|
Maip
''Maip'' is a genus of large megaraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, ''M. macrothorax'', known from an incomplete, disarticulated skeleton. ''Maip'' may represent the largest megaraptorid known from South America, and possibly the world. Discovery and naming The ''Maip'' holotype specimen, MPM 21545, was discovered by Alexis Rolando on the La Anita Farm, west of El Calafate, Santa Cruz province, Argentina, in 2019. The specimen was found disarticulated but in association over an area of . The known fossil material consists of the axis, several dorsal and caudal vertebrae, cervical and dorsal ribs, gastralia, a left coracoid, fragmentary scapula, partial right pubis, and partial metatarsal. Some of these bones were described in 2019 by Novas ''et al''. The holotype specimen includes some bones previously unknown in other megaraptorids. Although fragmentary, it r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maip Size Comparison
''Maip'' is a genus of large megaraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, ''M. macrothorax'', known from an incomplete, disarticulated skeleton. ''Maip'' may represent the largest megaraptorid known from South America, and possibly the world. Discovery and naming The ''Maip'' holotype specimen, MPM 21545, was discovered by Alexis Rolando on the La Anita Farm, west of El Calafate, Santa Cruz province, Argentina, in 2019. The specimen was found disarticulated but in association over an area of . The known fossil material consists of the axis, several dorsal and caudal vertebrae, cervical and dorsal ribs, gastralia, a left coracoid, fragmentary scapula, partial right pubis, and partial metatarsal. Some of these bones were described in 2019 by Novas ''et al''. The holotype specimen includes some bones previously unknown in other megaraptorids. Although fragmentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaraptora
Megaraptora is a clade of carnivorous Tetanurae, tetanuran theropod dinosaurs with controversial relations to other theropods. Its Derived (phylogenetics), derived members, the Megaraptoridae are noted for their elongated hand claws and proportionally large arms, which are usually reduced in size in other large theropods. Megaraptorans are incompletely known, and no complete megaraptoran skeleton has been found. However, they still possessed a number of unique features. Their forelimbs were large and strongly built, and the Glossary of dinosaur anatomy#ulna, ulna bone had a unique shape in members of the Family (biology), family Megaraptoridae, a subset of megaraptorans which excludes ''Fukuiraptor'' and ''Phuwiangvenator''. The first two fingers were elongated, with massive curved claws, while the third finger was small. Megaraptoran skull material is very incomplete, but a juvenile ''Megaraptor'' described in 2014 preserved a portion of the snout, which was long and slender. Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2022 In Archosaur Paleontology
This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that are scheduled described during the year 2022, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that are scheduled to occur in the year 2022. Pseudosuchians New pseudosuchian taxa General pseudosuchian research * A study on the mandible embryogenesis in extant caimans, and on its implications for the knowledge of the evolution of postdentary lower jaw of pseudosuchians, is published by Bona ''et al.'' (2022). * A study on the musculature of crocodylian and fossil suchian jaws, investigating the impact of the flattening of the skulls of suchians in their evolutionary history on their muscle anatomy, is published by Sellers ''et al.'' (2022). * Revision of ''Tsylmosuchus donensis'' and ''Scythosuchus basileus'' is published by Sennikov (2022), who interprets the latter taxon as a junior synonym of the former one, and interprets ''T. donensis'' as a likely member of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorrillo Formation
The Chorrillo Formation, also named as Chorillo Formation, at Fossilworks.org is a geologic in southern , . The formation is more than thick and underlies the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubis (bone)
In vertebrates, the pubic region ( la, pubis) is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic region is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat, which is covered by the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubic region is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic region. The bodies of the left and right pubic regions join at the pubic symphysis. The rough upper edge is the pubic crest, ending laterally in the pubic tubercle. This tubercle, found roughly 3 cm from the pubic symphysis, is a distinctive feature on the lower part of the abdominal wall; important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsal Bones
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side (the side of the great toe): the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal (often depicted with Roman numerals). The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. Structure The five metatarsals are dorsal convex long bones consisting of a shaft or body, a base (proximally), and a head (distally).Platzer 2004, p. 220 The body is prismoid in form, tapers gradually from the tarsal to the phalangeal extremity, and is curved longitudinally, so as to be concave below, slightly convex above. The base or posterior extremity is wedge-shaped, articulating proximally with the tarsal bones, and by its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preprint
In academic publishing, a preprint is a version of a scholarly or scientific paper that precedes formal peer review and publication in a peer-reviewed scholarly or scientific journal. The preprint may be available, often as a non-typeset version available free, before or after a paper is published in a journal. History Since 1991, preprints have increasingly been distributed electronically on the Internet, rather than as paper copies. This has given rise to massive preprint databases such as arXiv and HAL (open archive) etc. to institutional repositories. The sharing of preprints goes back to at least the 1960s, when the National Institutes of Health circulated biological preprints. After six years the use of these Information Exchange Groups was stopped, partially because journals stopped accepting submissions shared via these channels. In 2017, the Medical Research Council started supporting citations of preprints in grant and fellowship applications, and Wellcome Trust star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Code Of Zoological Nomenclature
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (which shares the acronym "ICZN"). The rules principally regulate: * How names are correctly established in the frame of binominal nomenclature * Which name must be used in case of name conflicts * How scientific literature must cite names Zoological nomenclature is independent of other systems of nomenclature, for example botanical nomenclature. This implies that animals can have the same generic names as plants (e.g. there is a genus ''Abronia'' in both animals and plants). The rules and recommendations have one fundamental aim: to provide the maximum universality and continuity in the naming of all animals, except where taxonomic judgment dictates otherwise. The code is meant to guid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
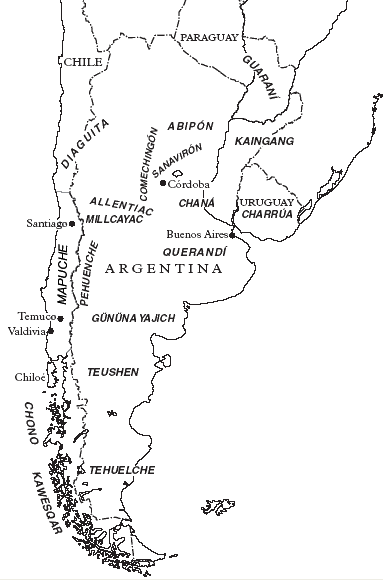
Tehuelche People
The Tehuelche people, also called the Aónikenk, are an indigenous people from eastern Patagonia in South America. In the 18th and 19th centuries the Tehuelche were influenced by Mapuche people, and many adopted a horseriding lifestyle. Once a nomadic people the lands of the Tehuelche were colonized in the 19th century by Argentina and Chile gradually disrupting their traditional economies. The establishment of large sheep farming estates in Patagonia was particularly detrimental to the Tehuelche. Contact with outsiders also brought in infectious diseases ushering deadly epidemics among Tehuelche tribes. Most existing members of the group currently reside the in cities and towns of Argentine Patagonia. The name "Tehuelche complex" has been used by researchers in a broad sense to group together indigenous peoples from Patagonia and the Pampas. Several specialists, missionaries and travelers have proposed grouping them together on account of the similarities in their cultural tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |