|
Mansaka
The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous people in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad (Literally: "indigenous people"), the autonym officially adopted by the delegates of the Lumad Mindanao Peoples Federation (LMPF) founding assembly on 26 June 1986 at the Guadalupe Formation Center, Balindog, Kidapawan, Cotabato, Philippines. Usage of the term was accepted in Philippine jurisprudence when President Corazon Aquino signed into law Republic Act 6734, where the word was used in Art. XIII sec. 8(2) to distinguish Lumad ethnic communities from the islands of Mindanao. Mindanao is home to a substantial part of the country's indigenous population, around 15% of the Philippine's total population of over 100 million.National Statistics Office. “Statistics on Filipino Children.” Journal of Philippine Statistics, vol. 59, no. 4, 2008, p. 119. History The name ''Lumad'' grew out of the polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansakan Languages
The Mansakan languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in the Philippines. Dabawenyo is the principal native language of the Davao region; however, there is a high degree of bilingualism in Cebuano among their speakers. Most speakers have shifted to Cebuano today. Classification Overview The Mansakan languages are: * Dabawenyo *Mandayan :* Mansaka :* Mandaya * Kamayo * Kalagan (a dialect cluster) *Mamanwa Gallman (1974) The Mansakan subgrouping below is from Gallman (1974).Gallman, Andrew Franklin. ''A Reconstruction of Proto-Mansakan''. M.A. dissertation. Arlington, Texas: Dept. of Linguistics, University of Texas at Arlington, 1974. Individual languages are marked by ''italics'', and primary branches by ''bold italics''. *''Mansakan'' **North Mansakan ***'' Kamayo North'' and '' Kamayo South'' **Dabaw ***'' Dabawenyo (Davaoeño)'' **Eastern Mansakan ***'' Isamal'' ***''Caraga (Karaga)'' ***'' Kabasagan, Boso, Mansaka, Mandayan'' **Western Mansakan ***'' K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manobo People
The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous people in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad (Literally: "indigenous people"), the autonym officially adopted by the delegates of the Lumad Mindanao Peoples Federation (LMPF) founding assembly on 26 June 1986 at the Guadalupe Formation Center, Balindog, Kidapawan, Cotabato, Philippines. Usage of the term was accepted in Philippine jurisprudence when President Corazon Aquino signed into law Republic Act 6734, where the word was used in Art. XIII sec. 8(2) to distinguish Lumad ethnic communities from the islands of Mindanao. Mindanao is home to a substantial part of the country's indigenous population, around 15% of the Philippine's total population of over 100 million.National Statistics Office. “Statistics on Filipino Children.” Journal of Philippine Statistics, vol. 59, no. 4, 2008, p. 119. History The name ''Lumad'' grew out of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
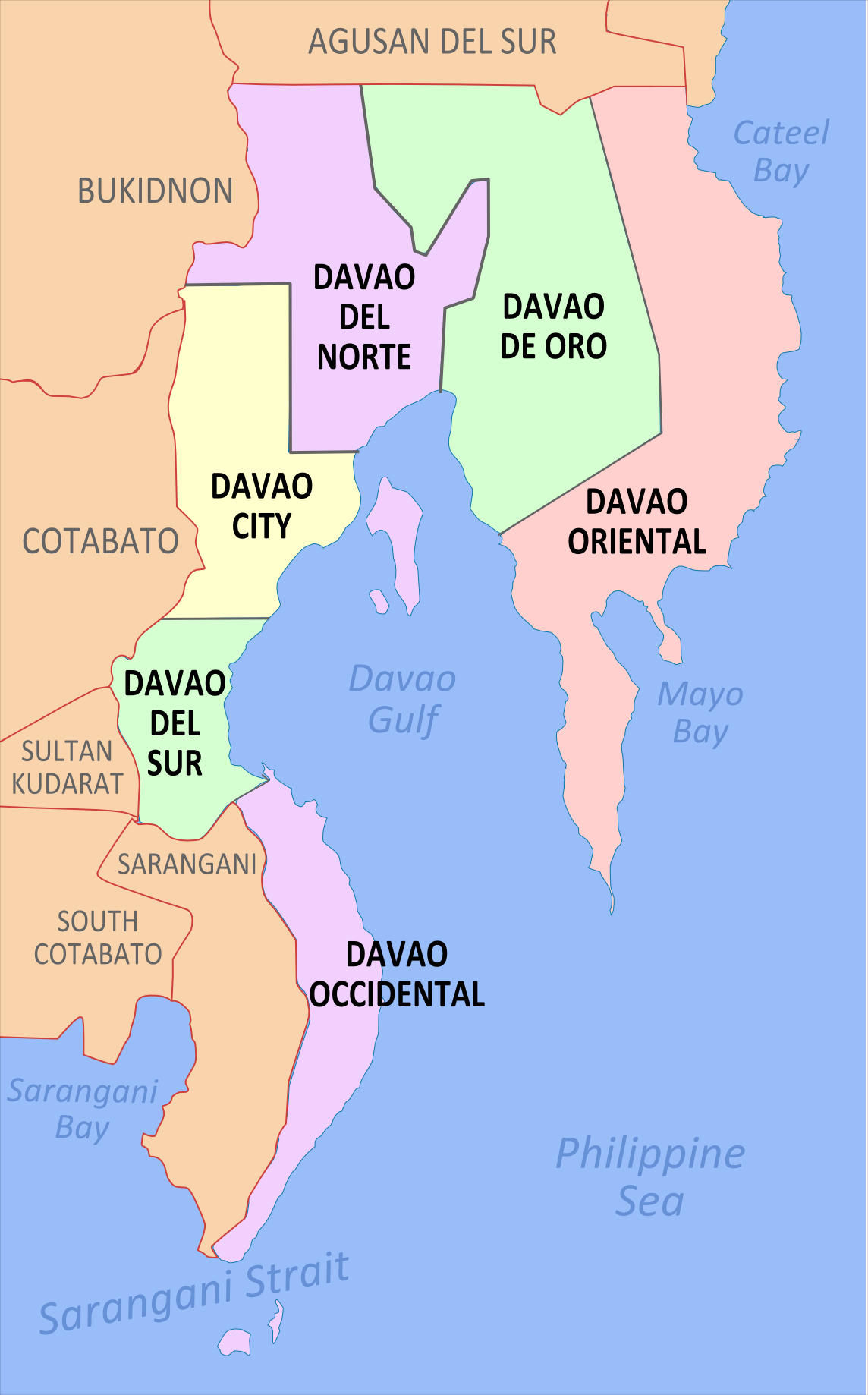
Davao Region
Davao Region, formerly called Southern Mindanao ( ceb, Rehiyon sa Davao; fil, Rehiyon ng Davao), is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region XI. It is situated at the southeastern portion of Mindanao and comprises five provinces: Davao de Oro, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Davao Oriental and Davao Occidental. The region encloses the Davao Gulf, and its regional center is Davao City. ''Dávao'' is the Hispanicized pronunciation of ''daba-daba'', the Bagobo word for "fire". Etymology Many historians believe that the name ''Davao'' is the mixture of the three names that three different tribes, the earliest settlers in the region, had for the Davao River. The Manobos, an aboriginal tribe, referred to the Davao Rivers as ''Davohoho''. Another tribe, the Bagobos, referred to the river as ''Davohaha'', which means "fire", while another tribe, the Guiangan tribe, called the river as ''Duhwow''. History The history of the region dates back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austronesian People
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austronesian languages. They also include indigenous ethnic minorities in Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand, Hainan, the Comoros, and the Torres Strait Islands. The nations and territories predominantly populated by Austronesian-speaking peoples are sometimes known collectively as Austronesia. Based on the current scientific consensus, they originated from a prehistoric seaborne migration, known as the Austronesian expansion, from pre- Han Taiwan, at around 1500 to 1000 BCE. Austronesians reached the northernmost Philippines, specifically the Batanes Islands, by around 2200 BCE. Austronesians used sails some time before 2000 BCE. In conjunction with their use of other maritime technologies (notably catamarans, outrigger boats, lashed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caraga
Caraga, officially the Caraga Administrative Region (or simply known as Caraga Region) and designated as Region XIII, is an administrative region in the Philippines occupying the northeastern section of Mindanao. The region was created through ''Republic Act No. 7901'' on February 23, 1995. The region comprises five provinces: Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Dinagat Islands, Surigao del Norte, and Surigao del Sur; six cities: Bayugan, Bislig, Butuan, Cabadbaran, Surigao and Tandag; 67 municipalities and 1,311 barangays. Butuan, the most urbanized city in Caraga, serves as the regional administrative center. Etymology Caraga is named after the Kalagan people ( Spanish "Caragan"), a Mansakan subgroup (related to Visayans) native to the regions of Davao and parts of Caraga who speak the Kalagan languages. The name itself is from ''kalagan'' (literally " trongspirited") which means "fierce" or "brave"; from ''kalag'' ("spirit" or "soul") in the native animistic ''anit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebuano Language
Cebuano (Cebuano on Merriam-Webster.com ), natively called by its generic term Bisaya or Binisaya (both translated into English as ''Visayan'', though this should not be confused with other Bisayan languages) and sometimes referred to in English sources as Cebuan ( ), is an Austronesian language spoken in the southern Philippines. It is spoken by the Visayan ethnolinguistic groups native to the islands of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austronesian Peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austronesian languages. They also include indigenous ethnic minorities in Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand, Hainan, the Comoros, and the Torres Strait Islands. The nations and territories predominantly populated by Austronesian-speaking peoples are sometimes known collectively as Austronesia. Based on the current scientific consensus, they originated from a prehistoric seaborne migration, known as the Austronesian expansion, from pre- Han Taiwan, at around 1500 to 1000 BCE. Austronesians reached the northernmost Philippines, specifically the Batanes Islands, by around 2200 BCE. Austronesians used sails some time before 2000 BCE. In conjunction with their use of other maritime technologies (notably catamarans, outrigger boats, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bajau People
The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah (formally A'a Sama, "Sama people"); or are known by the exonym Bajau (, also spelled Badjao, Bajaw, Badjau, Badjaw, Bajo or Bayao). They usually live a seaborne lifestyle and use small wooden sailing vessels such as the ''perahu'' (''layag'' in Meranau), '' djenging'' (''balutu''), '' lepa'', and '' vinta'' (''pilang''). Some Sama-Bajau groups native to Sabah are also known for their traditional horse culture. The Sama-Bajau are the dominant ethnic group of the islands of Tawi-Tawi in the Philippines. They are also found in other islands of the Sulu Archipelago, coastal areas of Mindanao, northern and eastern Borneo, Sulawesi, and throughout the eastern Indonesian islands. In the Philippines, they are grouped with the religiously similar Moro people. Within the last fifty years, many of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moro People
The Moro people or Bangsamoro people are the 13 Muslim-majority ethnolinguistic Austronesian groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan, native to the region known as the Bangsamoro (lit. ''Moro nation'' or ''Moro country''). As Muslim-majority ethnic groups, they form the largest non-Christian population in the Philippines, and comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people. Most Moros are followers of Sunni Islam of the Shafiʽi school of fiqh. The Moros were once independent under a variety of local states, including the Sultanate of Sulu, the Sultanate of Maguindanao, and the Confederation of sultanates in Lanao; withstanding repeated Spanish invasions, the Moro states remained de facto independent up until the Moro Rebellion of the early 20th century. Upon Philippine independence in 1946, the Moros continued their struggle for self-determination against a predominantly–Christian Philippines, culminating in a decades-long insurgency of armed re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visayans
Visayans ( Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group, they are both the most numerous in the entire country at around 33.5 million, as well as the most geographically widespread. The Visayans broadly share a maritime culture with strong Roman Catholic traditions integrated into a precolonial indigenous core through centuries of interaction and migration mainly across the Visayan, Sibuyan, Camotes, Bohol and Sulu seas. In more inland or otherwise secluded areas, ancient animistic-polytheistic beliefs and traditions either were reinterpreted within a Roman Catholic framework or syncretized with the new religion. Visayans are generally speakers of one or more of the Bisayan languages, the most widely spoken being Cebuano, followed by Hiligaynon (Ilonggo) and Waray-Waray. Terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or other Philippine languages. Currently, there are more than 185 ethnolinguistic groups in the Philippines; each with its own language, identity, culture and history. Names The name ''Filipino'', as a demonym, was derived from the term ''Las Islas Filipinas'' ("the Philippine Islands"), the name given to the archipelago in 1543 by the Spanish explorer and Dominican priest Ruy López de Villalobos, in honor of Philip II of Spain (Spanish: ''Felipe II''). During the Spanish colonial period, natives of the Philippine islands were usually known by the generic terms ''indio'' (" Indian") or ''indigenta'' ("indigents"). However, during the early Spanish colonial period the term ''Filipinos'' or ''Philipinos'' was sometimes used by Spanish wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)

.jpg)

