|
Majduddin
Majd ad-Dīn al-Madanī ( ar, ; d. 1813), also known as Madan Shāhjahānpūrī ( ar, ), was an 18th-century Indian Muslim theologian. He served as the first principal of the Aliah University, Calcutta Madrasa, the first Alia Madrasah Education Board, Alia Madrasa of Bengal. Early life and education Majduddin was born in the 18th-century to Tahir al-Husayni in Shahjahanpur district, Shahjahanpur, Bareilly division, greater Bareilly, North India. He studied under Shaykh Wahhaj ad-Din Gupamawi, Wahhaj ad-Din in Gopamau, Hardoi district, Hardoi, who was also the teacher of Muhammad Salih Bengali, It ialso said that Majduddin was a student of Qazi Mubarak, as well as being a senior student of Shah Waliullah Dehlawi, the erstwhile ''Imam al-India, Hind''. In addition to Islamic jurisprudence, Majduddin was trained in rhetoric and logic. Career In the last quarter of the 18th century, British administrators realised that it was essential to learn the various religious, social, and leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliah University
Aliah University (AU; ur, جامعہ عالیہ) is a state government controlled autonomous university in New Town, West Bengal, India. Previously known as Mohammedan College of Calcutta, it was elevated to university in 2008. It offers undergraduate and postgraduate programs in different Engineering, Arts, Science, Management and Nursing subjects. History The Aliah University (AU) is one of the oldest modern-style educational institutes in Asia, and first in India. It was set up in October 1780 by Warren Hastings, the British Governor general of East India Company near Sealdah in Calcutta. A number of titles were used for it, such as Islamic College of Calcutta, Calcutta Madrasah, Calcutta Mohammedan College and Madrasah-e-Aliah. Of these, Calcutta Mohammedan College was that used by Warren Hastings. The original building was completed in 1782 at Bow Bazaar (near Sealdah). The college moved to its campus on Wellesley Square in the 1820s. Initially it taught natural philoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahjahanpur District
Shahjahanpur district is a districts of Uttar Pradesh India. It is a part of Bareilly division. It was established in 1813 by the British Government. Previously it was a part of district Bareilly. Geographically the main town is Shahjahanpur which is its headquarters. Its 4 Tehsils are: Powayan, Tilhar, Jalalabad and Sadar. History Very little is known about the early history of this region. There are prominent ruins at Mati, Nigohi, and Gola Raipur. The area covered by Shahjahanpur district was likely part of the ancient kingdom of Ahichhatra, which is supported by numerous Ahichhatra coins found at Mati, which appears to have been an important city in ancient times. For a long time, tradition holds that this area was ruled by indigenous groups like the Gujars, the Ahirs, the Pasis, the Arakhs, the Bhihars, and the Bhils. Their rule appears to have been supplanted by the Rajputs and Muslims later than other places in the region. During the middle ages, Shahjahanpur di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Waliullah
Quṭb-ud-Dīn Aḥmad Walīullāh Ibn ʿAbd-ur-Raḥīm Ibn Wajīh-ud-Dīn Ibn Muʿaẓẓam Ibn Manṣūr Al-ʿUmarī Ad-Dehlawī ( ar, ; 1703–1762), commonly known as Shāh Walīullāh Dehlawī (also Shah Wali Allah), was an Islamic scholar seen by his followers as a renewer. Early life Shah Waliullah was born on 21 February 1703 to Shah Abdur Rahim, a prominent Islamic scholar of Delhi. He was known as Shah Waliullah because of his piety. He memorized the ''Qur'an'' by the age of seven. Soon thereafter, he mastered Arabic and Persian letters. He was married at fourteen. By sixteen he had completed the standard curriculum of Hanafi law, theology, geometry, arithmetic and logic. His father, Shah Abdur Rahim was the founder of the Madrasah-i Rahimiyah. He was on the committee appointed by Aurangzeb for compilation of the code of law, Fatawa-e-Alamgiri. Death He died on Friday the 29th of Muharram 1176 AH/ 20 August 1762 at Zuhr prayer in Old Delhi, aged 59. He was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alia Madrasah Education Board
Bangladesh Madrasah Education Board ( bn, বাংলাদেশ মাদ্রাসা শিক্ষা বোর্ড) or Alia Madrasah Education Board started its activity independently in 1979. With the passage of time in Bangladeshi madrasah education several amendments have come to pass. In 1978 humanities and science faculties were included at the ''Alim'' () level. In 1980 ''Fazil'' () degrees were granted the same standard of education as Higher Secondary School Certificate (HSC) degrees but this was changed in later years with ''Dakhil'' () level having the equivalency of Secondary School Certificate (SSC) since 1985, and ''Alim'' being considered as the HSC equivalent since 1987. Humanities, science, business and technical education has been included with madrasah education. Meanwhile, a law has been passed for ''Fazil'' and ''Kamil'' () levels to be considered equivalent with bachelor's and master's degrees in general education. Background Alia Madrasah Edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Salih Bengali
Shaykh Muhammad Salih Bengali ( bn, মুহম্মদ সালেহ বাঙ্গালী, fa, ) was an 18th-century Islamic scholar and teacher from Bengal. He is mentioned in the works of Abd al-Hayy al-Lucknawi and Muhammad Ishaq Bhatti, where he is described as one of the leading scholars in the fields of Islamic jurisprudence, its principles, ''hikmah'', ''kalam'' and logic. Biography Muhammad Salih originated from Bengal, hence the suffix ''Bengali'' is found attached to his name in historical literary works. He studied the Islamic sciences under Shihab ad-Din, the Qadi of Gopamau, in Hindustan. After that, he joined the halaqa of Mir Zahid Harawi (d. 1689) who was one of the teachers of Shah Abdur Rahim that was serving as a ''Qadi'' at the Mughal imperial court. He benefitted a lot from this teacher. Thereafter, Salih became a teacher of Islamic studies himself. Among his many students was Qutb ad-Din, the son of his former teacher Shihab ad-Din, who also bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Waliullah Dehlawi
Quṭb-ud-Dīn Aḥmad Walīullāh Ibn ʿAbd-ur-Raḥīm Ibn Wajīh-ud-Dīn Ibn Muʿaẓẓam Ibn Manṣūr Al-ʿUmarī Ad-Dehlawī ( ar, ; 1703–1762), commonly known as Shāh Walīullāh Dehlawī (also Shah Wali Allah), was an Islamic scholar seen by his followers as a renewer. Early life Shah Waliullah was born on 21 February 1703 to Shah Abdur Rahim, a prominent Islamic scholar of Delhi. He was known as Shah Waliullah because of his piety. He memorized the ''Qur'an'' by the age of seven. Soon thereafter, he mastered Arabic and Persian letters. He was married at fourteen. By sixteen he had completed the standard curriculum of Hanafi law, theology, geometry, arithmetic and logic. His father, Shah Abdur Rahim was the founder of the Madrasah-i Rahimiyah. He was on the committee appointed by Aurangzeb for compilation of the code of law, Fatawa-e-Alamgiri. Death He died on Friday the 29th of Muharram 1176 AH/ 20 August 1762 at Zuhr prayer in Old Delhi, aged 59. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide religious guidance. Thus for Sunnis, anyone can study the basic Islamic sciences and become an Imam. For most Shia Muslims, the Imams are absolute infallible leaders of the Islamic community after the Prophet. Shias consider the term to be only applicable to the members and descendents of the '' Ahl al-Bayt'', the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Twelver Shiasm there are 14 infallibles, 12 of which are Imams, the final being Imam Mahdi who will return at the end of times. The title was also used by the Zaidi Shia Imams of Yemen, who eventually founded the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen (1918–1970). Sunni imams Sunni Islam does not have imams in the same sense as the Shi'a, an importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mullah
Mullah (; ) is an honorific title for Shia and Sunni Muslim clergy or a Muslim mosque leader. The term is also sometimes used for a person who has higher education in Islamic theology and sharia law. The title has also been used in some Mizrahi and Sephardic Jewish communities to refer to the community's leadership, especially religious leadership. Etymology The word ''mullah'' is derived from the Arabic word ''mawlā'' ( ar, مَوْلَى), meaning "vicar", "master" and "guardian". Usage Historical usage The term has also been used among Persian Jews, Bukharan Jews, Afghan Jews, and other Central Asian Jews to refer to the community's religious and/or secular leadership. In Kaifeng, China, the historic Chinese Jews who managed the synagogue were called "mullahs". Modern usage It is the term commonly used for village or neighborhood mosque leaders, who may not have high levels of religious education, in large parts of the Muslim world, particularly Iran, Turkey, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
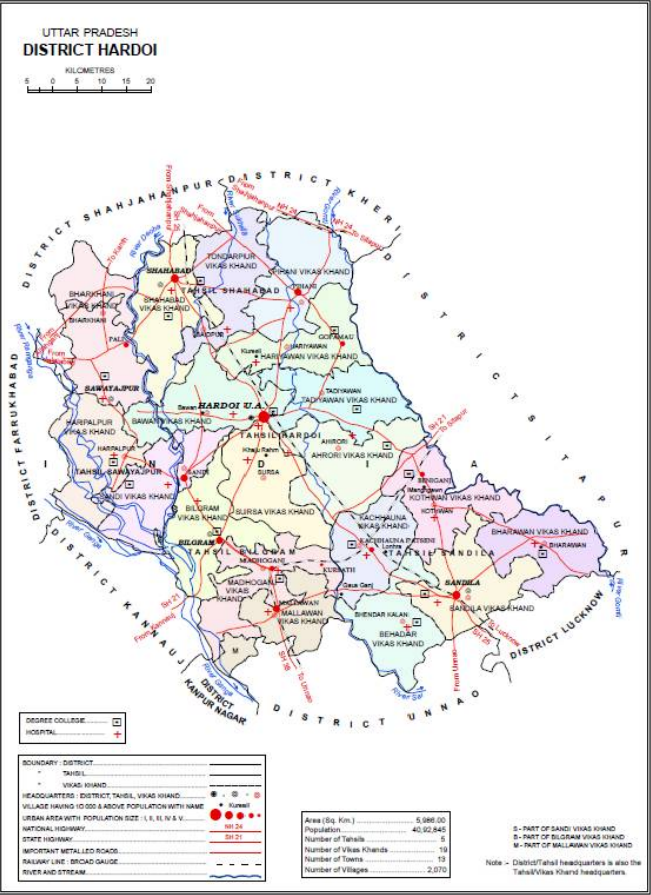
Hardoi District
Hardoi district is a district situated in the center of Uttar Pradesh, India. The district headquarters is in the city of Hardoi. Hardoi is the third largest district of Uttar Pradesh. It falls under Lucknow division in the history region of Awadh As of the 2011 census, the total population of Hardoi district is 4,092,845 people, in 730,442 households. It is the 13th-most populous district in Uttar Pradesh. History The present-day Hardoi district was created by the British after their takeover of Awadh in 1856. At the time of Akbar in the 1500s, the area of the modern district was divided between the sarkars of Lucknow and Khairabad. Five ''mahal''s were in Lucknow sarkar: Sandila, Mallanwan, Kachhandao, "Garanda" (probably a miscopying of Gundwa), and Bilgram. The Ain-i-Akbari does list a mahal of Hardoi in Lucknow district, but this was referring to the Hardoi in modern Rae Bareli district instead of the one in Hardoi district. As for the sarkar of Khairabad, the mahals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate particular audiences in specific situations. Aristotle defines rhetoric as "the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion" and since mastery of the art was necessary for victory in a case at law, for passage of proposals in the assembly, or for fame as a speaker in civic ceremonies, he calls it "a combination of the science of logic and of the ethical branch of politics". Rhetoric typically provides heuristics for understanding, discovering, and developing arguments for particular situations, such as Aristotle's three persuasive audience appeals: logos, pathos, and ethos. The five canons of rhetoric or phases of developing a persuasive speech were first codified in classical Rome: invention, arrangement, style ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka."Indian subcontinent". ''New Oxford Dictionary of English'' () New York: Oxford University Press, 2001; p. 929: "the part of Asia south of the Himalayas which forms a peninsula extending into the Indian Ocean, between the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Historically forming the whole territory of Greater India, the region is now divided into three countries named Bangladesh, India and Pakistan." The terms ''Indian subcontinent'' and ''South Asia'' are often used interchangeably to denote the region, although the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanistan, which may otherwise be classified as Central Asian.John McLeod, The history of India', page 1, Greenwood Publishing Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)