|
Marres
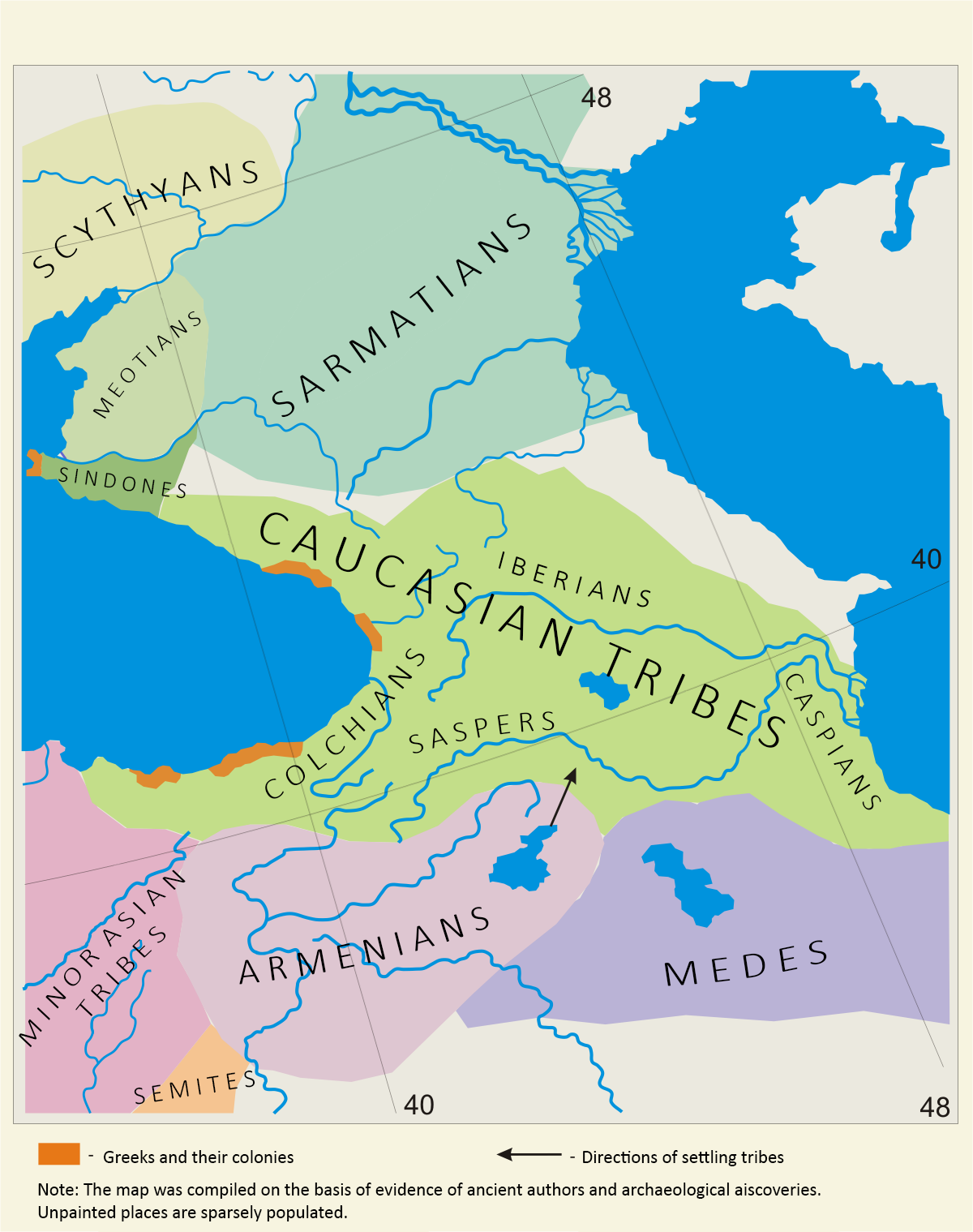
The Mares ( ka, მარები ) were an ancient Colchian tribe. They entered ancient history with the writings of Hecataeus of Miletus. He gives a brief description of the tribe and mentions that they lived between closely akin Colchian tribal groups Macrones and Mossynoeci. They inhabited the southeast periphery of the Black Sea, more precisely the mountains of Northeast Anatolia, which constitutes, along with South Caucasus, a proposed homeland of the Kartvelian languages and the convergent territory in which they were molded into a nation. According to Herodotus, they had the same leader as the Colchians, who were the larger entity created through a process of political consolidation and amalgamation of tribes. After the rapid rise of Achaemenid Empire, they were incorporated into the XIX Satrapy, along with other Colchian tribes Mushki, Tibareni, Macrones and Mossynoeci Mossynoeci (Georgian: მოსინიკები, grc, Μοσσύνοικοι, , modern Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Colchian Tribes
The following is a list of ancient Colchian In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia. Its population, the Colchians are generally thou ... tribes. Background This is a list of the ancient Colchian tribes.D. M. Lang, The Georgians, London 1966. chap. 6 List of ancient Colchian tribes References External linksIberiana - Georgian Tribes {{Ancient Georgians Ancient peoples of Georgia (country) Tribes in Greco-Roman historiography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrones
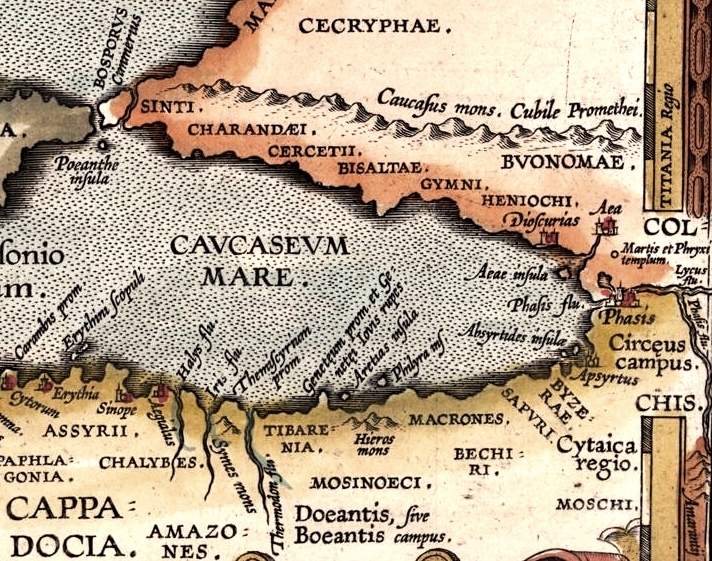
The Macrones ( ka, მაკრონები) ( grc, Μάκρωνες, ''Makrōnes'') were an ancient Colchian tribe in the east of Pontus, about the Moschici Mountains (modern Yalnizçam Dağlari, Turkey). The name is allegedly derived from the name of Kromni valley ( Κορούμ, located 13 km north-east of Gümüşhane) by adding Kartvelian ma- prefix which denotes regional descendance. History The Macrones are first mentioned by Herodotus (c. 450 BC), who relates that they, along with Moschi, Tibareni, Mossynoeci, and Marres, formed the nineteenth satrapy within the Achaemenid Persian Empire and fought under Xerxes I. There are many other subsequent references to them in the Classical accounts. Xenophon (430-355 BC) places them east of Trapezus (modern Trabzon, Turkey). They are described as a powerful and wild people wearing garments made of hair, and as using in war wooden helmets, small shields of wicker-work, and short lances with long points. Strabo (xii.3.18) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mossynoeci
Mossynoeci (Georgian: მოსინიკები, grc, Μοσσύνοικοι, , modern Greek ', "dwellers in wooden towers") is a name that the Greeks of the Euxine Sea (Black Sea) applied to the peoples of Pontus, the northern Anatolian coast west of Trebizond. The Mossynoeci were believed to be of proto-Georgian. Herodotus Writing soon after 430 BCE, Herodotus in Book 3 cites the Mossynoeci, along with the Moschoi, Tibareni The Tibareni ( ka, ტიბარენები, Tibarenebi; Greek: Τιβαρηνοί and Τιβαρανοί;) were a people residing on the coast of ancient Pontus referred to in Herodotus, Xenophon, Strabo and other classical authors. The Ti ..., the Macrones and Marres as comprising the Districts of the Achaemenid Empire, 19th satrapy established by Darius the Great, Darius of Persia. The satrapy as a whole was to yield three hundred talents. The Mossynoeci are also mentioned in Book 7 of the Histories. Xenophon In his ''Anabasis'' Xenophon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
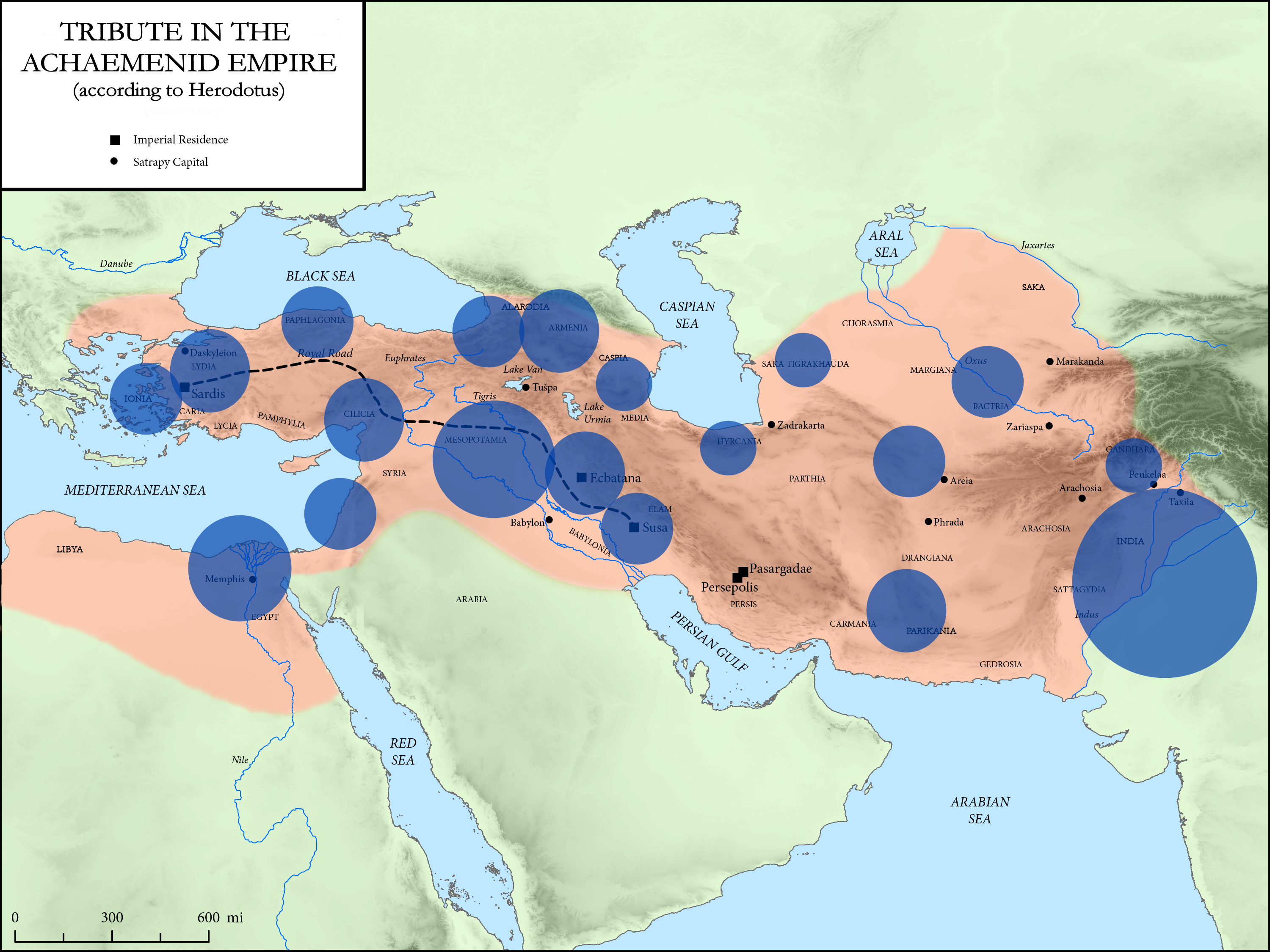
Districts Of The Achaemenid Empire
Herodotus divided the Achaemenid Empire into 20 districts for the purpose of tribute payments. The following is a description of the ethnic makeup of the districts and the amount they paid in taxes, translated from Herodotus' '' Histories''. Accounting units The quantities of silver are given in Babylonian talent (1 Babylonian talent = about 30.3 kg), while the quantities of gold (India only) are given in Euboïc/Euboean talent (1 Euboïc talent = about 26 kg). Only the Hindush paid in gold, the exchange rate of gold to silver being 1 to 13 by weight at the time of Herodotus. Tax districts The order of the districts given here follows Herodotus, ''Histories'', III.90–94. In hellenocentric way it starts with Ionia and Mysia. The official Persian order of the provinces, as devised under Darius I in 518 BCE, was different and started from the Empire's capital: 1. Media, 2. Susa, etc.Hermann Bengtson, Vladimir Milojčić (ed.), ''Grosser Historischer Weltatlas'', Erster T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hecataeus Of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Μιλήσιος; c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer. Biography Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Persian rule in the satrapy of Lydia. He was active during the time of the Greco-Persian Wars. After having travelled extensively, he settled in his native city, where he occupied a high position, and devoted his time to the composition of geographical and historical works. When Aristagoras, acting tyrant of Miletus, held a council of leading Ionians at Miletus to organize a revolt against Persian rule, Hecataeus tried in vain to dissuade his countrymen from the undertaking. In 494 BC, when the defeated Ionians were obliged to sue for terms, he was one of the ambassadors to the Persian satrap Artaphernes, whom he persuaded to restore the constitution of the Ionic cities. Hecataeus is the first known Greek historian and was one of the first c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea covers (not including the Sea of Azov), has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end of the Balkan Mountains; and the Dobruja Plateau considerably farth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the '' Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushki
The Mushki (sometimes transliterated as Muški) were an Iron Age people of Anatolia who appear in sources from Assyria but not from the Hittites. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi (Μόσχοι) of Greek sources and the Georgian tribe of the Meskhi. Josephus Flavius identified the ''Moschoi'' with the Biblical Meshech. Two different groups are called ''Muški'' in Assyrian sources ( Diakonoff 1984:115), one from the 12th to the 9th centuries BC near the confluence of the Arsanias and the Euphrates ("Eastern Mushki") and the other from the 8th to the 7th centuries BC in Cappadocia and Cilicia ("Western Mushki"). Assyrian sources clearly identify the Western Mushki with the Phrygians, but later Greek sources then distinguish between the Phrygians and the Moschoi. Identification of the Eastern Mushki with the Western Mushki is uncertain, but it is possible that at least some of the Eastern Mushki migrated to Cilicia in the 10th to the 8th centuries BC. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibareni
The Tibareni ( ka, ტიბარენები, Tibarenebi; Greek: Τιβαρηνοί and Τιβαρανοί;) were a people residing on the coast of ancient Pontus referred to in Herodotus, Xenophon, Strabo and other classical authors. The Tibareni were believed to be of proto-Kartvelian or Scythian origin.Schol. ad Apoll. Rhod. 2.378, 1010 History Tibareni occupied the country between the Chalybes and the Mosynoeci, on the east of the river Isis, and the country was called Tibarenia ( grc, Τιβαρηνία). They are mentioned as early as the time of Herodotus, According to the ancient Greeks, the Tibareni were Scythians. Strabo describes them as inhabiting the mountains branching off from the Montes Moschici and Colchici, and mentions Cotyura as their principal town. They appear to have been a harmless and happy people, who performed all their duties in a joyous manner. Their arms consisted of wooden helmets, small shields, and short spears with long points. Xenophon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelons And Mordvins
Vladimir Nikolayevich Semenkovich (russian: Владимир Николаевич Семенкович, 1861 – 1932) was a Russian ethnologist and archaeologist, best known for his work in historical geography of Upper Don and Oka '' Gelonians and Mordvins'' where he had identified some of the Herodotus's tribes with contemporary ethnic groups of the Russian Empire and described the difference between physical, and geographical conditions of European Russia in the fifth century BC and the modern period. Biography Valdimir Semenkovich was graduated from Kronstadt Higher Naval Technical School in 1883 and assigned to Chesma as Engineer Officer ( Lieutnant of Imperial Russian Navy) where he served until 1891. He had resigned in 1891 and bought estate Vaskino in Serpukhovsky Uyezd, Moscow Governorate in 1894. Anton Chekhov bought estate Melikhovo almost the same time and they became neighbours for more than 10 years. Vladimir Semenkovich devoted himself to ethnology, arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |