|
Marian Turkowski
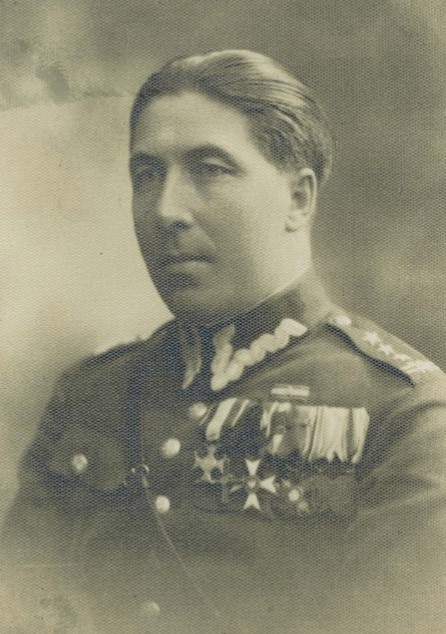
Marian Turkowski (1894–1948) was a soldier of Polish Legions in World War I and Polish II Corps in Russia, and officer, later General brygady of the Polish Army. Altogether, Turkowski served in different military units from 1914 until 1948, with the exception for World War II (1939 - 1945), during which he was kept as a German prisoner of war at Oflag VII-A Murnau. Turkowski was born on 28 July 1894 in the village of Iwkowa, which at that time belonged to Austrian Galicia. He attended a high school in nearby Bochnia, after which studied law at Jagiellonian University in Kraków. In 1914, Turkowski joined Polish Legions Second (then Third) Infantry Regiment. Wounded in the Battle of Kostiuchnówka (July 1916), he was captured by the Russians. Released in 1917, Turkowski joined Polish II Corps in Russia. Promoted to lieutenant, he fought in the Battle of Kaniów. In November 1918, Turkowski joined the newly created Polish Army. In January 1919, he served in Białystok Rifle R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marian Turkowski
Marian Turkowski (1894–1948) was a soldier of Polish Legions in World War I and Polish II Corps in Russia, and officer, later General brygady of the Polish Army. Altogether, Turkowski served in different military units from 1914 until 1948, with the exception for World War II (1939 - 1945), during which he was kept as a German prisoner of war at Oflag VII-A Murnau. Turkowski was born on 28 July 1894 in the village of Iwkowa, which at that time belonged to Austrian Galicia. He attended a high school in nearby Bochnia, after which studied law at Jagiellonian University in Kraków. In 1914, Turkowski joined Polish Legions Second (then Third) Infantry Regiment. Wounded in the Battle of Kostiuchnówka (July 1916), he was captured by the Russians. Released in 1917, Turkowski joined Polish II Corps in Russia. Promoted to lieutenant, he fought in the Battle of Kaniów. In November 1918, Turkowski joined the newly created Polish Army. In January 1919, he served in Białystok Rifle R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Invasion of Poland, Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of World War II, European theatre of the Second World War. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the Polish census of 1921, 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powązki Cemetery
Powązki Cemetery (; pl, Cmentarz Powązkowski), also known as Stare Powązki ( en, Old Powązki), is a historic necropolis located in Wola district, in the western part of Warsaw, Poland. It is the most famous cemetery in the city and one of the oldest, having been established in 1790. It is the burial place of many illustrious individuals from Polish history. Some are interred along the "Avenue of the Distinguished" - ''Aleja Zasłużonych'', created in 1925. It is estimated that over 1 million people are buried at Powązki. The cemetery is often confused with the newer Powązki Military Cemetery, which is located to the north-west of Powązki Cemetery. History Powązki Cemetery was established on 4 November 1790 on land donated by nobleman Melchior Szymanowski, and consecrated on 20 May 1792. Initially it covered an area of only about 2.5 ha. In the same year Saint Karol Boromeusz Church, designed by Dominik Merlini, was built on the northern edge of the cemetery. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Radom
The Battle of Radom, also known as the Battle of Iłża, was part of the Invasion of Poland during the Second World War. It lasted from 8 September 1939 to 9 September 1939. Polish troops of the Prusy Army, under General Stanisław Skwarczyński, defended the city of Iłża and the road from Sandomierz to Radom. The Poles were not ready to meet head on overwhelming German XV Army Corps (General Hermann Hoth), and were easily defeated after two days of fighting. Prusy Army, in the aftermath of the battle, ceased to exist. Some of the army's units joined other tactical groupings of the Polish armed forces. Background Armia Prusy, which was regarded as strategic reserve of Polish forces, remained deep behind front line, and was not planned to enter the battle before mid-September. To the surprise of Polish headquarters, after the first week of fighting, motorized and panzer units of German 10th Army broke through a gap between Army Krakow and Army Lodz, near Czestochowa, and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prusy Army
The Prusy Army ( pl, Armia Prusy) was one of the Polish armies to fight during the Invasion of Poland in 1939. Created in the summer of 1939 as the main reserve of the Commander in Chief, it was commanded by Gen. Stefan Dąb-Biernacki. The word ''Prusy'' in the Polish language means Prussia, but this name only served as a codename and the region of operations of this army was far from East Prussia. This is in contrast to other Polish armies in 1939 which were named after the geographical regions where they formed. The Prusy Army, whose original name was Warszawa Army, was named so after a folwark in central Poland called Prusy, which served as the headquarters of General Dąb-Biernacki. Tasks According to the "Plan West" ('' Plan Zachód'', the code name for the Polish mobilization plan) it was to be composed of units mobilized as the second and third waves, and its main purpose was to cooperate with the nearby armies "Łódź" and "Kraków". It was being mobilized in two group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Skwarczyński
Stanisław Skwarczyński (1888–1981) was a soldier of the Austro-Hungarian Army, officer of Polish Legions in World War I, and General brygady of the Polish Army. He fought in several conflicts, including World War I, Polish-Czechoslovak War, Polish-Ukrainian War, Polish-Soviet War and the Invasion of Poland. Furthermore, Skwarczynski was a freemason, member of a Masonic Lodge in Wilno. Skwarczynski was born on 17 November 1888 in the village of Wierzchnia, Kalusz County, Austrian Galicia. He studied architecture at Lwow Polytechnic, and was an active member of Polish paramilitary organizations, such as the Union of Active Struggle and the Riflemen's Association. In 1914, he joined Polish Legions in World War I. Appointed to the post of battalion commandant of 1st Legions Infantry Regiment, he was on 15 June 1915 promoted to the rank of Poruchik. After the Oath crisis, Skwarczynski was forced to join Austro-Hungarian Army, from which he deserted. In 1918 – 1917, he was co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operational Group
{{Unreferenced, date=October 2008 Operational Group ( pl, Grupa Operacyjna, abbreviated GO) was the highest level of tactical division of the Polish Army before and during World War II and the invasion of Poland. It was corps-sized, although various Operational Groups varied in size. Operational groups first appeared in Polish tactical scheme during the Polish-Bolshevik War, most probably under the influence of French Military Mission to Poland. After the war they were dissolved. Prior to World War II, the operational groups were recreated. Initially, in March 1939, they consisted only of staffs formed around existing corps commands. According to the Polish mobilization scheme, they were to become mobile reserves of the Polish armies and other major strategic-scale units. One of such groups, the Kutno Operational Group, was planned but never created. Also, in the autumn of 1938, the Independent Operational Group Silesia was created with the purpose of capturing Zaolzie from Czecho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
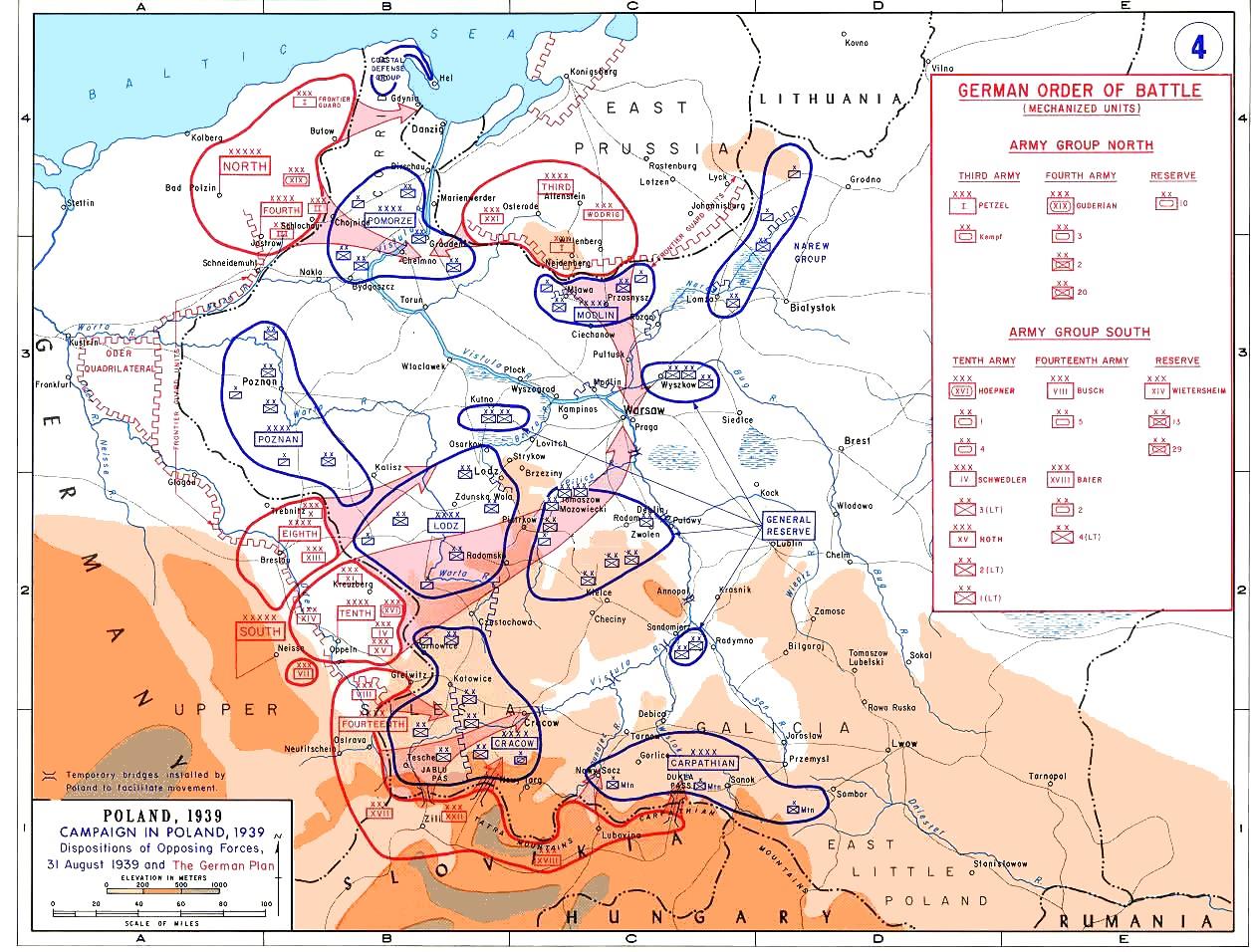
Polish September Campaign
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug). German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident. Slovak military forces advan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of the Vistula River and is about to the southeast of Warsaw by road. One of the events that greatly contributed to the city's development was the Polish-Lithuanian Union of Krewo in 1385. Lublin thrived as a centre of trade and commerce due to its strategic location on the route between Vilnius and Kraków; the inhabitants had the privilege of free trade in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The Lublin Parliament session of 1569 led to the creation of a real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, thus creating the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Lublin witnessed the early stages of Reformation in the 16th century. A Calvinist congregation was founded and groups of radical Arians appeared in the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zamość
Zamość (; yi, זאמאשטש, Zamoshtsh; la, Zamoscia) is a historical city in southeastern Poland. It is situated in the southern part of Lublin Voivodeship, about from Lublin, from Warsaw. In 2021, the population of Zamość was 62,021. Zamość was founded in 1580 by Jan Zamoyski, Grand Chancellor of Poland, who envisioned an ideal city. The historical centre of Zamość was added to the World Heritage List in 1992, following a decision of the sixteenth ordinary session of the World Heritage Committee, held between 7 and 14 December 1992 in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States; it was recognized for being "a unique example of a Renaissance town in Central Europe". Zamość is about from the Roztocze National Park. History Zamość was founded in 1580 by the Chancellor and Hetman (head of the army of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth), Jan Zamoyski, on the trade route linking western and northern Europe with the Black Sea. Modelled on Italian trading cities, and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd Legions Infantry Division (Poland)
Polish 3rd Legions Infantry Division (''3. Dywizja Piechoty Legionów'') was a tactical unit of the Polish Army between the World Wars. Formed in 1919, as a third unit composed significantly of veterans of the Polish Legions in World War I (after Polish 1st Legions Infantry Division and Polish 2nd Legions Infantry Division), it saw extensive action during the Polish-Bolshevik War and the Invasion of Poland. In the interbellum period, the headquarters of the division was stationed in Zamość, while its regiments were garrisoned in Chelm, Lublin, Zamosc and other locations. The division was officially formed on April 9, 1919, in former Austrian Galicia, during the ongoing Polish-Ukrainian War. At the beginning it consisted of three regiments (7th Legions Infantry, 8th Legions Infantry and 3rd Legions Light Artillery), but was later reinforced with 9th Infantry Regiment. The Division in September 1939 In accordance with Polish mobilization plan (see Plan West), the division, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |