|
Meat Emulsion
Meat emulsion is a two-phase system, with the dispersed phase consisting of either solid or liquid fat particles and the continuous phase being the water containing salts and dissolved, gelled and suspended proteins. Thus, they can be classified as oil-in-water emulsion. Meat emulsion is not a true emulsion since the two phases involved are not liquids and the fat droplets in a commercial emulsion are larger than 50 μm in diameter and thus do not conform to one of the requirement of a classical emulsion. Common examples of meat emulsions include bologna, frankfurters, sausages, and meatloaf. The continuous phase mainly consists of water, water-soluble proteins and salt-soluble proteins. The dispersed phase or discontinuous phase consists of fat droplets. The water-soluble proteins are sarcoplasmic proteins such as myoglobin and other pigments; salt-soluble proteins are myofibrillar proteins such as myosin, actin, and actinins. Meat emulsifiers When used in food products, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compound, inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic chemistry, inorganic, organic chemistry, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Stearoyl Lactylate
Sodium stearoyl-2-lactylate (sodium stearoyl lactylate or SSL) is a versatile, Regulation of food and dietary supplements by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration#Food additives, FDA approved food additive used to improve the mix tolerance and volume of processed foods. It is one type of a commercially available lactylate. SSL is Toxicity, non-toxic, Biodegradation, biodegradable, and typically manufactured using Renewable resource, biorenewable Raw material, feedstocks. Because SSL is a safe and highly effective food additive, it is used in a wide variety of products ranging from Baking, baked goods and desserts to pet foods. As described by the Food Chemicals Codex 7th edition, SSL is a cream-colored powder or brittle solid. SSL is currently manufactured by the esterification of stearic acid with lactic acid and partially neutralized with either food-grade soda ash (sodium carbonate) or caustic soda (concentrated sodium hydroxide). Commercial grade SSL is a mixture of sodium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrageenan
Carrageenans or carrageenins ( ; ) are a family of natural linear sulfation, sulfated polysaccharides. They are extracted from red algae, red edible seaweeds. Carrageenans are widely used in the food industry, for their gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties. Their main application is in dairy and meat products, due to their strong binding to food proteins. Carrageenans have emerged as a promising candidate in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications as they resemble animal glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). They are used for tissue engineering, wound coverage, and drug delivery. Carrageenans contain 15–40% ester-sulfate content, which makes them anionic polysaccharides. They can be mainly categorized into three classes based on their sulfate content. Kappa-carrageenan has one sulfate group per disaccharide, iota-carrageenan has two, and lambda-carrageenan has three. A common seaweed used for manufacturing the hydrophilic colloids to produce carrageenan is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
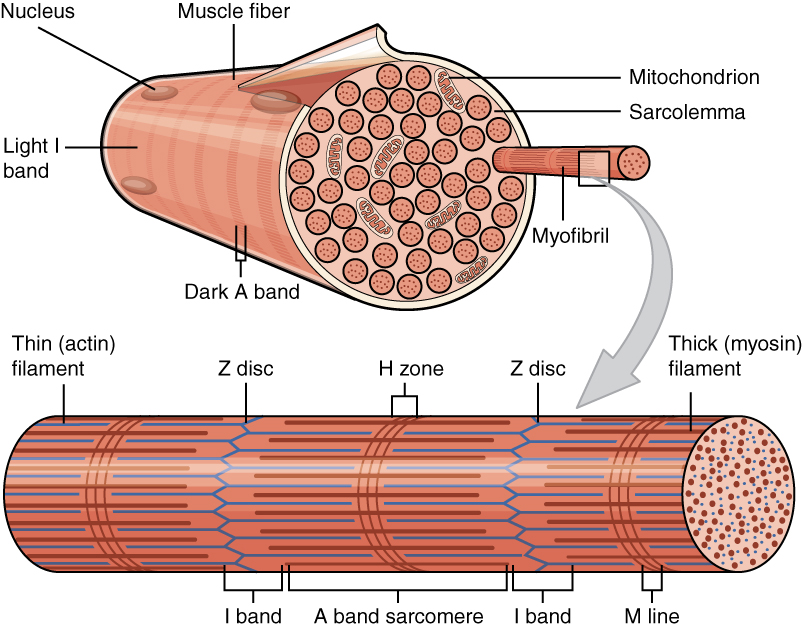
Actinin
Actinin is a microfilament protein. The functional protein is an anti-parallel dimer, which cross-links the thin filaments in adjacent sarcomeres, and therefore coordinates contractions between sarcomeres in the horizontal axis. Alpha-actinin is a part of the spectrin superfamily. This superfamily is made of spectrin, dystrophin, and their homologous and isoforms. In non-muscle cells, it is found by the actin filaments and at the adhesion sites. The lattice like arrangement provides stability to the muscle contractile apparatus. Specifically, it helps bind actin filaments to the cell membrane. There is a binding site at each end of the rod and with bundles of actin filaments. The non-sarcomeric alpha-actinins, encoded by '' ACTN1'' and '' ACTN4'', are widely expressed. '' ACTN2'' expression is found in both cardiac and skeletal muscle, whereas ''ACTN3'' is limited to the latter. Both ends of the rod-shaped alpha-actinin dimer contain actin-binding domains. Six different protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myosin
Myosins () are a Protein family, family of motor proteins (though most often protein complexes) best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are adenosine triphosphate, ATP-dependent and responsible for actin-based motility. The first myosin (M2) to be discovered was in 1864 by Wilhelm Kühne. Kühne had extracted a viscous protein from skeletal muscle that he held responsible for keeping the tension state in muscle. He called this protein ''myosin''. The term has been extended to include a group of similar ATPases found in the cell (biology), cells of both striated muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Following the discovery in 1973 of enzymes with myosin-like function in ''Acanthamoeba, Acanthamoeba castellanii'', a global range of divergent myosin genes have been discovered throughout the realm of eukaryotes. Although myosin was originally thought to be restricted to muscle cells (hence ''wikt:myo-#Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myofibrillar
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis. Myofibrils are composed of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. These proteins are organized into thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments, which repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomeres. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments along each other. Structure Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2 micrometres (μm). The filaments of myofibrils, myofilaments, consist of three types, thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thin filaments consist primarily of the protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle, skeletal Muscle, muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen and does not have cooperative binding with oxygen like hemoglobin does. Myoglobin consists of non-polar amino acids at the core of the globulin, where the heme group is non-covalently bounded with the surrounding polypeptide of myoglobin. In humans, myoglobin is found in the bloodstream only after Strain (injury), muscle injury. (Google books link is the 2008 edition) High concentrations of myoglobin in muscle cells allow organisms to hold their breath for a longer period of time. Diving mammals such as whales and seals have muscles with particularly high abundance of myoglobin. Myoglobin is found in Type I muscle, Type II A, and Type II B; although many older texts describe myo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally Miscibility, immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms ''colloid'' and ''emulsion'' are sometimes used interchangeably, ''emulsion'' should be used when both phases, dispersed and continuous, are liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid (the dispersed phase (matter), phase) is dispersion (chemistry), dispersed in the other (the continuous phase). Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, homogenized milk, liquid biomolecular condensates, and some cutting fluids for metal working. Two liquids can form different types of emulsions. As an example, oil and water can form, first, an oil-in-water emulsion, in which the oil is the dispersed phase, and water is the continuous phase. Second, they can form a water-in-oil emulsion, in which water is the dispersed phase and oil is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoplasm
Sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of a muscle cell. It is comparable to the cytoplasm of other cells, but it contains unusually large amounts of glycogen (a polymer of glucose), myoglobin, a red-colored protein necessary for binding oxygen molecules that diffuse into muscle fibers, and mitochondria.Roberts, Michael D.; Haun, Cody T.; Vann, Christopher G.; Osburn, Shelby C.; Young, Kaelin C. (2020). "Sarcoplasmic Hypertrophy in Skeletal Muscle: A Scientific "Unicorn" or Resistance Training Adaptation?". Frontiers in Physiology. 11. . . . . The calcium ion concentration in sarcoplasm is also a special element of the muscle fiber; it is the means by which muscle contractions take place and are regulated. The sarcoplasm plays a critical role in muscle contraction as an increase in Ca2+ concentration in the sarcoplasm begins the process of filament sliding. The decrease in Ca2+ in the sarcoplasm subsequently ceases filament sliding.Shahinpoor, Mohsen (2013). Muscular Biomimicry. Elsevier. pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodhead Publishing
Woodhead Publishing Limited was established in 1989 as an independent international publishing company of science and technical books. The company publishes books in association with The Textile Institute, Cambridge International Science Publishing. They have previously published books in association with The Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (IOM3) and the European Federation of Corrosion. History In December 2008 Woodhead Publishing acquired the backlist, future titles and imprint of Chandos Publishing in Witney, Oxford, UK, comprising over 250 books in the fields of library and information management, knowledge management and Asian Studies. In 2011 they launched Woodhead Publishing Online, a resource of scientific, technical and information trends, comprising over 800 e-books, containing 12,000 chapters. This resource was hosted by MetaPress, a division of EBSCO Industries Inc. Woodhead (and its imprint Chandos) was acquired by Elsevier in August 2013. Its curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |