|
Marc-Amable Girard
Marc-Amable Girard (April 25, 1822 – September 12, 1892) was the second premier of Manitoba, and the first Franco-Manitoban to hold that post. The ''Canadian Parliamentary Guide'' lists Girard as having been Premier (or ''Chief Minister'') from 1871 to 1872, but he did not have this title at the time and was not the government leader. In 1874, however, Girard led Manitoba's first ministry to be constituted on principles of "responsible government". In this sense, he may be regarded as the first Premier of Manitoba. Early life Girard was born in Varennes, Lower Canada (now Quebec). Political career He worked as a Notary Public between 1844 and 1870, and was active in local political life (serving as Mayor of Varennes at one stage). He lost an electoral bid for the Province of Canada's Legislative Council in 1858, and a further bid for the Canadian Assembly in 1863 (losing to Parti Rouge leader A.A. Dorion in Hochelaga). During the Riel Rebellion, Girard was sent to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Honourable
''The Honourable'' (British English) or ''The Honorable'' (American English; see spelling differences) (abbreviation: ''Hon.'', ''Hon'ble'', or variations) is an honorific style that is used as a prefix before the names or titles of certain people, usually with official governmental or diplomatic positions. Use by governments International diplomacy In international diplomatic relations, representatives of foreign states are often styled as ''The Honourable''. Deputy chiefs of mission, , consuls-general and consuls are always given the style. All heads of consular posts, whether they are honorary or career postholders, are accorded the style according to the State Department of the United States. However, the style ''Excellency'' instead of ''The Honourable'' is used for ambassadors and high commissioners. Africa The Congo In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the prefix 'Honourable' or 'Hon.' is used for members of both chambers of the Parliament of the Democratic Repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Party Of Canada (historical)
The Conservative Party of Canada (french: Parti conservateur du Canada), colloquially known as the Tories, is a federal political party in Canada. It was formed in 2003 by the merger of the two main right-leaning parties, the Progressive Conservative Party (PC Party) and the Canadian Alliance, the latter being the successor of the Western Canadian-based Reform Party. The party sits at the centre-right to the right of the Canadian political spectrum, with their federal rival, the Liberal Party of Canada, positioned to their left. The Conservatives are defined as a "big tent" party, practising "brokerage politics" and welcoming a broad variety of members, including "Red Tories" and " Blue Tories". From Canadian Confederation in 1867 until 1942, the original Conservative Party of Canada participated in numerous governments and had multiple names. However, by 1942, the main right-wing Canadian force became known as the Progressive Conservative Party. In the 1993 federal elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
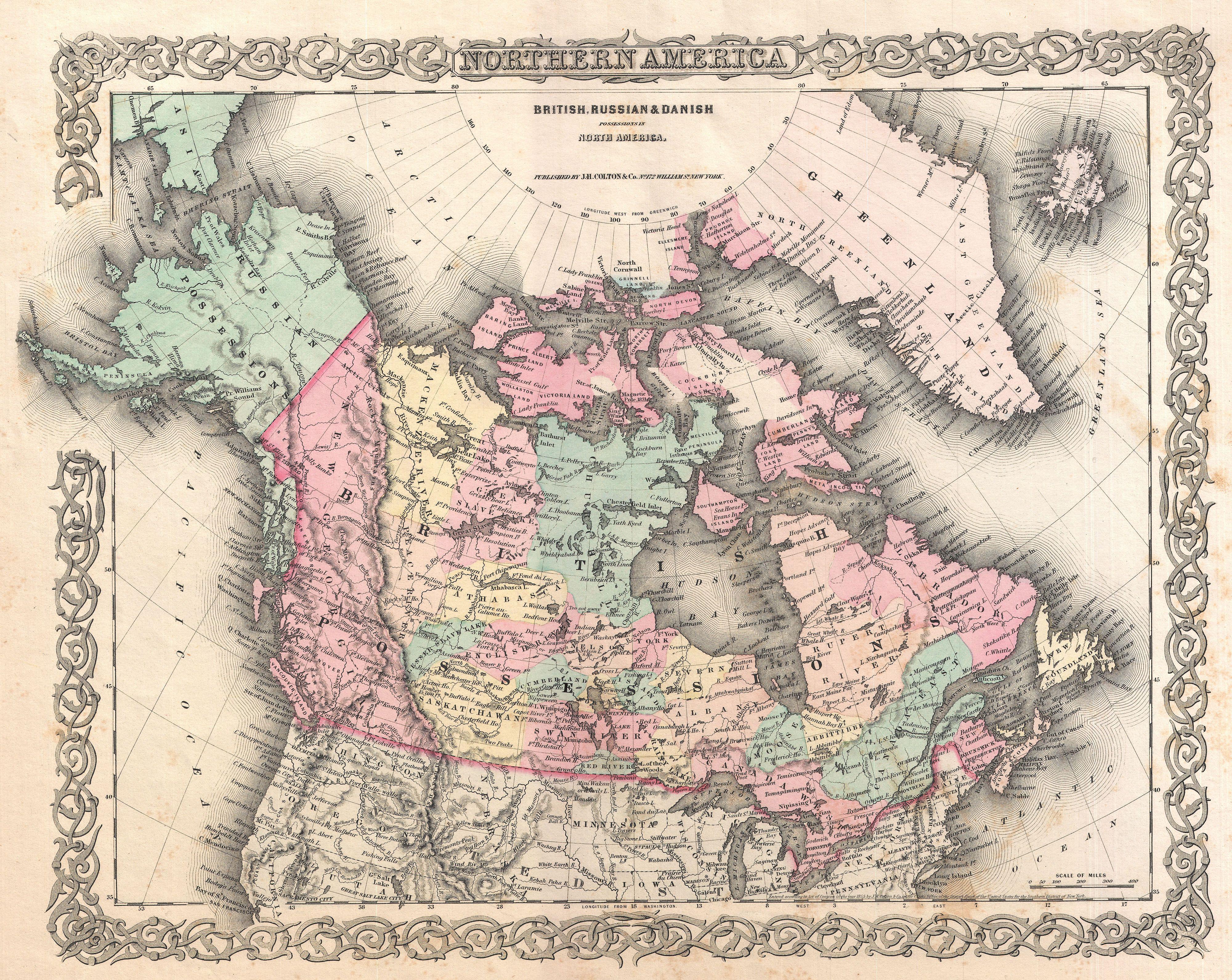
Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population of 1,342,153 as of 2021, of widely varied landscape, from arctic tundra and the Hudson Bay coastline in the Northern Region, Manitoba, north to dense Boreal forest of Canada, boreal forest, large freshwater List of lakes of Manitoba, lakes, and prairie grassland in the central and Southern Manitoba, southern regions. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have inhabited what is now Manitoba for thousands of years. In the early 17th century, British and French North American fur trade, fur traders began arriving in the area and establishing settlements. The Kingdom of England secured control of the region in 1673 and created a territory named Rupert's Land, which was placed under the administration of the Hudson's Bay Company. Rupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red River Rebellion
The Red River Rebellion (french: Rébellion de la rivière Rouge), also known as the Red River Resistance, Red River uprising, or First Riel Rebellion, was the sequence of events that led up to the 1869 establishment of a provisional government by Métis leader Louis Riel and his followers at the Red River Colony, in the early stages of establishing today's Canadian province of Manitoba. It had earlier been a territory called Rupert's Land and been under control of the Hudson's Bay Company before it was sold. The event was the first crisis the new federal government faced after Canadian Confederation in 1867. The Canadian government had bought Rupert's Land from the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869 and appointed an English-speaking governor, William McDougall. He was opposed by the French-speaking mostly-Métis inhabitants of the settlement. Before the land was officially transferred to Canada, McDougall had sent out surveyors to plot the land according to the square township sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hochelaga (electoral District)
