|
Michalo Lituanus
''De moribus tartarorum, lituanorum et moscorum'' ("On the Customs of Tatars, Lithuanians and Muscovites") is a 16th-century Latin treatise by Michalo Lituanus ("Michael the Lithuanian"). The work, which was originally dedicated to King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania Sigismund II Augustus, survived only in ten fragments that were first published in 1615 by Johann Jacob Grasser in Basel, Switzerland. Content The treatise is thought to date from around 1550: the author's ideas and writing style show the clear influence of humanism. While the treatise contains some useful historical information, this should be treated with care. The work is neither a chronicle nor a travel book, but rather a political essay which is critical of the author's motherland (Grand Duchy of Lithuania) and overly praises Muscovy and the Crimean Khanate for their centralized governments and united subjects. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Mythology
Lithuanian mythology ( lt, Lietuvių mitologija) is the mythology of Lithuanian polytheism, the religion of pre-Christian Lithuanians. Like other Indo-Europeans, ancient Lithuanians maintained a polytheistic mythology and religious structure. In pre-Christian Lithuania, mythology was a part of polytheistic religion; after Christianisation mythology survived mostly in folklore, customs and festive rituals. Lithuanian mythology is very close to the mythology of other Baltic nations – Prussians, Latvians, and is considered a part of Baltic mythology. Sources and evidence Early Lithuanian religion and customs were based on oral tradition. Therefore, the very first records about Lithuanian mythology and beliefs were made by travellers, Christian missionaries, chronicle writers and historians. Original Lithuanian oral tradition partially survived in national ritual and festive songs and legends which started to be written down in the 18th century. The first bits about Baltic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a population of 2.4 million. The peninsula is almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Sivash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. Crimea (called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period) has historically been at the boundary between the classical world and the steppe. Greeks colonized its southern fringe and were absorbed by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duke Of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Lithuania, which was established as an absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three ducal dynasties that managed to stay in power—House of Mindaugas, House of Gediminas, and House of Jagiellon. Despite this, the one and only King of Lithuania who has ever been crowned was King Mindaugas I, although there were two more instances of royal nobles who were not officially crowned due to unfortunate political circumstances, but ''de jure'' received recognition abroad as kings of Lithuania from the pope or the Holy Roman emperor—Vytautas the Great by Sigismund of LuxembourgNadveckė, Ineta (6 July 2019Trys Lietuvos karaliai: vienas tikras, vienas nelabai ir vienas beveik'' LRT''. and Mindaugas II by Pope Benedict XV, respectively. Others were seen as kings of Lithuania even though they had only considered it and never took further action to claim the throne, as in the case o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albertas Goštautas
Albertas Goštautas ( la, Albertus Gastold, links=no, pl, Olbracht Gasztołd, links=no, Belarusian/Ukrainian: ''Альберт Гаштольд'') ( – 1539) was a Lithuanian noble of the Goštautai family from ethnic Lithuanian lands of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Voivode of Navahrudak since 1508, Voivode of Polotsk since 1514, Voivode of Trakai since 1519 and Voivode of Vilnius since 1522. In 1522 he became Grand Chancellor of Lithuania. He was the initiator and the editor of the First Statute of Lithuania, as a successor of his staunch opponent Mikolaj Radziwiłł, who rivaled him in the precedence in the Council of Lords. His subsequent rival in influence in the Grand Duchy was Konstanty Ostrogski. Albertas was a son of Martynas Goštautas and father of Stanislovas Goštautas, last male heir of the Goštautai family. He was buried in Vilnius Cathedral, where his tomb remains till present day. He built the Hieraniony Castle (ruins survive in present-day Belarus). It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Chancellor Of Lithuania
Chancellor of Poland ( pl, Kanclerz - , from la, cancellarius) was one of the highest officials in the historic Poland. This office functioned from the early Polish kingdom of the 12th century until the end of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795. A respective office also existed in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since the 16th century. Today the office of the chancellor has been replaced by that of the Prime Minister. Chancellors' powers rose together with the increasing importance of written documents. In the 14th century the office of Chancellor of Kraków ( pl, Kanclerz krakowski) evolved into the Chancellor of the Crown ( pl, Kanclerz koronny) and from that period the chancellor powers were greatly increased, as they became responsible for the foreign policy of the entire Kingdom (later, the Commonwealth). The Chancellor was also supposed to ensure the legality of monarch's actions, especially whether or not they could be considered illegal in the context of pacta co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maišiagala
Maišiagala ( pl, Mejszagoła) is a historic town in Vilnius district municipality, Lithuania. It is located about northwest of Vilnius city municipality near the Vilnius–Panevėžys highway. According to the 2021 census, it had a population of 1 562, a decrease from 1,636, registered at the 2011 census. History Maišiagala, first mentioned in 1254, is one of the earliest Lithuanian settlements. It had a large defensive castle, which was part of the defensive network around Vilnius against the Teutonic Knights. The wooden castle was destroyed in 1365, but was rebuilt. According to Jan Długosz, Grand Duke of Lithuania Algirdas died in this castle in 1377. After the Christianization of Lithuania in 1387, Maišiagala was one of the seven towns in Lithuania where a Catholic church was built. In 1390, during the Lithuanian Civil War of 1389–1392, the castle was burned down and was not rebuilt. The town continued to exist, growing as a trading center, and was granted city privil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism. Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") Eastern Orthodox Church is organised into autocephalous churches independent from each other. In the 21st century, the number of mainstream autocephalous churches is seventeen; there also exist autocephalous churches unrecognized by those mainstream ones. Autocephalous churches choose their own primate. Autocephalous churches can have jurisdiction (authority) over other churches, some of which have the status of "autonomous" which means they have more autonomy than simple eparchies. Many of these jurisdictions correspond to the territories of one or more modern states; the Patriarchate of Moscow, for example, corresponds to Russia and some of the other post-Soviet states. They can also include metropolises, bishoprics, parishes, monas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
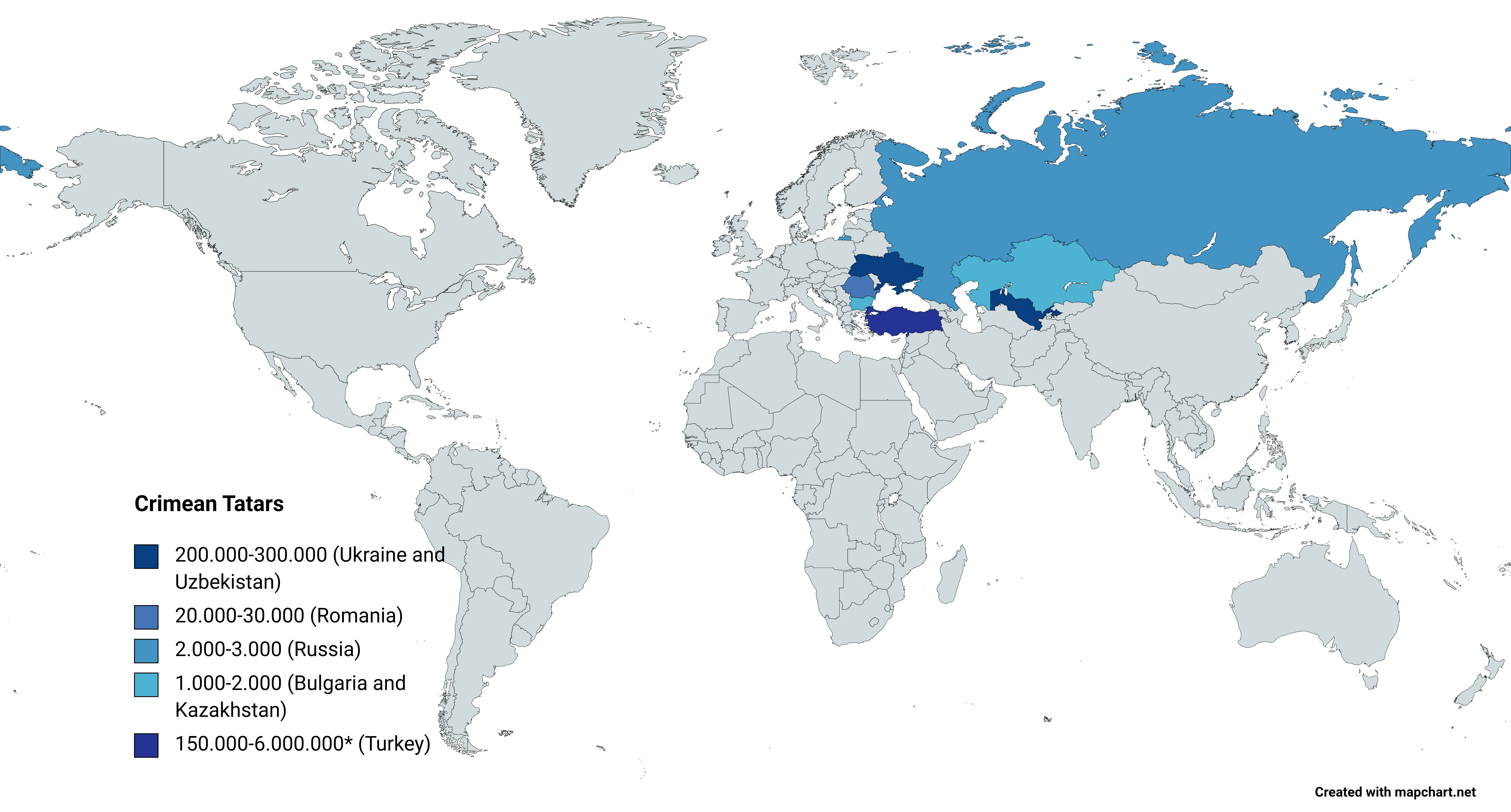
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michał Tyszkiewicz (envoy)
Michał Tyszkiewicz ( uk, Михайло Тишкевич, lt, Mykolas Tiškevičius; fl. 1533–1552) was a Ruthenian noble from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He was the youngest son of Tyszko, founder of the Tyszkiewicz family. He served as the diplomatic envoy to the Crimean Khanate in 1537 but was detained and released only in 1540. Biography Tyszkiewicz and his four brothers served at the royal court of Grand Duke Sigismund I the Old. Most successful of them was Vasyl Tyszkiewicz who became Voivode of Podlaskie and Voivode of Smolensk. Tyszkiewicz was mentioned in surviving records for the first time in 1533 when received permission from the Grand Duke to marry Petronilla, widow of Glinsky. She was older and wealthier and brought several estates as her dowry. Tyszkiewicz was sent as an envoy to the Crimean Khanate in 1537. At the time Poland–Lithuania feared an attack by Suleiman the Magnificent, returning victorious from the first campaign of the Ottoman–Safavid War. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)