|
Maginot Line
The Maginot Line (french: Ligne Maginot, ), named after the French Minister of War André Maginot, is a line of concrete fortifications, obstacles and weapon installations built by France in the 1930s to deter invasion by Germany and force them to move around the fortifications. The Maginot Line was impervious to most forms of attack. In consequence, the Germans invaded through the Low Countries in 1940, passing it to the north. The line, which was supposed to be fully extended further towards the west to avoid such an occurrence, was finally scaled back in response to demands from Belgium. Indeed, Belgium feared it would be sacrificed in the event of another German invasion. The line has since become a metaphor for expensive efforts that offer a false sense of security. Constructed on the French side of its borders with Italy, Switzerland, Germany, Luxembourg and Belgium, the line did not extend to the English Channel. French strategy therefore envisioned a move into Belgium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouvrage Schoenenbourg
Ouvrage Schoenenbourg is a Maginot Line fortification. It is located on the territory of the communes of Hunspach, Schœnenbourg and Ingolsheim, in the French ''département'' of Bas-Rhin, forming part of the Fortified Sector of Haguenau, facing Germany. At the east end of the Alsace portion of the Maginot Line, its neighbour is the ''gros ouvrage'' Ouvrage Hochwald, Hochwald. It is the largest such fortification open to the public in Alsace. Officially recorded as an historical monument, it retains all its original structural elements. Schoenenbourg was heavily bombarded during the Battle of France in 1940, receiving more enemy ordnance than any other position in France, with no significant damage. In 1945, retreating German troops used explosives to destroy much of the ''ouvrage''. After the war it was fully repaired and placed back into service as part of a programme to use Maginot fortifications to resist a potential Warsaw Pact advance through Europe. By the 1970s the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or (Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kanaal, "The Channel"; german: Ärmelkanal, "Sleeve Channel" (French: ''la Manche;'' also called the British Channel or simply the Channel) is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel was a key factor in Britain becoming a naval superpower and has been utilised by Britain as a natural d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moselle (department)
Moselle () is the most populous department in Lorraine, in the east of France, and is named after the river Moselle, a tributary of the Rhine, which flows through the western part of the department. It had a population of 1,046,543 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 57 Moselle INSEE Inhabitants of the department are known as ''Mosellans''. History 
 On March 4, 1790, Moselle became one of t ...
On March 4, 1790, Moselle became one of t ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitche
Bitche ( , ; German and Lorraine Franconian: ) is a commune in the Moselle department, administrative region of Grand Est, northeastern France. It is the Pays de Bitche's capital city and the seat of the Canton of Bitche and the communauté de communes du Pays de Bitche. The town belongs to the Northern Vosges Regional Nature Park and is rated 4-flowers at the towns and villages in bloom competition. The town's population at the 2013 census was 5,225. The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Bitchois'' and ''Bitchoises''. The town is known for its large citadel originating from a castle built at the beginning of the 13th century. The fortress is noted for its resistance during the Franco-Prussian War. Louis-Casimir Teyssier, its commander and chief, held the place for about eight months with 3,000 men against about 20,000 Prussian and Bavarian soldiers until the French government ordered him to surrender after the ceasefire in 1871. The town became part of German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barracks
Barracks are usually a group of long buildings built to house military personnel or laborers. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word "barraca" ("soldier's tent"), but today barracks are usually permanent buildings for military accommodation. The word may apply to separate housing blocks or to complete complexes, and the plural form often refers to a single structure and may be singular in construction. The main object of barracks is to separate soldiers from the civilian population and reinforce discipline, training, and ''esprit de corps''. They have been called "discipline factories for soldiers". Like industrial factories, some are considered to be shoddy or dull buildings, although others are known for their magnificent architecture such as Collins Barracks in Dublin and others in Paris, Berlin, Madrid, Vienna, or London. From the rough barracks of 19th-century conscript armies, filled with hazing and illness and ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorraine (province)
The Duchy of Lorraine (french: Lorraine ; german: Lothringen ), originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy. It was founded in 959 following the division of Lotharingia into two separate duchies: Upper and Lower Lorraine, the westernmost parts of the Holy Roman Empire. The Lower duchy was quickly dismantled, while Upper Lorraine came to be known as simply the Duchy of Lorraine. The Duchy of Lorraine was coveted and briefly occupied by the dukes of Burgundy and the kings of France. In 1737, the duchy was given to Stanisław Leszczyński, the former king of Poland, who had lost his throne as a result of the War of the Polish Succession, with the understanding that it would fall to the French crown on his death. When Stanisław died on 23 February 1766, Lorraine was annexed by France and reorganized as a province. History Lotharingia Lorraine's predecessor, Lotharingia, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkirk Evacuation
The Dunkirk evacuation, codenamed Operation Dynamo and also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, or just Dunkirk, was the evacuation of more than 338,000 Allied soldiers during the Second World War from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, in the north of France, between 26 May and 4 June 1940. The operation commenced after large numbers of Belgian, British, and French troops were cut off and surrounded by German troops during the six-week Battle of France. In a speech to the House of Commons, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill called this "a colossal military disaster", saying "the whole root and core and brain of the British Army" had been stranded at Dunkirk and seemed about to perish or be captured. In his " We shall fight on the beaches" speech on 4 June, he hailed their rescue as a "miracle of deliverance". After Germany invaded Poland in September 1939, France and the British Empire declared war on Germany and imposed an economic blockade. The British Expediti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of . History From 1301 the upper Meuse roughly marked the western border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Kingdom of France, after Count Henry III of Bar had to receive the western part of the County of Bar (''Barrois mouvant'') as a French fief from the hands of King Philip IV. In 1408, a Burgundian army led by John the Fearless went to the aid of John III against the citizens of Liège, who were in open revolt. After the battle which saw the men from Liège defeated, John ordered the drowning in the Meuse of suspicious burghers and noblemen in Liège. The border remained stable until the annexation of the Three Bishoprics Metz, Toul and Verdun by King Henry II in 1552 and the occupation of the Duchy of Lorraine b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manstein Plan
(Case Yellow), the invasion of France and the Low Countries , scope = Strategic , type = , location = South-west Netherlands, central Belgium, northern France , coordinates = , planned = 1940 , planned_by = Erich von Manstein , commanded_by = Gerd von Rundstedt , objective = Defeat of the Netherlands, Belgium and France , target = , date = , time = , time-begin = , time-end = , timezone = , executed_by = Army Group A , outcome = German victory , casualties = , fatalities = , injuries = The Manstein Plan or Case Yellow (german: Fall Gelb) also known as Operation Sichelschnitt (german: Sichelschnittplan, from the English term sickle cut), was the war plan of the German armed forces (german: Wehrmacht) during the Battle of France in 1940. The original invasion plan was an awkward compromise devised by General Franz Halder, the chief of staff of (OKH, Army High Command) that satisfied no one. Documents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French War Planning 1920–1940
The Dyle Plan or Plan D was the plan of the Commander-in-Chief of the French Army, Maurice Gamelin, to defeat a German attempt to invade France through Belgium. The Dyle (Dijle) river is long, from Houtain-le-Val through Flemish Brabant and Antwerp; Gamelin intended French, British and Belgian troops to halt a German invasion force along the line of the river. The Franco-Belgian Accord of 1920 had co-ordinated communication and fortification efforts of both armies. After the German Remilitarization of the Rhineland on 7 March 1936, the Belgian government abrogated the accord and substituted a policy of strict neutrality, now that the German Army () was on the German–Belgian border. French doubts about the Belgian Army led to uncertainty about whether French troops could move fast enough into Belgium to avoid an encounter battle and fight a defensive battle from prepared positions. The Escaut Plan/Plan E and Dyle Plan/Plan D were devised for a forward defence in Belgium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice Gamelin
Maurice Gustave Gamelin (, 20 September 1872 – 18 April 1958) was an army general in the French Army. Gamelin is remembered for his disastrous command (until 17 May 1940) of the French military during the Battle of France (10 May–22 June 1940) in World War II and his steadfast defence of republican values. The Commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces at the start of World War II, Gamelin was viewed as a man with significant intellectual ability. He was respected, even in Germany, for his intelligence and "subtle mind", though he was viewed by some German generals as stiff and predictable. Despite this, and his competent service in World War I, his command of the French armies during the critical days of May 1940 proved to be disastrous. Historian and journalist William L. Shirer presented the view that Gamelin used World War I methods to fight World War II, but with less vigor and slower response. Gamelin served with distinction under Joseph Joffre in World War I. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
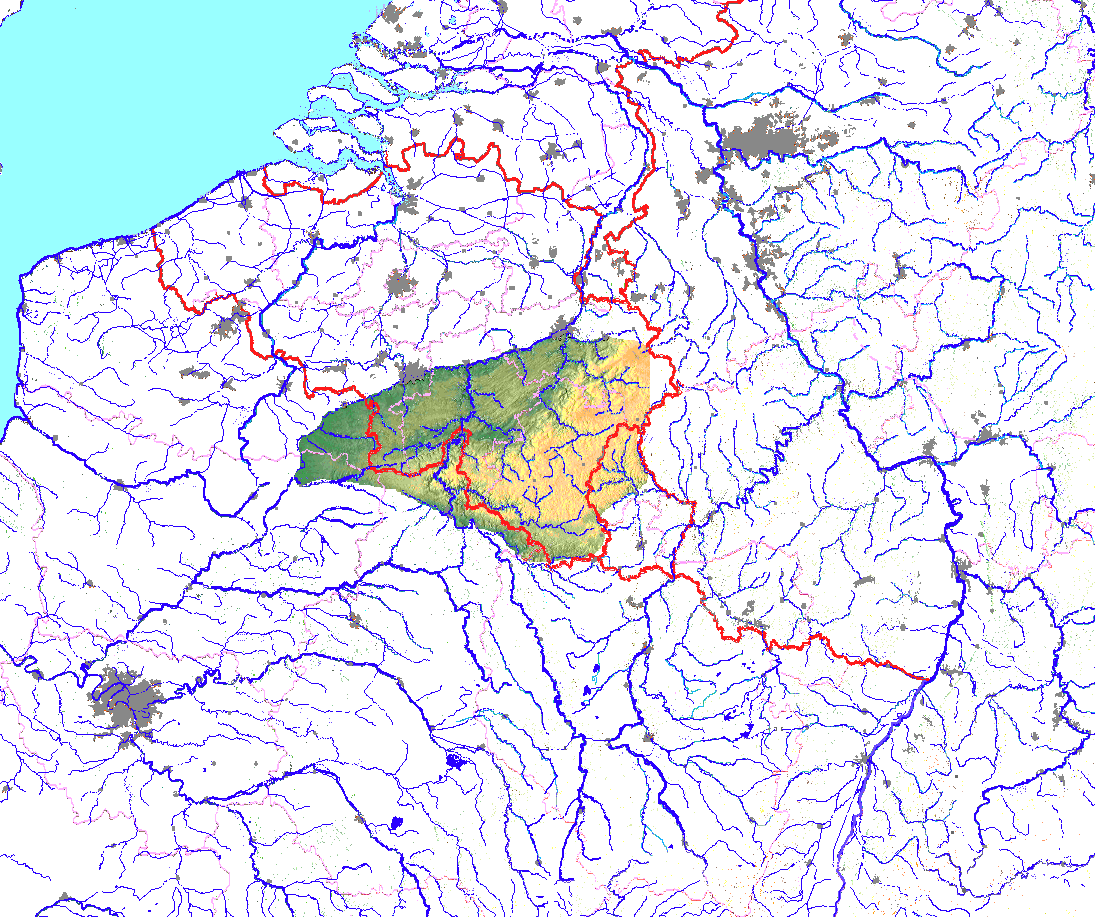
Ardennes
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, extending into Germany and France. Geologically, the range is a western extension of the Eifel; both were raised during the Givetian age of the Devonian (382.7 to 387.7 million years ago), as were several other named ranges of the same greater range. The Ardennes proper stretches well into Germany and France (lending its name to the Ardennes department and the former Champagne-Ardenne region) and geologically into the Eifel (the eastern extension of the Ardennes Forest into Bitburg-Prüm, Germany); most of it is in the southeast of Wallonia, the southern and more rural part of Belgium (away from the coastal plain but encompassing more than half of the country's total area). The eastern part of the Ardennes forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)