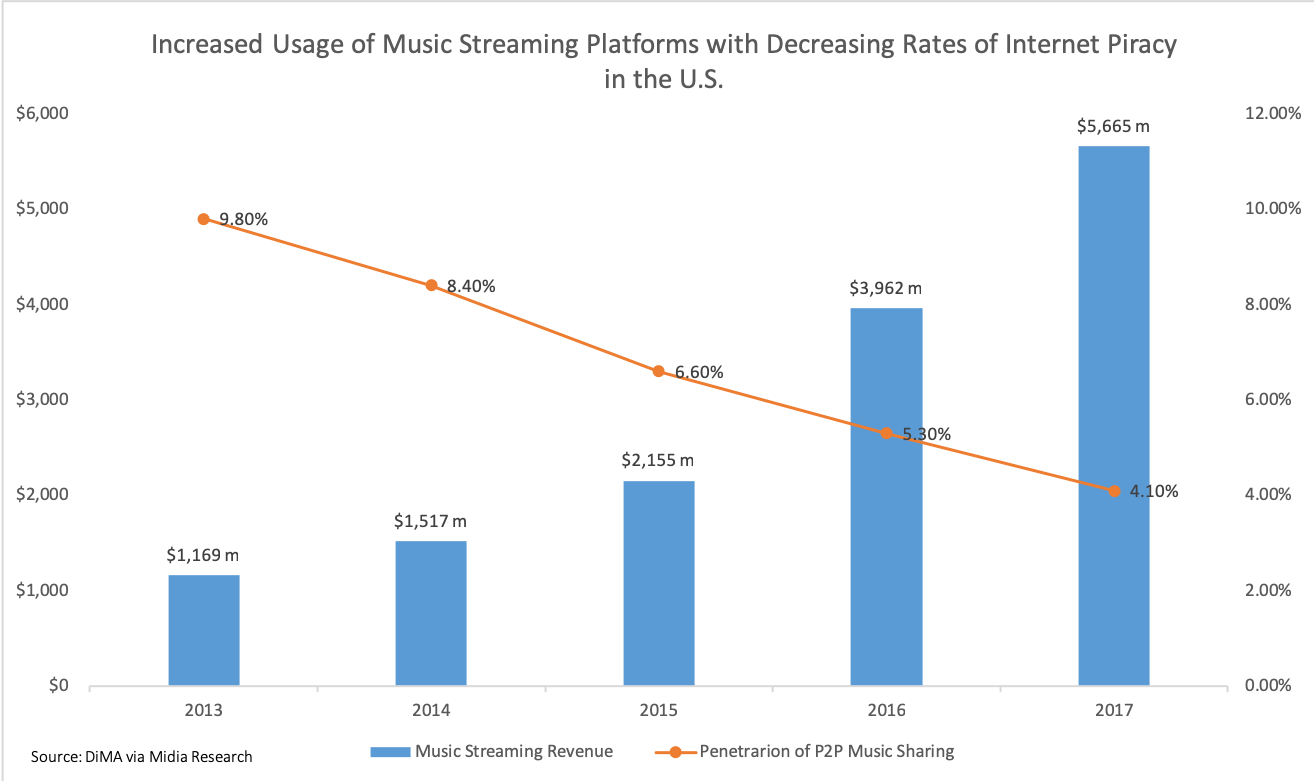
|
Enhanced Video Renderer
Media Foundation (MF) is a COM-based multimedia framework pipeline and infrastructure platform for digital media in Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11. It is the intended replacement for Microsoft DirectShow, Windows Media SDK, DirectX Media Objects (DMOs) and all other so-called "legacy" multimedia APIs such as Audio Compression Manager (ACM) and Video for Windows (VfW). The existing DirectShow technology is intended to be replaced by Media Foundation step-by-step, starting with a few features. For some time there will be a co-existence of Media Foundation and DirectShow. Media Foundation will not be available for previous Windows versions, including Windows XP. The first release, present in Windows Vista, focuses on audio and video playback quality, high-definition content (i.e. HDTV), content protection and a more unified approach for digital data access control for digital rights management (DRM) and its interoperability. It integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Mixing Renderer
DirectShow (sometimes abbreviated as DS or DShow), codename Quartz, is a multimedia framework and API produced by Microsoft for software developers to perform various operations with media files or streams. It is the replacement for Microsoft's earlier Video for Windows technology. Based on the Microsoft Windows Component Object Model (COM) framework, DirectShow provides a common interface for media across various programming languages, and is an extensible, filter-based framework that can render or record media files on demand at the request of the user or developer. The DirectShow development tools and documentation were originally distributed as part of the DirectX SDK. Currently, they are distributed as part of the Windows SDK (formerly known as the Platform SDK). Microsoft plans to completely replace DirectShow gradually with Media Foundation in future Windows versions. One reason cited by Microsoft is to provide "much more robust support for content protection systems" (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub, Inc. () is an Internet hosting service for software development and version control using Git. It provides the distributed version control of Git plus access control, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, it has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. As of June 2022, GitHub reported having over 83 million developers and more than 200 million repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the largest source code host . History GitHub.com Development of the GitHub.com platform began on October 19, 2007. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom Preston-Werner, Chris Wanstrath, P. J. Hyett and Scott Chacon after it had been made available for a few months prior as a beta release. GitHub has an annual keynote called GitHub Universe. Organizational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Media Path
The Protected Media Path is a set of technologies creating a "Protected Environment," first included in Microsoft's Windows Vista operating system, that is used to enforce digital rights management (or DRM) protections on content. Its subsets are ''Protected Video Path (PVP)'' and ''Protected User Mode Audio (PUMA)''. Any application that uses Protected Media Path in Windows uses Media Foundation. Overview The protected environment in which DRM content is played contains the media components that play DRM content, so the application only needs to provide remote control (play, rewind, pause, and so on), rather than having to handle unprotected content data. The protected environment also provides all the necessary support for Microsoft-approved ( signed) third-party software modules to be added. It provides a "wall" against outside copying, where within the walls, content can be processed without making the content available to unapproved software. In order to prevent users from co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media Streaming
Streaming media is multimedia that is delivered and consumed in a continuous manner from a source, with little or no intermediate storage in network elements. ''Streaming'' refers to the delivery method of content, rather than the content itself. Distinguishing delivery method from the media applies specifically to telecommunications networks, as most of the traditional media delivery systems are either inherently ''streaming'' (e.g. radio, television) or inherently ''non-streaming'' (e.g. books, videotape, audio CDs). There are challenges with streaming content on the Internet. For example, users whose Internet connection lacks sufficient bandwidth may experience stops, lags, or poor buffering of the content, and users lacking compatible hardware or software systems may be unable to stream certain content. With the use of buffering of the content for just a few seconds in advance of playback, the quality can be much improved. Livestreaming is the real-time delivery of cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-compressed Speech
Time-compressed speech refers to an audio recording of verbal text in which the text is presented in a much shorter time interval than it would through normally-paced real time speech. The basic purpose is to make recorded speech contain more words in a given time, yet still be understandable. For example: a paragraph that might normally be expected to take 20 seconds to read, might instead be presented in 15 seconds, which would represent a time-compression of 25% (5 seconds out of 20). The term "time-compressed speech" should not be confused with " speech compression", which controls the volume range of a sound, but does not alter its time envelope. Methods While some voice talents are capable of speaking at rates significantly in excess of general norms, the term "time-compressed speech" most usually refers to examples in which the time-reduction has been accomplished through some form of electronic processing of the recorded speech. In general, recorded speech can be elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverberation
Reverberation (also known as reverb), in acoustics, is a persistence of sound, after a sound is produced. Reverberation is created when a sound or signal is reflected causing numerous reflections to build up and then decay as the sound is absorbed by the surfaces of objects in the space – which could include furniture, people, and air. This is most noticeable when the sound source stops but the reflections continue, their amplitude decreasing, until zero is reached. Reverberation is frequency dependent: the length of the decay, or reverberation time, receives special consideration in the architectural design of spaces which need to have specific reverberation times to achieve optimum performance for their intended activity. In comparison to a distinct echo, that is detectable at a minimum of 50 to 100 ms after the previous sound, reverberation is the occurrence of reflections that arrive in a sequence of less than approximately 50 ms. As time passes, the amplitude of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Signal Processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a sequence of numbers that represent samples of a continuous variable in a domain such as time, space, or frequency. In digital electronics, a digital signal is represented as a pulse train, which is typically generated by the switching of a transistor. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing. DSP applications include audio and speech processing, sonar, radar and other sensor array processing, spectral density estimation, statistical signal processing, digital image processing, data compression, video coding, audio coding, image compression, signal processing for telecommunications, control systems, biomedical engineering, and seismology, among others. DSP can involve linear or nonli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Playlist
A playlist is a list of video or audio files that can be played back on a media player either sequentially or in a shuffled order. In its most general form, an audio playlist is simply a list of songs, but sometimes a loop. The term has several specialized meanings in the realms of television broadcasting, radio broadcasting and personal computers. A playlist can also be a list of recorded titles on a digital video disk. On the Internet, a playlist can be a list of chapters in a movie serial; for example, Flash Gordon in the Planet Mongo is available on YouTube as a playlist of thirteen consecutive video chapters. Radio The term originally came about in the early days of top 40 radio formats when stations would devise (and, eventually, publish) a limited list of songs to be played. The term would go on to refer to the entire catalog of songs that a given radio station (of any format) would draw from. Additionally, the term was used to refer to an ordered list of songs played ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interface (object-oriented Programming)
In object-oriented programming, an interface or protocol type is a data type describing a set of method signatures, the implementations of which may be provided by multiple classes that are otherwise not necessarily related to each other. A class which provides the methods listed in a protocol is said to ''adopt'' the protocol, or to ''implement'' the interface. If objects are fully encapsulated then the protocol is the only way in which they may be accessed by other objects. For example, in Java, the Comparable interface specifies a method compareTo() which implementing classes must implement. This means that a sorting method, for example, can sort a collection of any objects of types which implement the Comparable interface, without having to know anything about the inner nature of the class (except that two of these objects can be compared by means of compareTo()). Some programming languages provide explicit language support for protocols (Ada, C#, D, Dart, Delphi, Go, Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstraction (computer Science)
In software engineering and computer science, abstraction is: * The process of removing or generalizing physical, spatial, or temporal details or attributes in the study of objects or systems to focus attention on details of greater importance; it is similar in nature to the process of generalization; * the creation of abstract concept-objects by mirroring common features or attributes of various non-abstract objects or systems of study – the result of the process of abstraction. Abstraction, in general, is a fundamental concept in computer science and software development. The process of abstraction can also be referred to as modeling and is closely related to the concepts of ''theory'' and ''design''. Models can also be considered types of abstractions per their generalization of aspects of reality. Abstraction in computer science is closely related to abstraction in mathematics due to their common focus on building abstractions as objects, but is also related to other n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |