|
Media Player Classic
Media Player Classic (MPC), Media Player Classic - Home Cinema (MPC-HC), and Media Player Classic - Black Edition (MPC-BE) are a family of free and open-source, compact, lightweight, and customizable media players for 32- and 64-bit Microsoft Windows. The original MPC, along with the MPC-HC fork, mimic the simplistic look and feel of Windows Media Player 6.4, but provide most options and features available in modern media players. Variations of the original MPC and its forks are standard media players in the K-Lite Codec Pack and the Combined Community Codec Pack. This project is now principally maintained by the community at the Doom9 forum. The active forks are Media Player Classic - Home Cinema (MPC-HC) by clsid2 (same developer known aclsidresponsible foMPC 6.4.9.1, and Media Player Classic - Black Edition (MPC-BE) by aleksoid. Media Player Classic The original Media Player Classic was created and maintained by a programmer named "Gabest" who also created PCSX2 graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Its recommended unit symbol is MB. The unit prefix ''mega'' is a multiplier of (106) in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one megabyte is one million bytes of information. This definition has been incorporated into the International System of Quantities. In the computer and information technology fields, other definitions have been used that arose for historical reasons of convenience. A common usage has been to designate one megabyte as (220 B), a quantity that conveniently expresses the binary architecture of digital computer memory. Standards bodies have deprecated this binary usage of the mega- prefix in favor of a new set of binary prefixes, by means of which the quantity 220 B is named mebibyte (symbol MiB). Definitions The unit megabyte is commonly used for 10002 (one million) bytes or 10242 bytes. The interpretation of using base 1024 originated as technical jargon for the byte m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Free Software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (GNU) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that the source code—the preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pentium III
The Pentium III (marketed as Intel Pentium III Processor, informally PIII or P3) brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded processors. The most notable differences were the addition of the Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set (to accelerate floating point and parallel calculations), and the introduction of a controversial serial number embedded in the chip during manufacturing. Even after the release of the Pentium 4 in late 2000, the Pentium III continued to be produced with new models introduced up until early 2003. They were then discontinued in April 2004 for desktop units and May 2007 for mobile units. Processor cores Similarly to the Pentium II it superseded, the Pentium III was also accompanied by the Celeron brand for lower-end versions, and the Xeon for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of XMM (SIMD) registers on x86 instruction set architecture processors. These registers can load up to 128 bits of data and perform instructions, such as vector addition and multiplication, simultaneously. SSE2 introduced double-precision floating point instructions in addition to the single-precision floating point and integer instructions found in SSE. SSE2 extends earlier SSE instruction set by adding 144 new instructions to the previous 70 instructions. SSE2 intends to fully replace MMX, a SIMD instruction set found on IA-32 architecture processors. Competing chip-maker AMD added support for SSE2 with the introduction of their Opteron and Athlon 64 ranges of AMD64 64-bit CPUs in 2003. SSE2 was extended to create SSE3 in 2004, and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
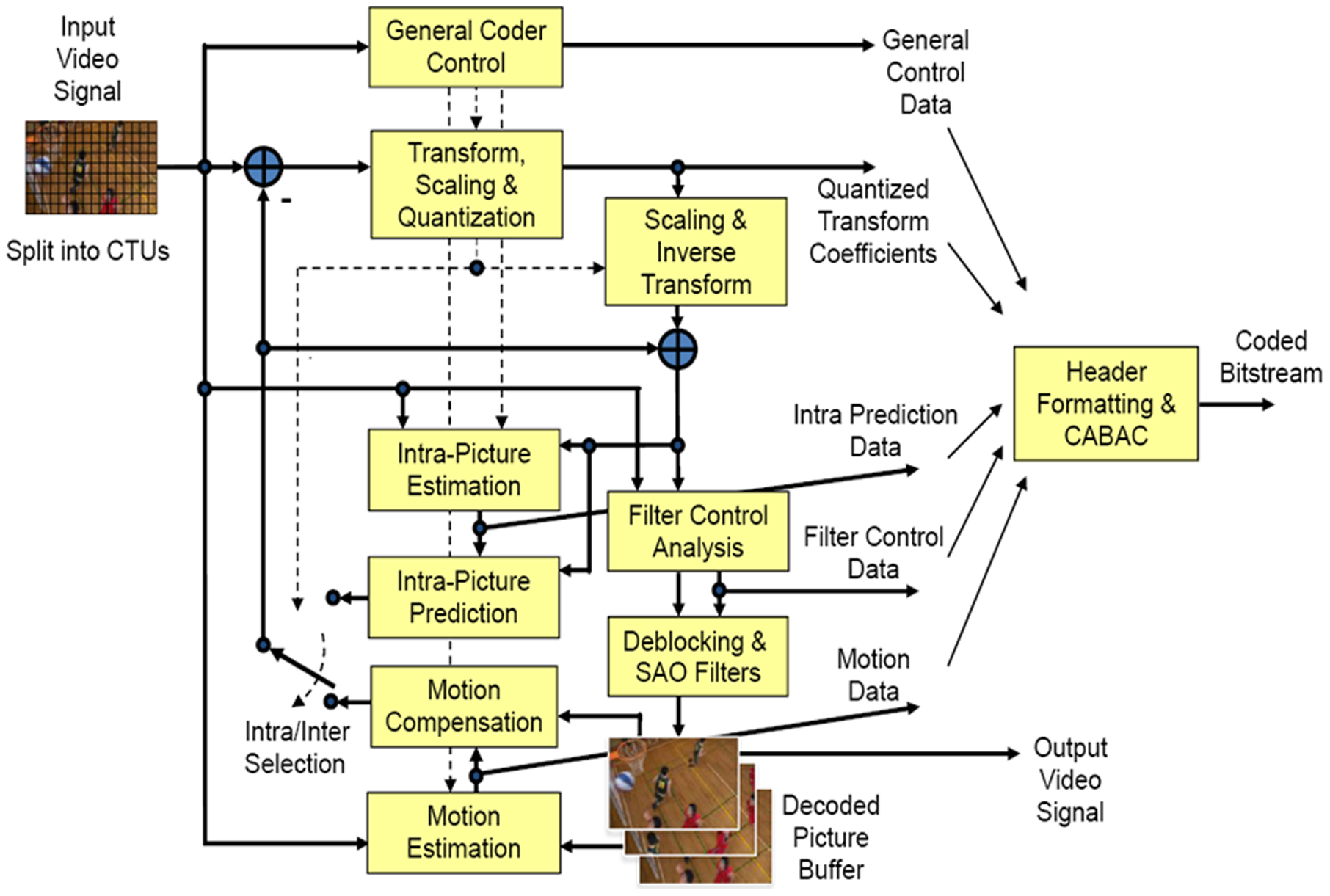
HEVC
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware. While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses both integer DCT and discrete sine transform (DST) with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC. Concept In most ways, HEVC is an extension of the concepts in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Both work by comparing different parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
MediaInfo
MediaInfo is a free software, free, cross-platform and open-source software, open-source program that displays technical information about media files, as well as tag information for many audio and video files. It is used in many programs such as XMedia Recode, MediaCoder, eMule, and K-Lite Codec Pack. It can be easily integrated into any program using a supplied . MediaInfo supports popular video formats (e.g. Matroska, WebM, Audio Video Interleave, AVI, Windows Media Video, WMV, QuickTime, RealMedia, Real, DivX, XviD) as well as lesser known or emerging formats. In 2012 MediaInfo 0.7.57 was also distributed in the PortableApps.com, PortableApps format. MediaInfo provides a command-line interface for displaying the provided information on all supported platforms. Additionally, a Graphical user interface, GUI for viewing the information on Microsoft Windows and macOS is provided. Technical information MediaInfo reveals information such as: * General: Title, author, director, alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
PortableApps
PortableApps.com is a website that distributes free applications for Windows that have been packaged for portability. These portable applications are intended to be used from removable storage devices such as USB flash drives. The site was founded by John T. Haller and includes contributions from over 100 people, including developers, designers, and translators. History PortableApps.com started out as a Haller's personal website hosting a portable version of Mozilla Firefox in March 2004. He then expanded the project to include Mozilla Thunderbird and OpenOffice.org. The open-source group of portable programs outgrew his personal website and he moved it to a community site, PortableApps.com. The site currently hosts various projects created by forum members, and is also used for bug reporting and suggestions. Some PortableApps distributions are hosted on SourceForge. Format Application installers designed for use with the PortableApps.com menu follow the convention of u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
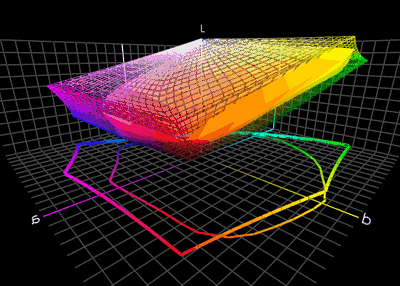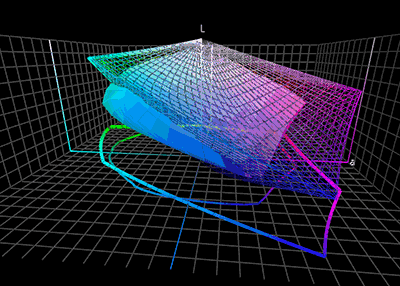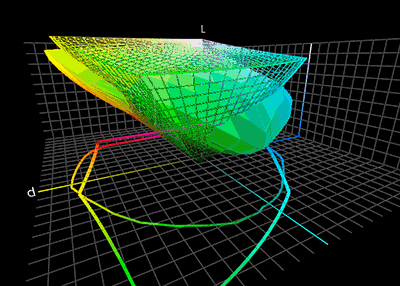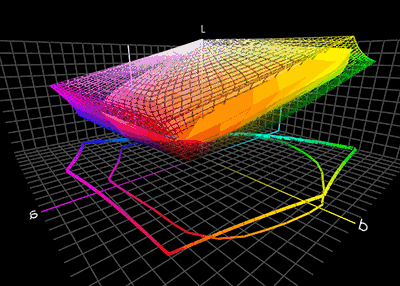
Color Management
Color management is the process of ensuring consistent and accurate colors across various devices, such as monitors, printers, and cameras. It involves the use of color profiles, which are standardized descriptions of how colors should be displayed or reproduced. Color management is necessary because different devices have different color capabilities and characteristics. For example, a monitor may display colors differently than a printer can reproduce them. Without color management, the same image may appear differently on different devices, leading to inconsistencies and inaccuracies. To achieve color management, a color profile is created for each device involved in the color workflow. This profile describes the device's color capabilities and characteristics, such as its color gamut (range of colors it can display or reproduce) and color temperature. These profiles are then used to translate colors between devices, ensuring consistent and accurate color reproduction. Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enhanced Video Renderer
Media Foundation (MF) is a Component Object Model, COM-based multimedia framework pipeline and infrastructure platform for digital media in Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11. It is the intended replacement for Microsoft DirectShow, Windows Media, Windows Media SDK, DirectX Media Objects, DirectX Media Objects (DMOs) and all other so-called "legacy" multimedia APIs such as Audio Compression Manager, Audio Compression Manager (ACM) and Video for Windows, Video for Windows (VfW). The existing DirectShow technology is intended to be replaced by Media Foundation step-by-step, starting with a few features. For some time there will be a co-existence of Media Foundation and DirectShow. Media Foundation will not be available for previous Windows versions, including Windows XP. The first release, present in Windows Vista, focuses on audio and video playback quality, High-definition video, high-definition content (i.e. HDTV), content protection and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DirectX Video Acceleration
DirectX Video Acceleration (DXVA) is a Microsoft API specification for the Microsoft Windows and Xbox 360 platforms that allows video decoding to be hardware-accelerated. The pipeline allows certain CPU-intensive operations such as iDCT, motion compensation and deinterlacing to be offloaded to the GPU. DXVA 2.0 allows more operations, including video capturing and processing operations, to be hardware-accelerated as well. DXVA works in conjunction with the video rendering model used by the video card. DXVA 1.0, which was introduced as a standardized API with Windows 2000 ( DirectX 7), and is currently available on Windows 98 or later, can use either the overlay rendering mode or VMR 7/9. DXVA 2.0, available only on Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and later OSs, integrates with Media Foundation (MF) and uses the Enhanced Video Renderer (EVR) present in MF. Overview The DXVA is used by software video decoders to define a codec-specific pipeline for hardware-acceler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |