|
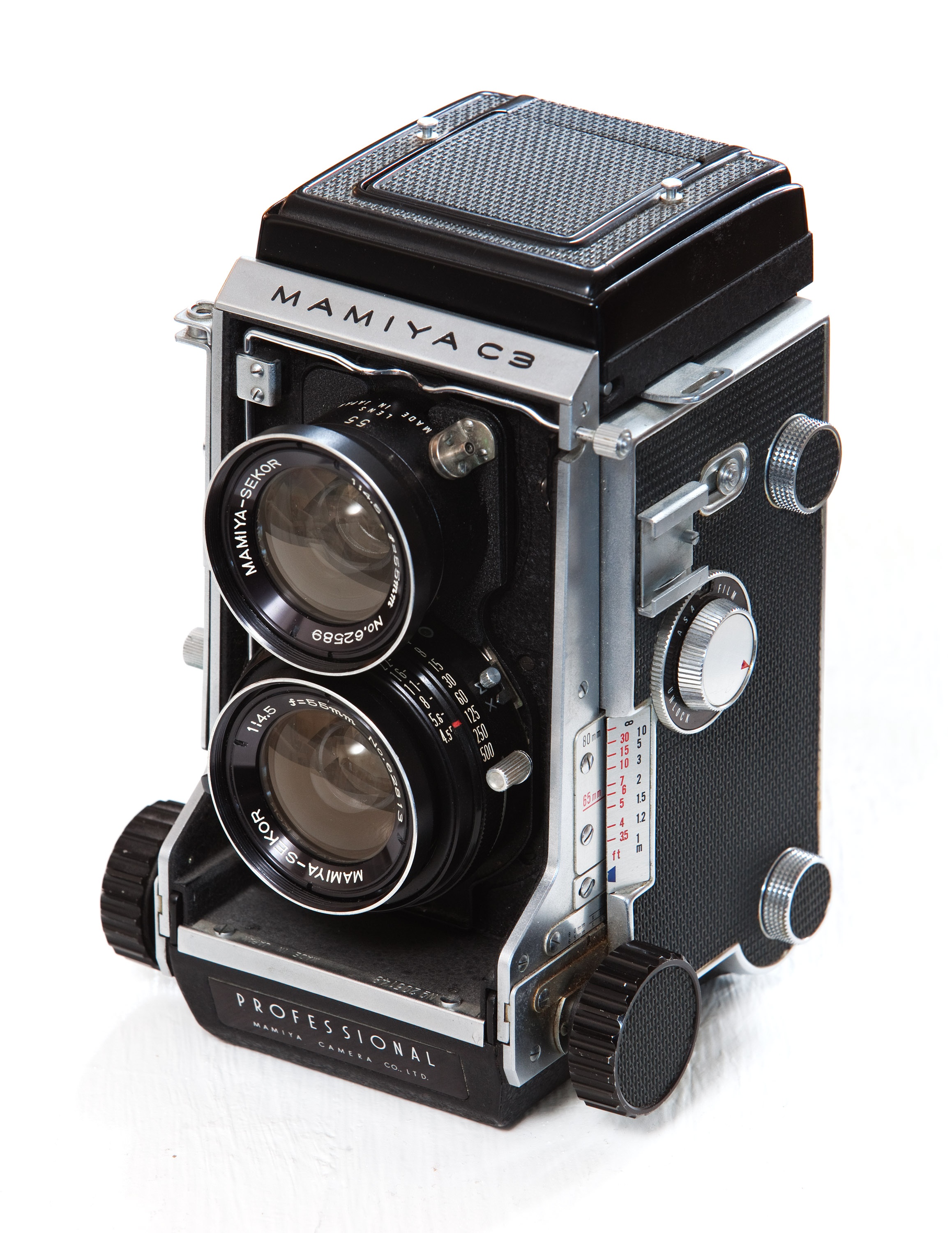
Mamiya C
The Mamiya C series is a line of twin-lens reflex medium-format system cameras manufactured by Mamiya between 1956 and 1994. It was developed from the Mamiyaflex series of cameras built from 1949 to 1956. The Mamiya C series was initially aimed at the professional market, but some later models were intended for amateurs. Common features Unlike most TLR cameras, the Mamiya C has interchangeable lenses. The upper and lower lenses come off as a unit, and are available in at least seven different focal lengths. The lower lens of each unit has an aperture diaphragm as well as a leaf shutter. A flash sync terminal is part of the lens unit, and the delay can be set to M or X mode. The camera has an interlocking baffle that enables lenses to be changed without exposing the film. Focusing is performed via a bellows system on the front side of the camera. Early models had separate film advance and shutter cocking mechanisms; on later models the shutter was automatically cocked as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamiya
is a Japanese company that manufactures high-end cameras and other related photographic and optical equipment. With headquarters in Tokyo, it has two manufacturing plants and a workforce of over 200 people. The company was founded in May 1940 by camera designer Seiichi Mamiya () and financial backer Tsunejiro Sugawara. History Mamiya originally achieved fame for its professional medium-format film cameras such as the Mamiya Six and the Mamiya Press series. It later developed the industry workhorse RB67 series, the RZ67, the 645 and the twin-lens reflex Mamiya C-series, used by advanced amateur and professional photographers. Many Mamiya models over the past six decades have become collectors' items. The earliest Mamiya Six medium-format folding camera, the 35 mm Mamiya-Sekor 1000DTL, the lightweight 35 mm Mamiya NC1000, the 6×6 cm medium-format C series of interchangeable-lens twin-lens reflex (TLR) cameras, and the press cameras of the Super/Universal seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seikosha
was a branch of the Japanese company Seiko that produced clocks, watches, shutters, computer printers and other devices. It was the root of the manufacturing companies of the Seiko Group. History *1881 — Kintarō Hattori opens the watch and jewelry shop " K. Hattori" (''Hattori Tokeiten'' in Japanese; currently named Seiko Holdings Corporation) in the Ginza area of Tokyo, Japan. *1892 — is established in Tokyo as the clock manufacturing arm of K. Hattori. *1917 — K. Hattori becomes a company (K. Hattori & Co., Ltd.). *1937 — The watch production division of Seikosha is split off as . *1942 — Daiwa Kogyo, Ltd. is founded in Suwa, Nagano by Hisao Yamazaki. *1943 — Daini Seikosha establishes a factory in Suwa for manufacturing watches with Daiwa Kogyo. *1959 — Daiwa Kogyo and the Suwa Plant of Daini Seikosha merge to form *1961 — Shinshu Seiki Co., Ltd. is established as a subsidiary of Suwa Seikosha. *1970 — Seikosha is sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mamiya Products
This is a list of products made by Mamiya, including cameras and lenses. Models made by Mamiya but marketed under other labels are shown in parentheses. Cameras 16 mm format * Mamiya 16 (1949) * Mamiya Super 16 (1953) * Mamiya Super 16 II (1957) * Mamiya Super 16 III (Tower 16) (1958) * Mamiya 16 Automatic (Revue 16 Automatic) (1959) * Mamiya 16 Deluxe (1961) * Mamiya 16 EE Deluxe (1962) 126 format * ( Argus 260 Automatic) (1964) * ( Keystone K1020) (1966) — fixed-lens single lens reflex 35 mm format Rangefinder * Mamiya 35 I (1949) * Mamiya 35 II (1955) * Mamiya 35 III (1957) * Mamiya Magazine 35 (1957) * Mamiya Wide (1957) * Mamiya Elca (1958) * Mamiya Crown (1958) * Mamiya Metra (1958) * Mamiya S (1958) * Mamiya Wide E (1959) * Mamiya Auto Metra (1959) * Mamiya Metra 2 (1959) * Mamiya Auto Metra 2 (1959) * Mamiya Sketch (1959) — square image format (24mm × 24mm) * Mamiya S2 (1959) * Mamiya Ruby (1959) * Mamiya Auto Deluxe (1960) * Mamiya Ruby Standard (1961) * Mamiy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Of Field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera. Factors affecting depth of field For cameras that can only focus on one object distance at a time, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus. "Acceptably sharp focus" is defined using a property called the "circle of confusion". The depth of field can be determined by focal length, distance to subject, the acceptable circle of confusion size, and aperture. Limitations of depth of field can sometimes be overcome with various techniques and equipment. The approximate depth of field can be given by: : \text \approx \frac for a given circle of confusion (c), focal length (f), f-number (N), and distance to subject (u). As distance or the size of the acceptable circle of confusion increases, the depth of field increases; however, increasing the size of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
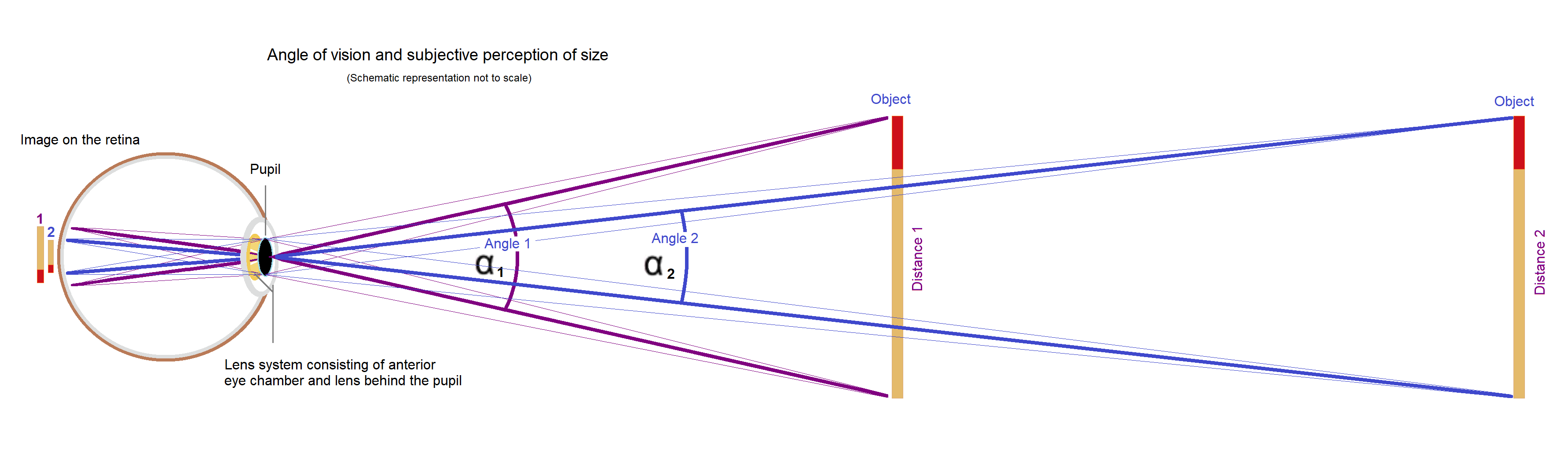
Angle Of View
The angle of view is the decisive variable for the visual perception of the size or projection of the size of an object. Angle of view and perception of size The perceived size of an object depends on the size of the image projected onto the retina. The size of the image depends on the angle of vision. A near and a far object can appear the same size if their edges produce the same angle of vision. With an optical device such as glasses or binoculars, microscope and telescope the angle of vision can be widened so that the object appears larger, which is favourable for the resolving power of the eye (see visual angle). Angle of view in photography In photography, angle of view (AOV) describes the angular extent of a given scene that is imaged by a camera. It is used interchangeably with the more general term field of view. It is important to distinguish the angle of view from the angle of coverage, which describes the angle range that a lens can image. Typically the image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. An optical system typically has many openings or structures that limit the ray bundles (ray bundles are also known as ''pencils'' of light). These structures may be the edge of a lens or mirror, or a ring or other fixture that holds an optical element in place, or may be a special element such as a diaphragm placed in the optical path to limit the light admitted by the system. In general, these structures are called stops, and the aperture stop is the stop that primarily determines the ray cone angle and brightness at the image point. In some contexts, especially in photography and astronomy, ''aperture'' refers to the diameter of the aperture stop rather than the physical stop or the opening itself. For example, in a telescope, the aperture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power. In most photography and all telescopy, where the subject is essentially infinitely far away, longer focal length (lower opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nidec Copal Corporation
The , or Copal, is a Japanese manufacturer of optical, electronic and mechanical equipment, primarily for the photographic industry. It has been a subsidiary of Nidec Corporation since 1998, and was formerly known as the Copal Corporation. The company began operation in 1946, with small-scale production of photographic shutters; these are still one of the company's best-known products. In the 1960s the company began producing the well-known Copal Square vertically travelling metal blade focal plane shutter, which was very successful and was used in cameras by many prominent manufacturers. The ''Copal Square-S'', for example used in the Konica T3s (1973-1978) and the Nikkormat FT, is very reliable. It works over a wide temperature range. The electronically controlled Copal ''Square E'' (1968) was used in the Yashica TL Electro X, the Canon EF, the Nikkormat EL. For Minolta XE and the Leica R3 the Copal-Leitz Shutter ''CLS'' was developed in 1972. For the professional Nikon F4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seiko
, commonly known as Seiko ( , ), is a Japanese maker of watches, clocks, electronic devices, semiconductors, jewelry, and optical products. Founded in 1881 by Kintarō Hattori in Tokyo, Seiko introduced one of the first quartz watches and the first quartz watch with a chronograph complication. Seiko was a wristwatch manufacturer for Japanese soldiers during World War II. History 1881 founding to 1929 In 1881, Seiko founder Kintarō Hattori opened a watch and jewelry shop called "K. Hattori" () in Tokyo. Kintarō Hattori had been working as clockmaker apprentice since the age of 13, with multiple stints in different watch shops, such as “Kobayashi Clock Shop”, ran by an expert technician named Seijiro Sakurai; “Kameda Clock Shop” in Nihonbashi; and “Sakata Clock Shop” in Ueno, where he learned how to both sell and repair timepieces. Around the time of Seiko's founding, watchmakers in Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya were studying and producing pocket watches based on Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamiya C330
The Mamiya C330 Professional is a traditional film twin-lens reflex camera introduced in the 1970s for the professional and advanced amateur photography markets. This model was 340 grams lighter than the previous model C33, which weighed 2040 grams (with 80 mm lens). The later C330f is an improvement on the C330 and was succeeded by the C330S with further improvements. * Uses 120 and 220 rollfilms * With the rack and pinion bellows type focusing system, close-up photography is possible without attachments. * Has a self-cocking one action 360° winding crank with a double exposure prevention device. Double exposure is also possible. The straight filmroll path has no right-angle turn and guarantees an absolutely flat film. * The backplate is changeable for single-exposure photography * Dimensions: 122 (w) × 168 (h) × 114 (d) * Weight: 1.7 kg (with standard lens) The Mamiya C-series cameras are one of the very few twin-lens reflex cameras with ''interchangeable lenses' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin-lens Reflex
A twin-lens reflex camera (TLR) is a type of camera with two objective lenses of the same focal length. One of the lenses is the photographic objective or "taking lens" (the lens that takes the picture), while the other is used for the viewfinder system, which is usually viewed from above at waist level. In addition to the objective, the viewfinder consists of a 45-degree mirror (the reason for the word ''reflex'' in the name), a matte focusing screen at the top of the camera, and a pop-up hood surrounding it. The two objectives are connected, so that the focus shown on the focusing screen will be exactly the same as on the film. However, many inexpensive 'pseudo' TLRs are fixed-focus models. Most TLRs use leaf shutters with shutter speeds up to 1/500 of a second with a bulb setting. For practical purposes, all TLRs are film cameras, most often using 120 film, although there are many examples which used 620 film, 127 film, and 35 mm film. Few general-purpose digital TLR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamiya C220
The Mamiya C220 is a lightweight twin-lens reflex camera made in the early 1970s by the Japanese camera manufacturer Mamiya. The camera has interchangeable lenses ranging from 55 mm wide-angle to 250 mm telephoto and accepts 120 and 220 rollfilms. The rack and pinion focusing system with a bellows makes it possible for close-up photography without attachments. The straight film path has no sharp turns for absolute flatness of the film. Variations of the Mamiya TLR line from the Mamiyaflex to the C330S Professional continued the evolution of the TLR camera with the final TLR, the c330S Pro. Changeable lenses on medium format SLR and rangefinder cameras such as the Hasselblad line or Koni-Omega Press were the norm. The Mamiya twin lens reflex cameras are among the very few medium-format TLR cameras with interchangeable lenses. * Dimensions: 118 mm (w) x 167 mm (h) x 113 mm (d) * Weight: 1.44 kg Lenses There are seven Mamiya Sekor lenses: ; 2 wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)