|
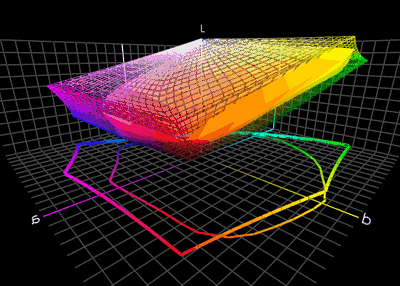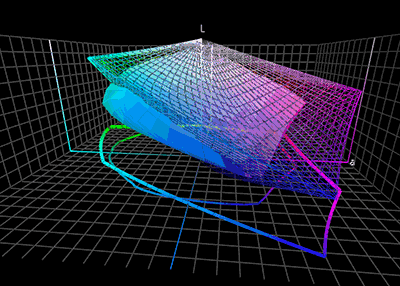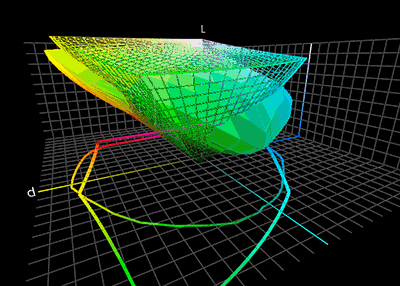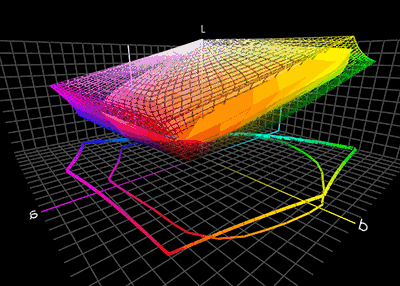
Gamut
In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut , is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device (e.g. printer or display) or measured by an input device (e.g. camera or visual system). Devices with a larger gamut can represent more colors. Similarly, gamut may also refer to the colors within a defined color space, which is not linked to a specific device. A trichromatic gamut is often visualized as a color triangle. A less common usage defines gamut as the subset of colors contained within an image, scene or video. Introduction The term ''gamut'' was adopted from the field of music, where the medieval Latin expression "gamma ut" meant the lowest tone of the G scale and, in time, came to imply the entire range of musical notes of which musical melodies are composed. William Shakespeare, Shakespeare's use of the term in ''The Taming of the Shrew'' is sometimes attributed to the author / musician Thom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Color
Primary colors are colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color printing, and paintings. Perceptions associated with a given combination of primary colors can be predicted by an appropriate mixing model (e.g., additive, subtractive) that uses the physics of how light interacts with physical media, and ultimately the retina to be able to accurately display the intended colors. The most common color mixing models are the additive primary colors (red, green, blue) and the subtractive primary colors (cyan, magenta, yellow). Red, yellow and blue are also commonly taught as primary colors (usually in the context of subtractive color mixing as opposed to additive color mixing), despite some criticism due to its lack of scientific basis. Primary colors can also be conceptual (not necessarily real), either as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SRGB
sRGB (standard RGB) is a colorspace, for use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was initially proposed by HP and Microsoft in 1996 and became an official standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999. It is the current standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that do not have an embedded color profile. The sRGB standard uses the same color primaries and white point as the ITU-R BT.709 standard for HDTV, but a different transfer function (or gamma) compatible with the era's CRT displays, and assumes a viewing environment closer to typical home and office viewing conditions. Matching the behavior of PC video cards and CRT displays greatly aided sRGB's popularity. History By the 1970s, most computers translated 8-bit digital data fairly linearly to a signal that was sent to a video monitor. However video monitors and TVs produced a brightness that was not linear with the input ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color
Color (or colour in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorption, emission spectra, emission, Reflection (physics), reflection and Transmittance, transmission. For most humans, colors are perceived in the visible light spectrum with three types of cone cells (trichromacy). Other animals may have a different number of cone cell types or have eyes sensitive to different wavelengths, such as bees that can distinguish ultraviolet, and thus have a different color sensitivity range. Animal perception of color originates from different light wavelength or spectral sensitivity in cone cell types, which is then processed by the brain. Colors have perceived properties such as hue, colorfulness (saturation), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burned (image)
An image is said to be burned or burnt when its original gamut considerably exceeds the target gamut, or when the result of processing considerably exceeds the image's gamut, resulting in clipping.Langford, Fox, and Smith. ''Langford's Basic Photography'', p. 354 Colloquially, an image is burned when it contains uniform blobs of color, black, or white where there should actually be detail. All media for storing or capturing images, both analog and digital, are capable of storing only a limited number of color hues, and are bound to a certain gamut. Squeezing an image with a given gamut into a medium with a smaller gamut is done either by adapting the whole range of colors to the new gamut, or by ''trimming'' the colors out of gamut. Trimming colors at the extremes results in burning the image. While converting and capturing images is usually a "smart" process that tries to accommodate the entire gamut of the original into the target color space, extreme processing of an imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names (including discrete numbers infor examplethe Pantone collection), or structured with mathematical rigor (as with the NCS System, Adobe RGB and sRGB). A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised. A "color model" is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMYK Color Model
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers to the four ink plates used: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (most often black). The CMYK model works by partially or entirely masking colors on a lighter, usually white, background. The ink reduces the light that would otherwise be reflected. Such a model is called ''subtractive'', as inks ''subtract'' some colors from white light; in the CMY model, white light minus red leaves cyan, white light minus green leaves magenta, and white light minus blue leaves yellow. In additive color models, such as RGB, white is the ''additive'' combination of all primary colored lights, and black is the absence of light. In the CMYK model, it is the opposite: white is the natural color of the paper or other background, and black results from a full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RYB Color Model
RYB (an abbreviation of red–yellow–blue) is a subtractive color model used in art and applied design in which red, yellow, and blue pigments are considered primary colors. Under traditional color theory, this set of primary colors was advocated by Moses Harris, Michel Eugène Chevreul, Johannes Itten and Josef Albers, and applied by countless artists and designers. The RYB color model underpinned the color curriculum of the Bauhaus, Ulm School of Design and numerous art and design schools that were influenced by the Bauhaus, including the IIT Institute of Design (founded as the New Bauhaus), Black Mountain College, Design Department Yale University, the Shillito Design School, Sydney, and Parsons School of Design, New York. In this context, the term ''primary color'' refers to three exemplar colors (red, yellow, and blue) as opposed to specific pigments. As illustrated, in the RYB color model, red, yellow, and blue are intermixed to create secondary color segments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Perception
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different frequencies independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of the larger visual system and is mediated by a complex process between neurons that begins with differential stimulation of different types of photoreceptors by light entering the eye. Those photoreceptors then emit outputs that are propagated through many layers of neurons ultimately leading to higher cognitive functions in the brain. Color vision is found in many animals and is mediated by similar underlying mechanisms with common types of biological molecules and a complex history of the evolution of color vision within different animal taxa. In primates, color vision may have evolved under selective pressure for a variety of visual tasks including the foraging for nutritious young leaves, ripe fruit, and flowers, as well as detecting predator camouflage and emotional states in other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Triangle
A color triangle is an arrangement of colors within a triangle, based on the additive or subtractive combination of three primary colors at its corners. An additive color space defined by three primary colors has a chromaticity gamut that is a color triangle, when the amounts of the primaries are constrained to be nonnegative. Before the theory of additive color was proposed by Thomas Young and further developed by James Clerk Maxwell and Hermann von Helmholtz, triangles were also used to organize colors, for example around a system of red, yellow, and blue primary colors. After the development of the CIE system, color triangles were used as chromaticity diagrams, including briefly with the trilinear coordinates representing the chromaticity values. Since the sum of the three chromaticity values has a fixed value, it suffices to depict only two of the three values, using Cartesian co-ordinates. In the modern ''x,y'' diagram, the large triangle bounded by the imaginary p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICC Profile
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes of a particular device or viewing requirement by defining a mapping between the device source or target color space and a ''profile connection space'' (PCS). This PCS is either CIELAB (L*a*b*) or CIEXYZ. Mappings may be specified using tables, to which interpolation is applied, or through a series of parameters for transformations. Every device that captures or displays color can be profiled. Some manufacturers provide profiles for their products, and there are several products that allow an end-user to generate their own color profiles, typically through the use of a tristimulus colorimeter or a spectrophotometer (sometimes called a spectrocolorimeter). The ICC defines the format precisely but does not define algorithms or processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |