|
Metropolis (northern Phrygia)
Metropolis ( grc, Μητρόπολις) was an ancient town in the north of Phrygia, and, as the name seems to indicate, a capital of the ancient kings of Phrygia, though Stephanus of Byzantium derives the name from the mother of the gods. It was situated to the north of Synnada (Athen. 13.574.), and must not be confounded with another town of the same name in the south of Phrygia. Its site is, in all probability, indicated by the ruins of Pismesh Kalasi, north of Doganlu, which show a very antique style of architecture, and mainly consist of tombs cut into the rocks; one of these tombs is that of king Midas. Although William Martin Leake is inclined to think that these ruins mark the site of Nicoleia; William Smith credits other travelers who identify them with Metropolis. From the extent of the ruins, it would seem that in the time of the Roman emperors Metropolis was an important town; but afterwards it declined, though it is still mentioned by Hierocles. Modern scholars lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires of the time. Stories of the heroic age of Greek mythology tell of several legendary Phrygian kings: * Gordias, whose Gordian Knot would later be cut by Alexander the Great * Midas, who turned whatever he touched to gold * Mygdon, who warred with the Amazons According to Homer's ''Iliad'', the Phrygians participated in the Trojan War as close allies of the Trojans, fighting against the Achaeans. Phrygian power reached its peak in the late 8th century BC under another, historical, king Midas, who dominated most of western and central Anatolia and rivaled Assyria and Urartu for power in eastern Anatolia. This later Midas was, however, also the last independent king of Phrygia before Cimmerians sacked the Phrygian capital, Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synecdemus
The ''Synecdemus'' or ''Synekdemos'' ( el, Συνέκδημος) is a geographic text, attributed to Hierocles, which contains a table of administrative divisions of the Byzantine Empire and lists of their cities. The work is dated to the reign of Justinian but prior to 535, as it divides the 912 listed cities in the Empire among 64 Eparchies. The ''Synecdemus'', along with the work of Stephanus of Byzantium were the principal sources of Constantine VII's work on the Themes (''De Thematibus''). The ''Synecdemus'' was published in various editions beginning in 1735, notably by Gustav Parthey (''Hieroclis Synecdemus''; Berlin, 1866) and slightly later in a corrected text by A. Burckhardt in the Teubner series. The most recent major publication was by E. Honigmann (Le Synekdèmos d'Hiéroklès et l'opuscule géographique de Georges de Chypre; Brussels, 1939). References Sources * * * * . (''Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium The ''Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'' (ODB) is a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Eskişehir Province
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Archaeological Sites In Turkey
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Towns And Cities In Turkey
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television * Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμα ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Phrygia
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
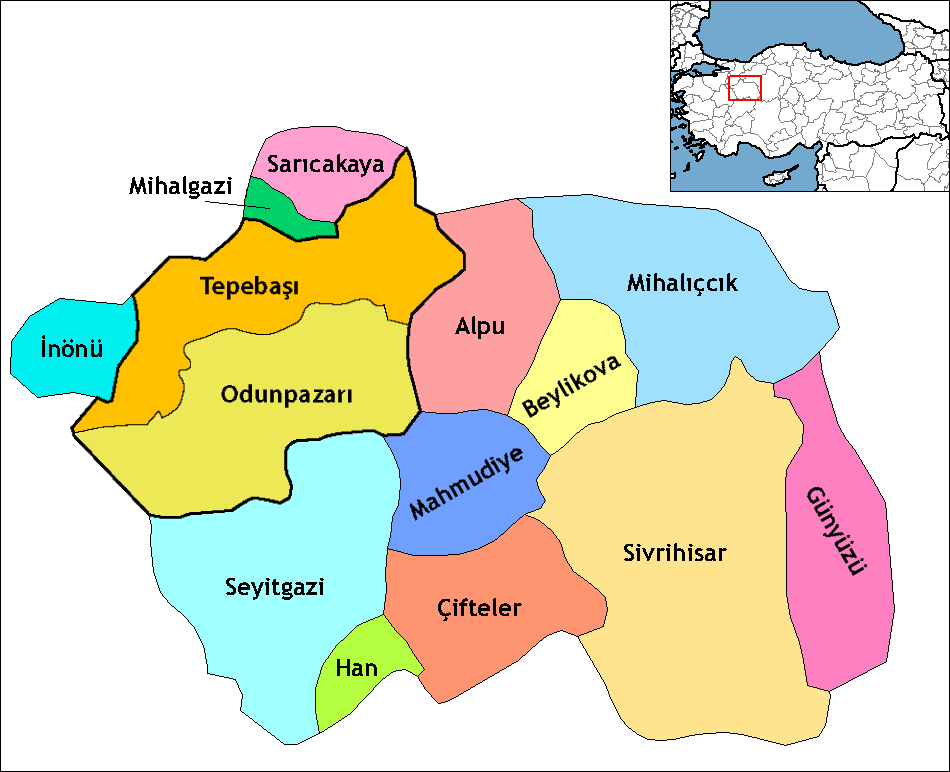
Eskişehir Province
Eskişehir Province ( tr, ) is a province in northwestern Turkey. Its adjacent provinces are Bilecik to the northwest, Kütahya to the west, Afyon to the southwest, Konya to the south, Ankara to the east, and Bolu to the north. The provincial capital is Eskişehir. Most of the province is laid down in Central Anatolia Region. Northern parts of Mihalıççık district and ones of Mihalgazi and Sarıcakaya are located in the Black Sea Region and one of them belong to the Aegean Region. Eskişehir is an old, culturally developed province of Turkey. It has a population of 844,842. Its urban population is 734,837. Eskişehir has 2 universities, Eskişehir Osmangazi University and Anadolu University, which is the largest university in Turkey and which has some branch offices in Europe. Districts Eskişehir province is divided into 14 districts, two of which are included in the greater municipality of Eskişehir (shown in boldface letters). *Odunpazarı * Tepebaşı *Alpu *Beyli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierocles (author Of Synecdemus)
Hierocles (Greek: Ἱεροκλῆς ''Hierokles'') was a Byzantine geographer of the sixth century and the attributed author of the ''Synecdemus'' or ''Synekdemos'', which contains a table of administrative divisions of the Byzantine Empire and lists of the cities of each. The work is dated to the reign of Justinian but prior to 535, as it divides the 912 listed cities in the Empire among 64 Eparchies. The ''Synecdemus'' is thus one of the most invaluable monuments which we have to study the political geography of the sixth century East. The work of Hierocles along with that of Stephanus of Byzantium were the principal sources of Constantine VII's work on the Themes (''De Thematibus''). Hierocles was published by Parthey (Hieroclis Synecdemus; Berlin, 1866) then in a corrected text, by A. Burckhardt in the Teubner seriesHieroclis Synecdemus; Leipzig, 1893. The most recent major publication was by E. Honigmann (''Le Synekdèmos d'Hiéroklès et l'opuscule géographique de George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephanus Of Byzantium
Stephanus or Stephan of Byzantium ( la, Stephanus Byzantinus; grc-gre, Στέφανος Βυζάντιος, ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD), was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethnica'' (). Only meagre fragments of the dictionary survive, but the epitome is extant, compiled by one Hermolaus, not otherwise identified. Life Nothing is known about the life of Stephanus, except that he was a Greek grammarian who was active in Constantinople, and lived after the time of Arcadius and Honorius, and before that of Justinian II. Later writers provide no information about him, but they do note that the work was later reduced to an epitome by a certain Hermolaus, who dedicated his epitome to Justinian; whether the first or second emperor of that name is meant is disputed, but it seems probable that Stephanus flourished in Byzantium in the earlier part of the sixth century AD, under Justinian I. The ''Ethnica'' Even as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)