Color Management on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In digital imaging systems, color management (or colour management) is the controlled conversion between the
Cambridge in Color Before the actual rendering intent is carried out, one can temporarily simulate the rendering by
 Apple's classic Mac OS and
Apple's classic Mac OS and
color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are assoc ...
representations of various devices, such as image scanner
An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop ''flatbed scanner'' ...
s, digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devic ...
s, monitors, TV screens, film printers, computer printer
In computing, a printer is a peripheral machine which makes a persistent representation of graphics or text, usually on paper. While most output is human-readable, bar code printers are an example of an expanded use for printers. Diffe ...
s, offset presses, and corresponding media.
The primary goal of color management is to obtain a good match across color devices; for example, the colors of one frame of a video should appear the same on a computer LCD monitor, on a plasma TV screen, and as a printed poster. Color management helps to achieve the same appearance on all of these devices, provided the devices are capable of delivering the needed color intensities. With photography, it is often critical that prints or online galleries appear how they were intended. Color management cannot guarantee identical color reproduction, as this is rarely possible, but it can at least give more control over any changes which may occur.
Parts of this technology are implemented in the operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
(OS), helper libraries, the application, and devices. A cross-platform view of color management is the use of an ICC-compatible color management system. The International Color Consortium (ICC) is an industry consortium that has defined:
* An open standard for a ''Color Matching Module'' (CMM) at the OS level
* color profiles for:
** Devices, including devicelink-profiles that represent a complete color transformation from source device to target device
** ''Working spaces'', the color spaces in which color data is meant to be manipulated
There are other approaches to color management besides using ICC profiles. This is partly due to history and partly because of other needs than the ICC standard covers. The film and broadcasting industries make use of some of the same concepts, but they frequently rely on more limited boutique solutions. The film industry, for instance, often uses 3D LUT
In the film industry, 3D lookup tables (3D LUTs) are used to map one color space to another. They are commonly used to calculate preview colors for a monitor or digital projector of how an image will be reproduced on another display device, typica ...
s ( lookup table) to represent a complete color transformation for a specific RGB encoding.
At the consumer level, system wide color management is available in most of Apple's products (macOS, iOS, iPadOS, watchOS). Microsoft Windows lacks system wide color management and virtually all applications do not employ color management. Windows' media player API is not color space aware, and if applications want to color manage videos manually, they have to incur significant performance and power consumption penalties. Android supports system wide color management, but most devices ship with color management disabled.
Overview
# Characterize. Every color-managed device requires a personalized table, or "color profile," which characterizes the color response of that particular device. # Standardize. Each color profile describes these colors relative to a standardized set of reference colors (the "Profile Connection Space"). # Translate. Color-managed software then uses these standardized profiles to translate color from one device to another. This is usually performed by a color management module (CMM).Hardware
Characterization
To describe the behavior of various output devices, they must be compared (measured) in relation to a standardcolor space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representa ...
. Often a step called linearization is performed first, to undo the effect of gamma correction that was done to get the most out of limited 8-bit color paths. Instruments used for measuring device colors include colorimeters and spectrophotometers. As an intermediate result, the device gamut is described in the form of scattered measurement data. The transformation of the scattered measurement data into a more regular form, usable by the application, is called ''profiling''. Profiling is a complex process involving mathematics, intense computation, judgment, testing, and iteration. After the profiling is finished, an idealized color description of the device is created. This description is called a ''profile''.
Calibration
Calibration is like characterization, except that it can include the adjustment of the device, as opposed to just the measurement of the device. Color management is sometimes sidestepped by calibrating devices to a common standard color space such as sRGB; when such calibration is done well enough, no color translations are needed to get all devices to handle colors consistently. This avoidance of the complexity of color management was one of the goals in the development of sRGB.Color profiles

Embedding
Image formats themselves (such as TIFF, JPEG, PNG,EPS
EPS, EPs or Eps may refer to:
Commerce and finance
* Earnings per share
* Electronic Payment Services, in Hong Kong, Macau, and Shenzhen, China
* Express Payment System, in the Philippines
Education
* Edmonton Public Schools, in Edmonton, Al ...
, PDF, and SVG) may contain embedded color profiles but are not required to do so by the image format. The International Color Consortium standard was created to bring various developers and manufacturers together. The ICC standard permits the exchange of output device characteristics and color spaces in the form of metadata. This allows the embedding of color profiles into images as well as storing them in a database or a profile directory.
Working spaces
Working spaces, such as sRGB, Adobe RGB or ProPhoto are color spaces that facilitate good results while editing. For instance, pixels with equal values of R,G,B should appear neutral. Using a large (gamut) working space will lead to posterization, while using a small working space will lead to clipping. This trade-off is a consideration for the critical image editor.Color transformation
Color transformation, or color space conversion, is the transformation of the representation of a color from onecolor space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representa ...
to another. This calculation is required whenever data is exchanged inside a color-managed chain and carried out by a Color Matching Module. Transforming profiled color information to different output devices is achieved by referencing the profile data into a standard color space. It makes it easier to convert colors from one device to a selected standard color space and from that to the colors of another device. By ensuring that the reference color space covers the many possible colors that humans can see, this concept allows one to exchange colors between many different color output devices. Color transformations can be represented by two profiles (source profile and target profile) or by a devicelink profile. In this process there are approximations involved which make sure that the image keeps its important color qualities and also gives an opportunity to control on how the colors are being changed.
Profile connection space
In the terminology of the International Color Consortium, a translation between two color spaces can go through a ''profile connection space'' (PCS): Color Space 1 → PCS ( CIELAB or CIEXYZ) → Color space 2; conversions into and out of the PCS are each specified by a profile.Gamut mapping
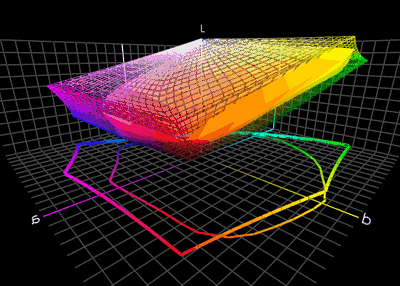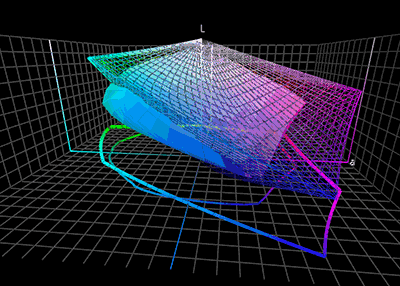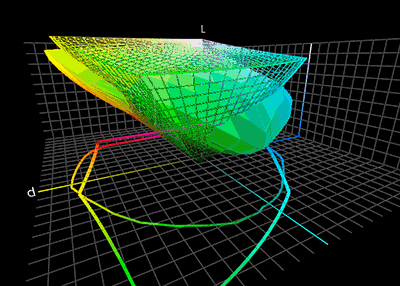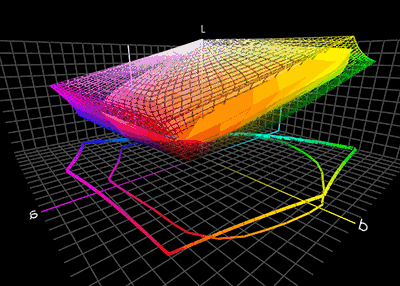
In nearly every translation process, we have to deal with the fact that the color gamut of different devices vary in range which makes an accurate reproduction impossible. They therefore need some rearrangement near the borders of the gamut. Some colors must be shifted to the inside of the gamut, as they otherwise cannot be represented on the output device and would simply be clipped. This so-called gamut mismatch occurs for example, when we translate from the RGB color space with a wider gamut into the CMYK color space with a narrower gamut range. In this example, the dark highly saturated purplish-blue color of a typical computer monitor's "blue" primary is impossible to print on paper with a typical CMYK printer. The nearest approximation within the printer's gamut will be much less saturated. Conversely, an inkjet printer's "cyan" primary, a saturated mid-brightness blue, is outside the gamut of a typical computer monitor. The color management system can utilize various methods to achieve desired results and give experienced users control of the gamut mapping behavior.Rendering intent
When the gamut of source color space exceeds that of the destination, saturated colors are liable to becomeclipped
''Clipped'' is a video featuring five tracks by the Australian hard rock band AC/DC. First released in 1991, it contained three tracks from '' The Razors Edge'' and two from ''Blow Up Your Video''.
In 2002 a DVD version was released which al ...
(inaccurately represented), or more formally burned
Burned or burnt may refer to:
* Anything which has undergone combustion
* Burned (image), quality of an image transformed with loss of detail in all portions lighter than some limit, and/or those darker than some limit
* ''Burnt'' (film), a 2015 ...
. The color management module can deal with this problem in several ways. The ICC specification includes four different rendering intents, listed below.Color Management: Color Space ConversionCambridge in Color Before the actual rendering intent is carried out, one can temporarily simulate the rendering by
soft proofing
Monitor proofing or soft-proofing is a step in the prepress printing process. It uses specialized computer software and hardware to check the accuracy of text and images used for printed products. Monitor proofing differs from conventional forms of ...
. It is a useful tool as it predicts the outcome of the colors and is available as an application in many color management systems:
In practice, photographers almost always use relative or perceptual intent, as for natural images, absolute causes color cast, while saturation produces unnatural colors. If an entire image is in-gamut, relative is perfect, but when there are out of gamut colors, which is preferable depends on a case-by-case basis. CMMs may offer options for BPC and partial chromatic adaptation.
A black point correction (BPC) is not applied for absolute colorimetric or devicelink profiles. For ICCv4, it is always applied to the perceptual intent. ICCv2 sRGB profiles differ among each other in a number of ways, one of which being whether BPC is applied.
Implementation
Color management module
''Color matching module'' (also -''method'' or -''system'') is a software algorithm that adjusts the numerical values that get sent to or received from different devices so that the perceived color they produce remains consistent. The key issue here is how to deal with a color that cannot be reproduced on a certain device in order to show it through a different device as if it were visually the same color, just as when the reproducible color range between color transparencies and printed matters are different. There is no common method for this process, and the performance depends on the capability of each color matching method. Some well known CMMs are ColorSync, Adobe CMM,Little CMS
Little CMS or LCMS is an open-source color management system, released as a software library for use in other programs which will allow the use of International Color Consortium profiles. It is licensed under the terms of the MIT License.
LCMS wa ...
, and ArgyllCMS.
Operating system level
 Apple's classic Mac OS and
Apple's classic Mac OS and macOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of ...
operating systems have provided OS-level color management A