Hochelaga (formerly known as Sainte-Marie and Montreal—Sainte-Marie) is a federal electoral district in Quebec, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1867 to 1988 and since 2004. Geography The district includes the neighbourhood of Hochelaga-Maisonneuve and the western part of the neighbourhood of Longue-Pointe in the Borough of Mercier–Hochelaga-Maisonneuve, the eastern part of the neighbourhood of Rosemont in the Borough of Rosemont–La Petite-Patrie and the eastern part of the neighbourhood of Centre-Sud in the Borough of Ville-Marie. Political geography Until 2011, this working class riding strongly favoured the Bloc, which in 2008, won most polls. The New Democrats placed second in the 2009 by-election; as in much of Quebec, Bloc support collapsed in the 2011 election and the New Democrats swept the riding. Demographics :''According to the Canada 2006 Census'' * Ethnic groups: 83.5% White, 4.5% Black, 2.8% Latin American, 2.5% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parti Rouge
The Red Party (french: Parti rouge, or french: Parti démocratique) was a political group that contested elections in the Eastern section of the Province of Canada. It was formed around 1847 by radical French-Canadians inspired by the ideas of Louis-Joseph Papineau, the '' Institut canadien de Montréal'', and the reformist movement led by the Parti patriote of the 1830s. The Red Party did not experience electoral success in the same manner as the Blue Party, their electoral rivals in Canada East. Because of their anti-clerical beliefs, the Red Party was condemned by the Catholic Church, contributing to their lack of electoral success. The party did form government as part of a coalition with the Clear Grits and Liberals from Canada West on some occasions before confederation, but never held a majority in their section of the province. After confederation, the party was dissolved, with members forming the Liberal Party of Canada at the federal level, and the Liberal Party of Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British North America, British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of 1837–1838. The Act of Union 1840, passed on 23 July 1840 by the British Parliament and proclaimed by the Monarchy of Great Britain, Crown on 10 February 1841, merged the Colonies of Upper Canada and Lower Canada by abolishing their separate parliaments and replacing them with a Parliament of the Province of Canada, single one with two houses, a Legislative Council of the Province of Canada, Legislative Council as the upper chamber and the Legislative Assembly of the Province of Canada, Legislative Assembly as the lower chamber. In the aftermath of the Rebellions of 1837–1838, unification of the two Canadas was driven by two factors. Firstly, Upper Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as the means by which a mayor is elected or otherwise mandated. Depending on the system chosen, a mayor may be the chief executive officer of the municipal government, may simply chair a multi-member governing body with little or no independent power, or may play a solely ceremonial role. A mayor's duties and responsibilities may be to appoint and oversee municipal managers and employees, provide basic governmental services to constituents, and execute the laws and ordinances passed by a municipal governing body (or mandated by a state, territorial or national governing body). Options for selection of a mayor include direct election by the public, or selection by an elected governing council or board. The term ''mayor'' shares a linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area and the second-largest by population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York in the United States. Between 1534 and 1763, Quebec was called ''Canada'' and was the most developed colony in New France. Following the Seven Years' War, Quebec b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsible Government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive branch) in Westminster democracies are responsible to parliament rather than to the monarch, or, in a colonial context, to the imperial government, and in a republican context, to the president, either in full or in part. If the parliament is bicameral, then the government is responsible first to the parliament's lower house, which is more representative than the upper house, as it usually has more members and they are always directly elected. Responsible government of parliamentary accountability manifests itself in several ways. Ministers account to Parliament for their decisions and for the performance of their departments. This requirement to make announcements and to answer questions in Parliament means that ministers must have the priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)