroxyl radical (OH.). Superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals are a class of compounds known as reactive oxygen species (ROS), highly reactant products that are damaging to microbes, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obligate Aerobe
An obligate aerobe is an organism that requires oxygen to grow. Through cellular respiration, these organisms use oxygen to metabolise substances, like sugars or fats, to obtain energy. In this type of respiration, oxygen serves as the terminal electron acceptor for the electron transport chain. Aerobic respiration has the advantage of yielding more energy ( adenosine triphosphate or ATP) than fermentation or anaerobic respiration, but obligate aerobes are subject to high levels of oxidative stress."Obligate aerobe - definition from Biology-Online.org." ''Biology Online.'' Biology-Online, n.d. Web. 12 Dec 2009. Examples Among organisms, almost all animals, most fungi, and several bacteria are obligate aerobes. Examples of obligately aerobic bacteria include ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (acid-fast), ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' (Gram-negative), ''Bacillus'' (Gram-positive), and ''Nocardia asteroides'' (Gram-positive). With the exception of the yeasts, most fungi are obligate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. In microorganisms, fermentation is the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the degradation of organic nutrients anaerobically. Humans have used fermentation to produce foodstuffs and beverages since the Neolithic age. For example, fermentation is used for preservation in a process that produces lactic acid found in such sour foods as pickled cucumbers, kombucha, kimchi, and yogurt, as well as for producing alcoholic beverages such as wine and beer. Fermentation also occurs within the gastrointestinal tracts of all a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facultative Anaerobic Organism
A facultative anaerobic organism is an organism that makes Adenosine triphosphate, ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to Fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation if oxygen is absent. Some examples of facultatively anaerobic bacteria are ''Staphylococcus'' Species, spp., ''Escherichia coli'', ''Salmonella'', ''Listeria'' spp., ''Shewanella oneidensis'' and ''Yersinia pestis''. Certain eukaryotes are also facultative anaerobes, including fungi such as ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' and many aquatic invertebrates such as Nereid (worm), nereid polychaetes. See also * Aerobic respiration * Anaerobic respiration * Fermentation * Obligate aerobe * Obligate anaerobe * Microaerophile References External links Facultative Anaerobic Bacteria {{Bacteria Anaerobic respiration Cellular respiration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O2). Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain. In aerobic organisms undergoing respiration, electrons are shuttled to an electron transport chain, and the final electron acceptor is oxygen. Molecular oxygen is an excellent electron acceptor. Anaerobes instead use less-oxidizing substances such as nitrate (), fumarate (), sulfate (), or elemental sulfur (S). These terminal electron acceptors have smaller reduction potentials than O2. Less energy per oxidized molecule is released. Therefore, anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic. As compared with fermentation Anaerobic cellular respiration and fermentation generate ATP in very different ways, and the terms should not be treated as synonyms. Cellular respiration (both aerobic and anaerobic) uses highly reduced chemical compounds such as NADH and FADH2 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell releases chemical energy to fuel cellular activity. The overall reaction occurs in a series of biochemical steps, some of which are redox reactions. Although cellular respiration is technically a combustion reaction, it is an unusual one because of the slow, controlled release of energy from the series of reactions. Nutrients that are commonly used by animal and pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetotactic Bacteria
Magnetotactic bacteria (or MTB) are a polyphyletic group of bacteria that orient themselves along the magnetic field lines of Earth's magnetic field. Discovered in 1963 by Salvatore Bellini and rediscovered in 1975 by Richard Blakemore, this alignment is believed to aid these organisms in reaching regions of optimal oxygen concentration. To perform this task, these bacteria have organelles called magnetosomes that contain magnetic crystals. The biological phenomenon of microorganisms tending to move in response to the environment's magnetic characteristics is known as magnetotaxis. However, this term is misleading in that every other application of the term taxis involves a stimulus-response mechanism. In contrast to the magnetoreception of animals, the bacteria contain fixed magnets that force the bacteria into alignment—even dead cells are dragged into alignment, just like a compass needle. Introduction The first description of magnetotactic bacteria was in 1963 by Salvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |