|
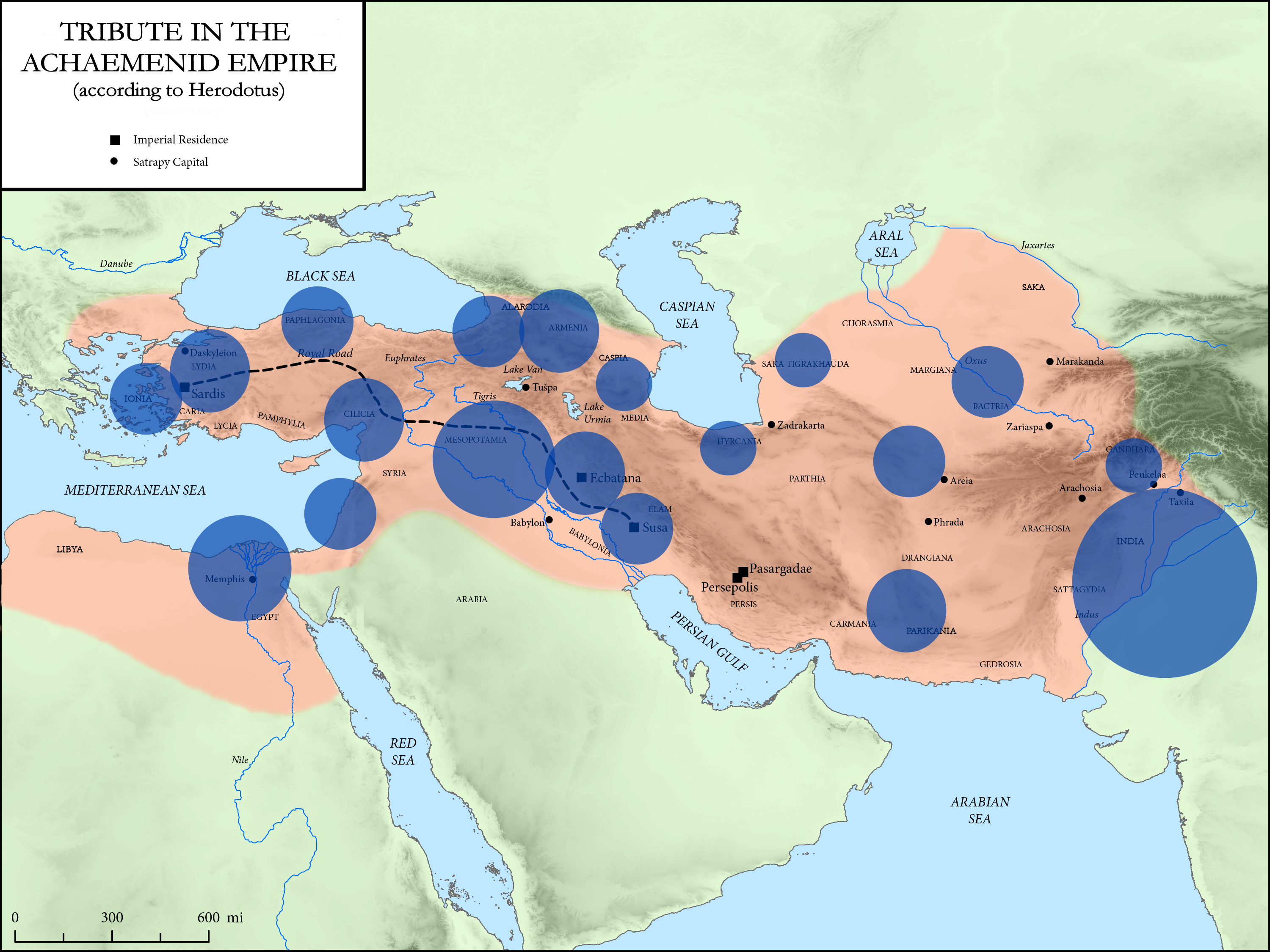
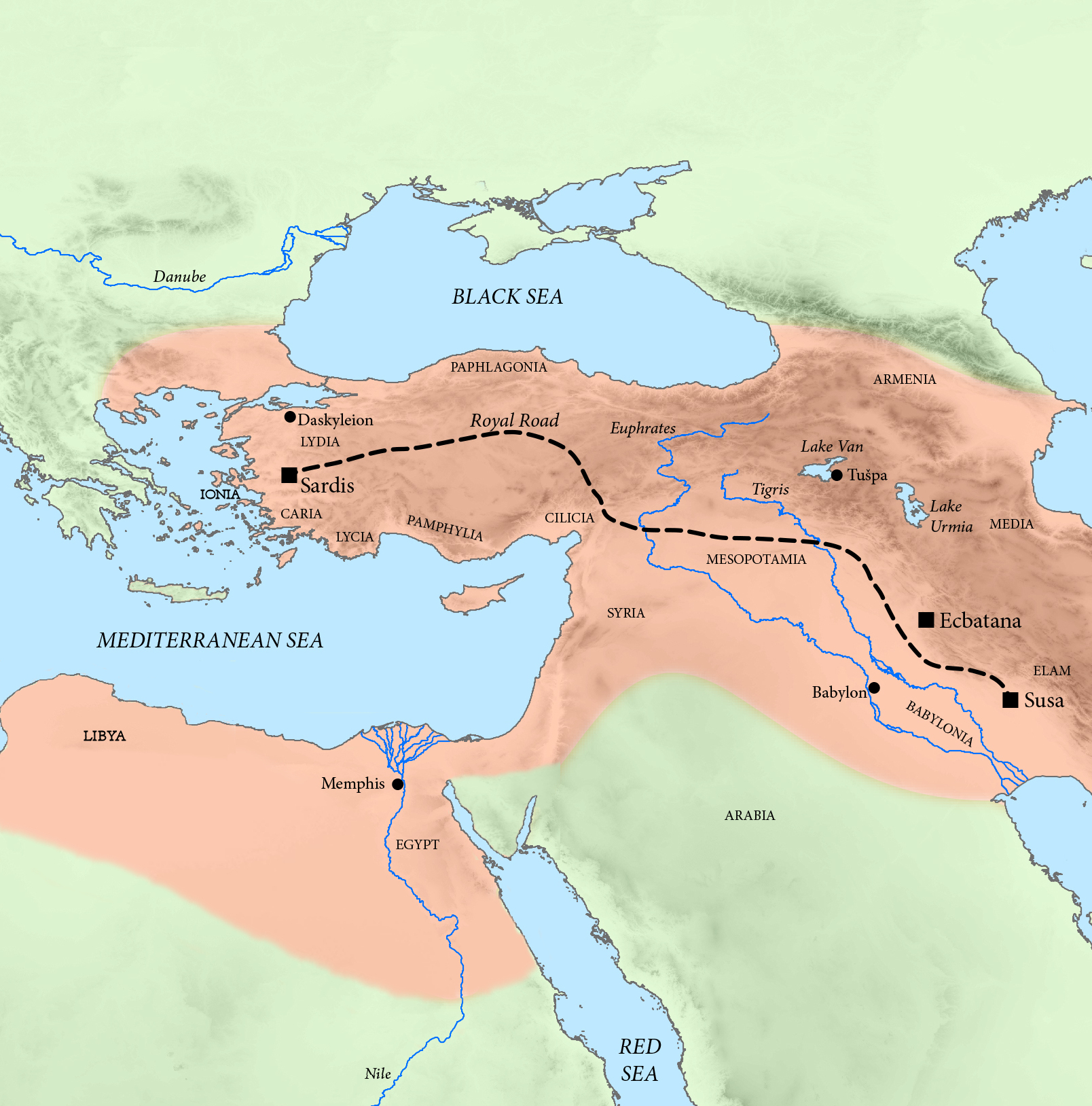
Districts Of The Achaemenid Empire
Herodotus divided the Achaemenid Empire into 20 districts for the purpose of tribute payments. The following is a description of the ethnic makeup of the districts and the amount they paid in taxes, translated from Herodotus' '' Histories''. Accounting units The quantities of silver are given in Babylonian talent (1 Babylonian talent = about 30.3 kg), while the quantities of gold (India only) are given in Euboïc/Euboean talent (1 Euboïc talent = about 26 kg). Only the Hindush paid in gold, the exchange rate of gold to silver being 1 to 13 by weight at the time of Herodotus. Tax districts The order of the districts given here follows Herodotus, ''Histories'', III.90–94. In hellenocentric way it starts with Ionia and Mysia. The official Persian order of the provinces, as devised under Darius I in 518 BCE, was different and started from the Empire's capital: 1. Media, 2. Susa, etc.Hermann Bengtson, Vladimir Milojčić (ed.), ''Grosser Historischer Weltatlas'', Erster T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribute In The Achaemenid Empire
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conquered or otherwise threatened to conquer. In case of alliances, lesser parties may pay tribute to more powerful parties as a sign of allegiance and often in order to finance projects that would benefit both parties. To be called "tribute" a recognition by the payer of political submission to the payee is normally required; the large sums, essentially protection money, paid by the later Roman and Byzantine Empires to barbarian peoples to prevent them attacking imperial territory, would not usually be termed "tribute" as the Empire accepted no inferior political position. Payments ''by'' a superior political entity to an inferior one, made for various purposes, are described by terms including "subsidy". The ancient Persian Achaemenid Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geographically in Western Asia, its cultural ties and geopolitics are overwhelmingly Southern European. Cyprus is the third-largest and third-most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is located north of Egypt, east of Greece, south of Turkey, and west of Lebanon and Syria. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. The northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which was established after the 1974 invasion and which is recognised as a country only by Turkey. The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC. Archaeological remains include the well-preserved ruins from the Hellenistic period such as Salamis and Kourion, and Cypr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yehud Medinata
Yehud, also known as Yehud Medinata or Yehud Medinta (), was an administrative province of the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire in the region of Judea that functioned as a Autonomy, self-governing region under its local Jews, Jewish population. The province was a part of the Persian satrapy of Eber-Nari, and continued to exist for two centuries until its incorporation into the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empires following the conquests of Alexander the Great. The area of Persian Yehud corresponded to the previous Neo-Babylonian Empire, Babylonian Yehud (Babylonian province), province of Yehud, which was formed after the fall of the Kingdom of Judah, the southern Israelites, Israelite kingdom History of ancient Israel and Judah, that had existed in the region prior to the Jewish–Babylonian war, Jewish–Babylonian War and subsequent Babylonian captivity. It had a considerably smaller population than that of the fallen kingdom. Yehud Medinata was the Aramaic, Aramai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posidium
Ras al-Bassit ( ar, رأس البسيط), the classical Posidium or Posideium ( grc-gre, Ποσιδήιον and Ποσείδιον, ''Posidḗion''), is a small town in Syria named for a nearby cape. It has been occupied since at least the late Bronze Age and was a fortified port under Greek and Roman rule. Herodotus—although not later classical geographers—made it the northwestern point of Syria. Its beaches have a distinctive black sand and are a popular resort destination within Syria. Name "Raʾs" () is the Arabic word for "head", used for headlands and capes. "Bassit" is a transcription of its former name Posidium, as standard Arabic is only able to voice bilabial stops. The Roman name Posidium or Posideium was a latinization of the Greek name Posideion, meaning "laceof Poseidon", the Greek seagod. It was known as "Bosyt" under Ottoman rule. The Syrian municipality is also known as simply Al-Bassit. Geography Ras al-Bassit is a small cape on the Syrian coast of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilicia (satrapy)
Cilicia was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, with its capital being Tarsus. It was conquered sometime in the 540's BC by Cyrus the Great. Cilicia was a vassal, and although it had a vassal king it had to pay a tribute of 360 horses and 500 talents of silver, according to Herodotus. The fertile Cilician plains were the most important part of the satrapy. There were several sanctuaries that remained more or less independent from Persian rule. Some of these included Castabala, Mazaca, and Mallus. The last vassal king of Cilicia became involved in the civil war between Artaxerxes II and Cyrus the Younger. Having sided with Cyrus the Younger, who was defeated, the king was dethroned and Cilicia became an ordinary satrapy. The second to last satrap (governor) of Cilicia was the Babylonian Mazaios. Shortly afterwards, his successor was expelled by Alexander the Great. The region was later incorporated by the Roman Empire. See also *Cilicia * Çukurova *Adana *Cilician Gates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria (region)
Syria (Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other synonyms are Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. In modern times, the term "Syria" alone is used to refer to the Arab Republic of Syria. The term is originally derived from Assyria, an ancient civilization centered in northern Mesopotamia, modern-day Iraq. During the Hellenistic period, the term Syria was applied to the entire Levant as Coele-Syria. Under Roman rule, the term was used to refer to the province of Syria, later divided into Syria Phoenicia and Coele Syria, and to the province of Syria Palaestina. Under the Byzantines, the provinces of Syria Prima and Syria Secunda emerged out of Coele Syria. After the Muslim conquest of the Levant, the term was superseded by the Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus to the east, and separated from Phrygia (later, Galatia) by a prolongation to the east of the Bithynian Olympus. According to Strabo, the river Parthenius formed the western limit of the region, and it was bounded on the east by the Halys River. ''Paphlagonia'' was said to be named after Paphlagon, a son of the mythical Phineus.Eustath. ad Horn. II. ii. 851, ad Dion. Per. 787; Steph. B. t.v.; Const. Porph. de Them. i. 7. Geography The greater part of Paphlagonia is a rugged mountainous country, but it contains fertile valleys and produces a great abundance of hazelnuts and fruit – particularly plums, cherries and pears. The mountains are clothed with dense forests, notable for the quantity of boxwood that they furnish. Hence, its coasts were occupied by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracia
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD. Confines From the perspective of classical Greece, Thracia included the territory north of Thessaly, with no definite boundaries, sometimes to the inclusion of Macedonia and Scythia Minor. Later, Thracia proper was understood to include the territory bordered by the Danube on the north, by the Black Sea on the east, by Macedonia in the south and by Illyria to the west, roughly equivalent with the territory of the Thracian kingdom as it stood during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. With the annexation of the Thracian kingdom by the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia (Roman Province)
The Asia ( grc, Ἀσία) was a Roman province covering most of western Anatolia, which was created following the Roman Republic's annexation of the Attalid Kingdom in 133 BC. After the establishment of the Roman Empire by Augustus, it was the most prestigious of the Senatorial province, governed by a proconsul. This arrangement endured until the province was subdivided in the fourth century AD. The province was one of the richest of the Empire and was at peace for most of the Imperial period. It contained hundreds of largely self-governing Greek city-states, who competed fiercely with one another for status, through appeals to the Imperial authorities and the cultivation of prestigious cultural institutions such as festival games, religious cults, and oratory. Geography The province of Asia originally consisted of the territories of Mysia, the Troad, Aeolis, Lydia, Ionia, Caria, and the land corridor through Pisidia to Pamphylia. The Aegean islands, with the exception of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |