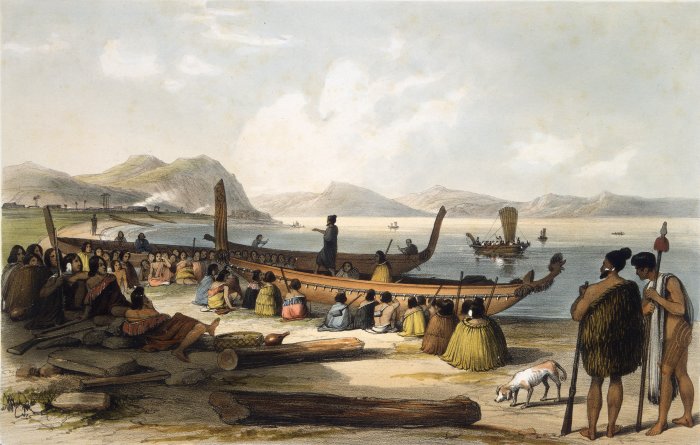|
Mackaytown
Mackaytown is a settlement in the Hauraki District and Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island, located at the north-western end of the Karangahake Gorge just south of Paeroa. It is named after local Government administrator and politician James Mackay. The settlement consists of eight roads branching off State Highway 2. It is bordered by Turner's Hill, Doherty's Creek, Ohinemuri River, and the sacred Tapu Ariki burial grounds on Te Moananui's Hill. History Pre-European history The Ohinemuri River is within the ''rohe'' (traditional tribal area) of Ngāti Hako and Ngāti Tara Tokanui. Ohinemuri is a Māori word, meaning "the girl left behind", referring to a legend about a chief's daughter who was detained by a taniwha at Turner's Hill. Early Māori settlers travelled the area extensively, mostly by waka, but also by crossing the forest and stream fords on foot. Missionary Samuel Marsden was across the river, when passing through the area on his way from Thames to Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hauraki District
Hauraki District is a territorial authority within the Hauraki region of New Zealand. The seat of the council is at Paeroa. The area covered by the district extends from the southwest coast of the Firth of Thames southeast towards Te Aroha, although that town lies beyond its boundaries. It extends eastwards to the Bay of Plenty coast, taking in the southernmost part of the Coromandel Peninsula. The rest of the peninsula is part of Thames-Coromandel District. Features of the district include the Karangahake Gorge, Whiritoa, the Hauraki Plains, Ngatea and the gold mining town of Waihi. Demographics Hauraki District covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. live in Paeroa and in Waihi. Hauraki District had a population of 20,022 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 2,214 people (12.4%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 2,166 people (12.1%) since the 2006 census. There were 7,869 households, comprising 9,8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohinemuri River
The Ohinemuri River is located in the northern half of New Zealand's North Island, at the base of the Coromandel Peninsula. The river's source is north-east of the town of Waihi, close to the shore of the Bay of Plenty, but flows west rather than into the bay. It runs through the steep-sided Karangahake Gorge, forming a break between the Coromandel Range and the Kaimai Ranges. After , it joins the Waihou River near the town of Paeroa, south of the Firth of Thames, into which the Waihou River empties. Tributaries * Mataora Stream, running through the Golden Valley from a source only 1.5 km from the Bay of Plenty coastline. * Mangatoetoe Stream, which bisects the town of Waihi. * Waitete Stream, originating in the Coromandel Range near Waihi. This stream forms a natural boundary on the north-western side of Waihi and joins the Ohinemuri River immediately after Black Pool Dam. * Waimata Stream, starting in the Kaimai Ranges near the Athenree Gorge. * Waitekauri River, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Tara Tokanui
Ngāti Tara Tokanui is a Māori iwi of New Zealand. Treaty settlement Deed of Settlement was signed on 28 July 2022 after 13 years of negotiation. The deed saw nine culturally significant sites returned to the iwi, including Ngā Ure Tara, Mimitu Pā, Tawhitiaraia and Karangahake. As well as a compensation payout of $6 million and an apology from the crown for the confiscation of large tracts of land, as well as for its policies and laws that designed to dislocate Ngāti Tara Tokanui from their land and erode their tribal structure. See also *List of Māori iwi This is a list of iwi (New Zealand Māori tribes). List of iwi This list includes groups recognised as iwi (tribes) in certain contexts. Many are also hapū (sub-tribes) of larger iwi. Moriori are included on this list. Although they are distinc ... References External links Official website {{Maori-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Tungstate
Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula Ca W O4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Scheelite is originally named after Swedish chemist K. Scheele (1742-1786). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors and are occasionally fashioned into gemstones when suitably free of flaws. Scheelite has been synthesized using the Czochralski process; the material produced may be used to imitate diamond, as a scintillator, or as a solid-state lasing medium. It was also used in radium paint in the same fashion as was zinc sulphide, and Thomas Edison invented a fluoroscope with a calcium tungstate-coated screen, making the images six times brighter than those with barium platinocyanide; the latter chemical allowed Röntgen to discover X-rays in early November 1895. Properties Its crystals are in the tetragonal crystal system, appearing as dipyramidal pseudo-octahedra. Colors include golden yellow, brownish green to dark brown, pinkish to reddish gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tauranga
Tauranga () is a coastal city in the Bay of Plenty region and the fifth most populous city of New Zealand, with an urban population of , or roughly 3% of the national population. It was settled by Māori late in the 13th century, colonised by Europeans in the early 19th century, and was constituted as a city in 1963. The city lies in the north-western corner of the Bay of Plenty, on the south-eastern edge of Tauranga Harbour. The city extends over an area of , and encompasses the communities of Bethlehem, New Zealand, Bethlehem, on the south-western outskirts of the city; Greerton, on the southern outskirts of the city; Matua, west of the central city overlooking Tauranga Harbour; Maungatapu; Mount Maunganui, located north of the central city across the harbour facing the Bay of Plenty; Otūmoetai; Papamoa, Tauranga's largest suburb, located on the Bay of Plenty; Tauranga City; Tauranga South; and Welcome Bay. Tauranga is one of New Zealand's main centres for business, interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames, New Zealand
Thames () ( mi, Pārāwai) is a town at the southwestern end of the Coromandel Peninsula in New Zealand's North Island. It is located on the Firth of Thames close to the mouth of the Waihou River. The town is the seat of the Thames-Coromandel (district), New Zealand, Thames-Coromandel District Council. The Māori people, Māori iwi are Ngāti Maru (Hauraki), Ngāti Maru, who are descendants of Marutuahu's son Te Ngako. Ngāti Maru is part of the Ngati Marutuahu confederation of tribes or better known as Hauraki Iwi. Thames had an estimated population of 15,000 in 1870, but this declined to 4,500 in 1881, and it has increased modestly since. It is still the biggest town on the Coromandel. Until 2016, a historical Oak, oak tree that was planted by Governor George Grey stood on the corner of Grey and Rolleston streets. Demographics Thames covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Thames had a population of 7,293 at the 2018 Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Marsden
Samuel Marsden (25 June 1765 – 12 May 1838) was an English-born priest of the Church of England in Australia and a prominent member of the Church Missionary Society, believed to have introduced Christianity to New Zealand. Marsden was a prominent figure in early New South Wales and Australian history, partly through his ecclesiastical offices as the colony's senior Church of England cleric and as a pioneer of the Australian wool industry, but also for his employment of convicts for farming and his actions as a magistrate at Parramatta, both of which attracted contemporary criticism. Early life Born in Farsley, near Pudsey, Yorkshire in England as the son of a Wesleyan blacksmith turned farmer, Marsden attended the village school and spent some years assisting his father on the farm. In his early twenties his reputation as a lay preacher drew the attention of the evangelical Elland Society, which sought to train poor men for the ministry of the Church of England. With a scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (canoe)
Waka () are Māori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka tīwai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long. The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time. Since the 1970s about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia, as well as Polynesia. Waka taua (war canoes) ''Waka taua'' (in Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and ''taua'' means "army" or "war party") are large canoes manned by up to 80 paddlers and are up to in length. Large waka, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taniwha
In Māori mythology, taniwha () are large supernatural beings that live in deep pools in rivers, dark caves, or in the sea, especially in places with dangerous currents or deceptive breakers (giant waves). They may be considered highly respected kaitiaki (protective guardians) of people and places, or in some traditions as dangerous, predatory beings, which for example would kidnap women to have as wives. Etymology and Pacific analogues Linguists have reconstructed the word ''taniwha'' to Proto-Oceanic *''tanifa'', with the meaning "shark species". In Tongan and Niuean, ''tenifa'' refers to a large dangerous shark, as does the Samoan ''tanifa''; the Tokelauan ''tanifa'' is a sea-monster that eats people. In most other Polynesian languages, the cognate words refer to sharks or simply fish. Some anthropologists have stated that the taniwha has "analogues that appear within other Polynesian cosmologies".A. Asbjørn Jøn,The Road and the Taniwha in ''Australian Folklore: A Yearly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Language
Māori (), or ('the Māori language'), also known as ('the language'), is an Eastern Polynesian language spoken by the Māori people, the indigenous population of mainland New Zealand. Closely related to Cook Islands Māori, Tuamotuan, and Tahitian, it gained recognition as one of New Zealand's official languages in 1987. The number of speakers of the language has declined sharply since 1945, but a Māori-language revitalisation effort has slowed the decline. The 2018 New Zealand census reported that about 186,000 people, or 4.0% of the New Zealand population, could hold a conversation in Māori about everyday things. , 55% of Māori adults reported some knowledge of the language; of these, 64% use Māori at home and around 50,000 people can speak the language "very well" or "well". The Māori language did not have an indigenous writing system. Missionaries arriving from about 1814, such as Thomas Kendall, learned to speak Māori, and introduced the Latin alphabet. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rohe
The Māori people of New Zealand use the word ''rohe'' to describe the territory or boundaries of ''iwi'' (tribes), although some divide their rohe into several ''takiwā''. The areas shown on the map (right) are indicative only, and some iwi areas may overlap. The term ''rohe'' also combines with other words to form more modern terms. These include ''rohe pōti'', meaning an electoral district or constituency, ''rohe wā'', meaning time zone, and ''whatunga rohe paetata'', meaning a local area network. The term ''rohe'' on its own has also been adopted to mean an internet domain. The term is also used for the mission districts (''rohe mihana'') of Te Pīhopatanga o Aotearoa, the Māori Anglican Church in Aotearoa/New Zealand. See also * List of Māori iwi This is a list of iwi (New Zealand Māori tribes). List of iwi This list includes groups recognised as iwi (tribes) in certain contexts. Many are also hapū (sub-tribes) of larger iwi. Moriori are included on this list. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Hako
Ngāti Hako is a Māori iwi of New Zealand. The people of Ngati Hako are acknowledged as the earliest settlers in the Hauraki region. Although Ngati Hako endured long periods of conflict with the Marutūāhu peoples, they were never completely overcome. They have maintained a presence in Hauraki to the present day. Their origins are not known, but it is suggested that they belonged to the ancient Te Tini o Toi people, who were descendants of the Polynesian navigator Toitehuatahi. The survival of Ngati Hako through the period of Marutūāhu expansion was assisted by a strategic marriage. The high-born Ngati Hako woman Ruawehea was married to Tamatera, the son of Marutūāhu. The special relationship between Ngati Hako and the lands of Hauraki is recalled in their traditional call of welcome. See also *List of Māori iwi This is a list of iwi (New Zealand Māori tribes). List of iwi This list includes groups recognised as iwi (tribes) in certain contexts. Many are also hapū ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)