Waka (canoe) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
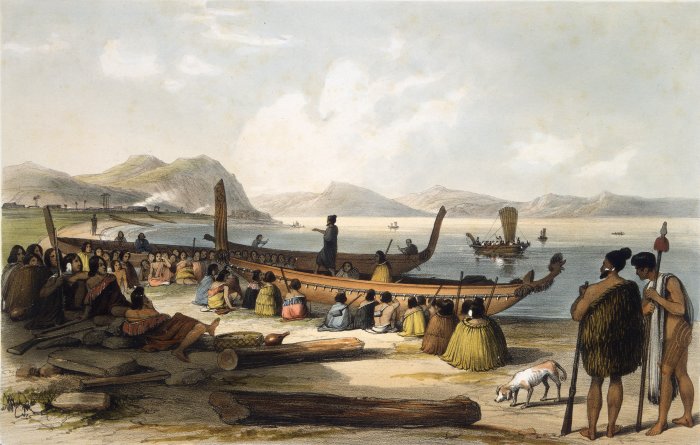 Waka () are Māori watercraft, usually
Waka () are Māori watercraft, usually
 ''Waka taua'' (in Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and '' taua'' means "army" or "war party") are large canoes manned by up to 80 paddlers and are up to in length. Large waka, such as Ngā Toki Matawhaorua which are usually elaborately carved and decorated, consist of a main hull formed from a single hollowed-out log, along with a carved upright head and tailboard. The gunwale is raised in some by a continuous plank, which gives increased freeboard and prevents distortion of the main hull components when used in a rough seas. Sometimes the hull is further strengthened, as in the case of ''Te Winika'', a 200-year-old design, by a batten or stringer running lengthwise both inside and outside the hull just above the loaded waterline. The resurgence of Māori culture has seen an increase in the numbers of ''waka taua'' built, generally on behalf of a tribal group, for use on ceremonial occasions.
Traditionally the war canoe was highly '' tapu'' (sacred). No cooked food was allowed in the craft and the waka had to be entered over the gunwales, not the bow or stern, which were highly decorated with powerful symbols. Canoes were often painted with black or white with black representing death. The main colour was red which stood for tapu. Sometimes a waka would be placed upright as a marker for a dead chief with the curved bottom of the hull carved. Māori told missionaries during the Musket Wars that battles between waka took place at sea with the aim being to ram an enemy's waka amidships at high speed. The ramming vessel would ride up over the gunwale and either force it under water or cause it to roll over. The enemies were either killed, left to drown or captured to be used in cannibal feasts or as slaves if they were female. This description matches the attack on the ship's boat of Abel Tasman in Golden Bay in 1642 when a Māori catamaran rammed a cock boat and four Dutch sailors were killed.
''Waka taua'' (in Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and '' taua'' means "army" or "war party") are large canoes manned by up to 80 paddlers and are up to in length. Large waka, such as Ngā Toki Matawhaorua which are usually elaborately carved and decorated, consist of a main hull formed from a single hollowed-out log, along with a carved upright head and tailboard. The gunwale is raised in some by a continuous plank, which gives increased freeboard and prevents distortion of the main hull components when used in a rough seas. Sometimes the hull is further strengthened, as in the case of ''Te Winika'', a 200-year-old design, by a batten or stringer running lengthwise both inside and outside the hull just above the loaded waterline. The resurgence of Māori culture has seen an increase in the numbers of ''waka taua'' built, generally on behalf of a tribal group, for use on ceremonial occasions.
Traditionally the war canoe was highly '' tapu'' (sacred). No cooked food was allowed in the craft and the waka had to be entered over the gunwales, not the bow or stern, which were highly decorated with powerful symbols. Canoes were often painted with black or white with black representing death. The main colour was red which stood for tapu. Sometimes a waka would be placed upright as a marker for a dead chief with the curved bottom of the hull carved. Māori told missionaries during the Musket Wars that battles between waka took place at sea with the aim being to ram an enemy's waka amidships at high speed. The ramming vessel would ride up over the gunwale and either force it under water or cause it to roll over. The enemies were either killed, left to drown or captured to be used in cannibal feasts or as slaves if they were female. This description matches the attack on the ship's boat of Abel Tasman in Golden Bay in 1642 when a Māori catamaran rammed a cock boat and four Dutch sailors were killed.
 During the classic period (about 1500 to 1770) a '' hapū'' would select a '' totara'' tree and prepare it years ahead for felling. ''Totara'' is a lightweight wood with a high natural oil content that helps prevent rot. This would include the removal of bark from one side of the trunk and the clearing of the ground and the planting of food crops for workers. After chants and prayers the tree would be felled by a combination of fires around the base and chopping with hand
During the classic period (about 1500 to 1770) a '' hapū'' would select a '' totara'' tree and prepare it years ahead for felling. ''Totara'' is a lightweight wood with a high natural oil content that helps prevent rot. This would include the removal of bark from one side of the trunk and the clearing of the ground and the planting of food crops for workers. After chants and prayers the tree would be felled by a combination of fires around the base and chopping with hand
 The head of the triangle sail was the shortest—about —and often decorated with tufts of feathers that may have served as wind indicators. The mast was held in place by a forestay, a backstay and two side stays. The sheet to control the sail angle led from the top of the yard directly to the sheet handler, although early British sailors were critical of the sheet being tied off. The sail was only used downwind, as the waka lacked a keel or centre-board to prevent leeway, therefore preventing windward sailing. Rarely, two sails of the same size, were used in larger waka.
Due to its slim hull the waka could sail at considerable speed down wind. When struck, the sail was wrapped around the two spars and laid along the centre of the waka thwarts, between the paddlers. Sometimes a pattern was woven into the sail, using a different material. The only known example of a traditional waka sail is in the British Museum. Capsizes were not unknown, with the hull being tipped to get rid of water, then bailed out. This type of triangular sail, with straight mast and high angled sprit, is identical to that used in the Marquesan Islands. Although there are references to the use of the Society Island–type crescent-shaped sail in New Zealand, these appear to have been rare and no examples exist.
The head of the triangle sail was the shortest—about —and often decorated with tufts of feathers that may have served as wind indicators. The mast was held in place by a forestay, a backstay and two side stays. The sheet to control the sail angle led from the top of the yard directly to the sheet handler, although early British sailors were critical of the sheet being tied off. The sail was only used downwind, as the waka lacked a keel or centre-board to prevent leeway, therefore preventing windward sailing. Rarely, two sails of the same size, were used in larger waka.
Due to its slim hull the waka could sail at considerable speed down wind. When struck, the sail was wrapped around the two spars and laid along the centre of the waka thwarts, between the paddlers. Sometimes a pattern was woven into the sail, using a different material. The only known example of a traditional waka sail is in the British Museum. Capsizes were not unknown, with the hull being tipped to get rid of water, then bailed out. This type of triangular sail, with straight mast and high angled sprit, is identical to that used in the Marquesan Islands. Although there are references to the use of the Society Island–type crescent-shaped sail in New Zealand, these appear to have been rare and no examples exist.
 Some waka, particularly in the
Some waka, particularly in the
"CORONATION GIFT"
Te Ao Hou In current
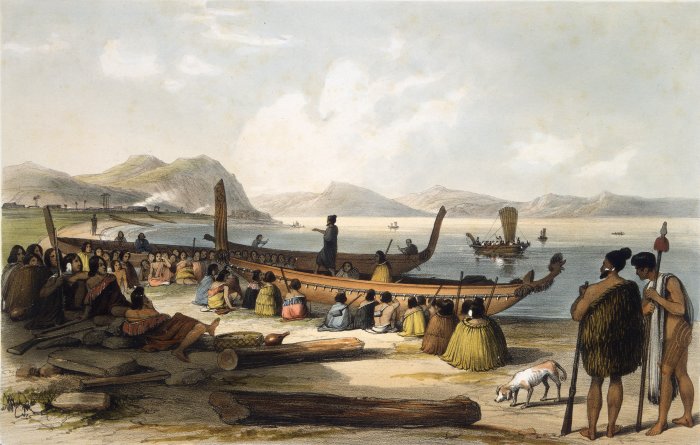 Waka () are Māori watercraft, usually
Waka () are Māori watercraft, usually canoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the term ...
s ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka tīwai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long.
The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time.
Since the 1970s about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, ...
, as well as Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
.
Waka taua (war canoes)
 ''Waka taua'' (in Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and '' taua'' means "army" or "war party") are large canoes manned by up to 80 paddlers and are up to in length. Large waka, such as Ngā Toki Matawhaorua which are usually elaborately carved and decorated, consist of a main hull formed from a single hollowed-out log, along with a carved upright head and tailboard. The gunwale is raised in some by a continuous plank, which gives increased freeboard and prevents distortion of the main hull components when used in a rough seas. Sometimes the hull is further strengthened, as in the case of ''Te Winika'', a 200-year-old design, by a batten or stringer running lengthwise both inside and outside the hull just above the loaded waterline. The resurgence of Māori culture has seen an increase in the numbers of ''waka taua'' built, generally on behalf of a tribal group, for use on ceremonial occasions.
Traditionally the war canoe was highly '' tapu'' (sacred). No cooked food was allowed in the craft and the waka had to be entered over the gunwales, not the bow or stern, which were highly decorated with powerful symbols. Canoes were often painted with black or white with black representing death. The main colour was red which stood for tapu. Sometimes a waka would be placed upright as a marker for a dead chief with the curved bottom of the hull carved. Māori told missionaries during the Musket Wars that battles between waka took place at sea with the aim being to ram an enemy's waka amidships at high speed. The ramming vessel would ride up over the gunwale and either force it under water or cause it to roll over. The enemies were either killed, left to drown or captured to be used in cannibal feasts or as slaves if they were female. This description matches the attack on the ship's boat of Abel Tasman in Golden Bay in 1642 when a Māori catamaran rammed a cock boat and four Dutch sailors were killed.
''Waka taua'' (in Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and '' taua'' means "army" or "war party") are large canoes manned by up to 80 paddlers and are up to in length. Large waka, such as Ngā Toki Matawhaorua which are usually elaborately carved and decorated, consist of a main hull formed from a single hollowed-out log, along with a carved upright head and tailboard. The gunwale is raised in some by a continuous plank, which gives increased freeboard and prevents distortion of the main hull components when used in a rough seas. Sometimes the hull is further strengthened, as in the case of ''Te Winika'', a 200-year-old design, by a batten or stringer running lengthwise both inside and outside the hull just above the loaded waterline. The resurgence of Māori culture has seen an increase in the numbers of ''waka taua'' built, generally on behalf of a tribal group, for use on ceremonial occasions.
Traditionally the war canoe was highly '' tapu'' (sacred). No cooked food was allowed in the craft and the waka had to be entered over the gunwales, not the bow or stern, which were highly decorated with powerful symbols. Canoes were often painted with black or white with black representing death. The main colour was red which stood for tapu. Sometimes a waka would be placed upright as a marker for a dead chief with the curved bottom of the hull carved. Māori told missionaries during the Musket Wars that battles between waka took place at sea with the aim being to ram an enemy's waka amidships at high speed. The ramming vessel would ride up over the gunwale and either force it under water or cause it to roll over. The enemies were either killed, left to drown or captured to be used in cannibal feasts or as slaves if they were female. This description matches the attack on the ship's boat of Abel Tasman in Golden Bay in 1642 when a Māori catamaran rammed a cock boat and four Dutch sailors were killed.
Traditional construction
 During the classic period (about 1500 to 1770) a '' hapū'' would select a '' totara'' tree and prepare it years ahead for felling. ''Totara'' is a lightweight wood with a high natural oil content that helps prevent rot. This would include the removal of bark from one side of the trunk and the clearing of the ground and the planting of food crops for workers. After chants and prayers the tree would be felled by a combination of fires around the base and chopping with hand
During the classic period (about 1500 to 1770) a '' hapū'' would select a '' totara'' tree and prepare it years ahead for felling. ''Totara'' is a lightweight wood with a high natural oil content that helps prevent rot. This would include the removal of bark from one side of the trunk and the clearing of the ground and the planting of food crops for workers. After chants and prayers the tree would be felled by a combination of fires around the base and chopping with hand adze
An adze (; alternative spelling: adz) is an ancient and versatile cutting tool similar to an axe but with the cutting edge perpendicular to the handle rather than parallel. Adzes have been used since the Stone Age. They are used for smoothing ...
s. On an especially large tree with aerial roots a stage about 3 m high was built of wood. On this was built a framework on which was suspended a giant upside-down ''toki'' (axe), about 2.5 m long. The long axis of the ''toki'' was tied to the crossmember of the upper framework so that it could pivot back and forth, like a swing. Heavy rocks were tied to each side of the long axis at its lowest point to give momentum. The ''toki'' was pulled back and released so that the cutting edge bit into the wood that was weakened by fire. It could take two to three weeks to cut down a large tree in this manner.
The head of the tree and branches were removed, then the hull was roughly shaped ''in situ'', using fire and hand adzes, under the guidance of the chief designer. A stone adze was used by relatively gentle, but regular and repeated blows. The head was soaked in water to make the binding swell and hold the stone blade more firmly. Once the shaping was complete, the log of 3–4 tonnes was pulled by teams of men to a stream or river, using multiple ropes made from ''raupō
''Typha orientalis'', commonly known as bulrush, cumbungi, or raupō, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the genus ''Typha''. It is native to Australia, New Zealand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Mongolia, Myanmar, Philippines, China and the ...
''. Some men pulled the waka forward while others restrained it on downhill slopes. Accidents at this stage were apparently common. Saplings were used as skids and rollers over uneven ground.
The final shaping was done closer to the ''papakainga'' to be nearer to food. A waka could take a year to make if the construction went smoothly, but it could be abandoned if there was an accident or a death of an important person. Such abandoned, uncompleted waka have been found in post-contact times. Most large waka were built in several main interlocking sections and stitched together with flax rope. Small pegs were put into the holes, which swelled and sealed when wet. Tree gum could also seal the holes. A large finished waka weighed about three tonnes and could remain in use for many decades. All large waka had names and were objects of pride and admiration.
The image above shows a ''waka taua'' with unusually high freeboard. A noticeable feature of a loaded ''waka taua'' was its very low freeboard of 400–500 mm, which made the vessel unseaworthy in all but good weather, despite the presence of one or two young men on board dedicated to bailing. The normal timber used, ''totara'', is a lightweight native podocarp
Podocarpaceae is a large family of mainly Southern Hemisphere conifers, known in English as podocarps, comprising about 156 species of evergreen trees and shrubs.James E. Eckenwalder. 2009. ''Conifers of the World''. Portland, Oregon: Timber Pre ...
, which retains its natural oils even when cut down. This prevented the timber opening up and splitting. Angela Ballara noted that they only put to sea when it was fine. One voyage across the stormy Cook Strait was delayed for a week while the travellers waited for fine weather. The missionary William Williams, son of Henry Williams, noted that the voyage of a waka taua was a leisurely affair due to the requirements of foraging for food and waiting for fine weather.
The 1974 National Film Unit documentary - Taahere Tikitiki - the making of a Maori canoe - records the 18 month long construction of a waka taua - the Taahere Tikitiki. The waka was commissioned by the Māori Queen, Te Arikinui Dame Te Atairangikaahu, and constructed at Tūrangawaewae Marae by master carver Piri Poutapu. The film, directed by David Sims David Sims is the name of:
*David Sims (running back) (born 1955), former American football running back with the Seattle Seahawks
* David Sims (safety) (born 1986), American football safety for the Indianapolis Colts
*Dave Sims (born 1953), Seattl ...
, is a visual insight into the building of this cultural taonga.
Traditional sails
Tasman noted that two of the waka which attacked his ships in Golden Bay in today's Tasman District in December 1642, had a sail that Tasman referred to as a Tingang sail—a small triangular sail often temporarily hoisted. Later, early Europeans from the 1830s onwards gave detailed descriptions of the use, appearance and materials used in Māori sails. Although there were regional variations within New Zealand, most sails were temporary and could be hoisted or struck in a few minutes. The roughly triangular sail, usually made from either flax, '' tī'' leaves or ''raupō'' ( bulrushes) or a combination, was set about one-third back from the bow. The ''raupō'' sail was much lighter. The mast and yard spars were small diameter, with the yard being thinner, about high, long, and permanently attached to the sail so the rig was raised as a single unit. Loops were woven into both the luff and the leech of the sail for attachment to the spars. ''Tanekaha'' ( celery pine) branches were favoured, as it was common, as far south as Nelson. It was a straight, strong and flexible wood. An added advantage may have been that the wood bled red tannin, a colour strongly favoured by Māori. The head of the triangle sail was the shortest—about —and often decorated with tufts of feathers that may have served as wind indicators. The mast was held in place by a forestay, a backstay and two side stays. The sheet to control the sail angle led from the top of the yard directly to the sheet handler, although early British sailors were critical of the sheet being tied off. The sail was only used downwind, as the waka lacked a keel or centre-board to prevent leeway, therefore preventing windward sailing. Rarely, two sails of the same size, were used in larger waka.
Due to its slim hull the waka could sail at considerable speed down wind. When struck, the sail was wrapped around the two spars and laid along the centre of the waka thwarts, between the paddlers. Sometimes a pattern was woven into the sail, using a different material. The only known example of a traditional waka sail is in the British Museum. Capsizes were not unknown, with the hull being tipped to get rid of water, then bailed out. This type of triangular sail, with straight mast and high angled sprit, is identical to that used in the Marquesan Islands. Although there are references to the use of the Society Island–type crescent-shaped sail in New Zealand, these appear to have been rare and no examples exist.
The head of the triangle sail was the shortest—about —and often decorated with tufts of feathers that may have served as wind indicators. The mast was held in place by a forestay, a backstay and two side stays. The sheet to control the sail angle led from the top of the yard directly to the sheet handler, although early British sailors were critical of the sheet being tied off. The sail was only used downwind, as the waka lacked a keel or centre-board to prevent leeway, therefore preventing windward sailing. Rarely, two sails of the same size, were used in larger waka.
Due to its slim hull the waka could sail at considerable speed down wind. When struck, the sail was wrapped around the two spars and laid along the centre of the waka thwarts, between the paddlers. Sometimes a pattern was woven into the sail, using a different material. The only known example of a traditional waka sail is in the British Museum. Capsizes were not unknown, with the hull being tipped to get rid of water, then bailed out. This type of triangular sail, with straight mast and high angled sprit, is identical to that used in the Marquesan Islands. Although there are references to the use of the Society Island–type crescent-shaped sail in New Zealand, these appear to have been rare and no examples exist.
Technology changes
From the arrival of James Cook in 1769 and especially Marion Du Fresne's longer stay in New Zealand in 1772, Māori were able to obtain iron and steel, which did not exist in pre-contact Māori culture. Māori quickly learned the superiority of this material, especially for carving. Māori learnt to ask sailors to sharpen ships' nails to a chisel point on a ship's wheel in exchange for fish. This period between 1779 and 1820 has been called the golden age of Māori wood carving. Much of the carving was confined to ''waka taua''. During the middle 19th century, from 1835, the arrival of large numbers of European settlers and ships meant that ship's boats were far more commonly available and were increasingly used by Māori in preference to waka. In 1839 100 ships visited The Bay of Islands. This was a trend that the missionaries such as Marsden and Williams had noted had begun in the 1830s. The beamier, lighter, ship's boat was a better load carrier with more stability, and was sometimes equipped with sails for windward sailing. Use of ship's boats became common, as many Māori worked on a wide variety of sealing, whaling and trading sailing vessels, both in New Zealand and in the Pacific. Few waka were used for movement of warriors during the Land Wars: When the Waikato campaign started in 1863, the government forces made a point of sinking all the waka they could find on the Waikato River and its tributaries to slow rebel communication. Later, some fine examples of these were placed in the Auckland War Memorial Museum.Ocean-going canoes
Ocean-going waka, whatever their size, could be paddled, but achieved their best speeds when propelled by sail. ThePolynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
n settlers of New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
migrated to New Zealand in large waka; according to legend, some of these were possibly ''waka hourua'', double-hulled vessels. The names and stories associated with those waka were passed on in oral history (''kōrero o mua''), but dates, names, times, and routes were frequently muddled as the descendants of the settlers multiplied and separated into iwi
Iwi () are the largest social units in New Zealand Māori culture, Māori society. In Māori-language, Māori roughly means "people" or "nation", and is often translated as "tribe", or "a confederation of tribes". The word is both singular and ...
(tribes) and hapū (sub-tribes). Consequently, the word ''waka'' is used to denote a confederation of iwi descended from the people of one migratory canoe.
In 1992, Hekenukumai Busby built Te Aurere, a ''waka hourua'', using traditional methods and materials. It has since voyaged across the Pacific, to Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only ...
, Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Aust ...
, the Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in ...
, New Caledonia and Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together w ...
, as well as repeatedly circumnavigating Te Ika-a-Māui using Polynesian navigation methods.
Waka ama (outrigger canoes)
Early European explorers saw Māori using ''waka ama'' (outrigger canoe
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger ...
s). " Sydney Parkinson, an artist on Captain James Cook's first voyage to New Zealand in 1769, and the German scientist Johann Reinhold Forster
Johann Reinhold Forster (22 October 1729 – 9 December 1798) was a German Reformed (Calvinist) pastor and naturalist of partially Scottish descent who made contributions to the early ornithology of Europe and North America. He is best known ...
, who sailed with Cook in 1773, described waka fitted with outriggers (ama, amatiatia or korewa)". Already rare in Cook's time, ''waka ama'' had largely faded from memory by the early 19th century. However, the term ''waka ama'' occurs in old stories, such as the story of Māui published by Grey in 1854 and in a few old ''waiata''; Tregear also mentions the ''waka ama'' as "a possession of the Māori", adding that "It was beneath the outrigger of such a canoe that the famous Maui crushed his wife's brother Irawaru before turning him into a dog. Both the double canoe and the outrigger have entirely disappeared from among the Māoris, and it is doubtful if any native now alive has seen either of them in New Zealand".
Two outrigger floats were found in swamps along the Horowhenua coast of Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
, and another float was found in Moncks Cave
Moncks Cave is a cave located in Redcliffs, Christchurch. It is notable for the amount of wooden artefacts discovered there in 1889 by workmen while quarrying for road metal.
History
The cave was discovered in 1889 by workmen who were quarrying ...
near Christchurch. All three floats were short, suggesting that Māori outriggers were small and used only in sheltered waters.
The Māori words for the parts of the outrigger, such as ''ama'' and ''kiato'', recorded in the early years of European settlement, suggest that Māori outrigger canoes were similar in form to those known from central Polynesia
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
.
Since the 1990s, '' waka ama'' racing, introduced from Pasifika Pasifika may refer to:
*Pacific Islander people, indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands
**Pasifika New Zealanders, Pacific peoples living in New Zealand
*Pacific islands, including Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia
*The Pasifika Festival, an an ...
nations into New Zealand during the 1980s and 1990s, using high-tech canoes of Hawaiian or Tahitian design and with the ingenious support of work schemes, has become an increasingly popular sport among Māori, often performed as part of cultural festivals held in summer.
Other materials used
 Some waka, particularly in the
Some waka, particularly in the Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands ( ) ( Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about east of New Zealand's South Island. They are administered as part of New Zealand. The archipelago consists of about t ...
, were not conventional canoes, but were constructed from ''raupō'' ( bulrushes) or flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. Textiles made from flax are known i ...
stalks.
In 2009, the Okeanos Foundation for the Sea and Salthouse Boatbuilders built a fleet of ''vaka moana'' / ''waka hourua'' with fibreglass hulls. One of these, the Haunui, was gifted to the Te Toki Voyaging Trust in New Zealand.
In April 2011 Te Puni Kokiri, The Māori Development Agency, announced a joint venture with an Auckland tribe to build a PVC plastic pavilion in the shape of a waka as a promotion for local Māori. The "Tupper waka", as it was called in the media, was a small conference facility for well-off visitors during the world rugby competition held in New Zealand in September 2011. Most of the $2 million funding came from the government, but the tribe was contributing $100,000 and would retain ownership after the event. The graphic on television showed that it is largely a promotional device with seating, tables and a bar. It will not be open to the general public, according to the media briefing.
The waka taua ''Te Tuhono'' in the National Museum of Scotland was restored and partially reconstructed by the Māori craftsman George Nuku, using carved poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) to recreate missing sections.
Related meanings
The word "waka" is also used in broader senses that can be translated as "vessel", "container", or "vehicle". A '' waka huia'' is a hollowed and carved vessel used for storing of '' taonga'' (treasures) such as the prized tail feathers of the now-extinct '' huia'' (''Heteralocha acutirostris'') that are worn as ornaments in the hair.Te Ao Hou In current
Māori language
Māori (), or ('the Māori language'), also known as ('the language'), is an Eastern Polynesian language spoken by the Māori people, the indigenous population of mainland New Zealand. Closely related to Cook Islands Māori, Tuamotuan, an ...
usage, ''waka'' is used to refer to cars, (along with the transliterated term ''motokā''), ''waka-rere-rangi'' for aircraft and a ''waka hari hinu'' is an oil tanker – a ''waka niho'' (gear container) is a car's gearbox. ''Waka'' can be used to refer transport in general, such as in "Te Manatū Waka" ( Ministry of Transport) and "Waka Kotahi" ( NZ Transport Agency).
See also
* Chundan vallam *Dragon boat
A dragon boat is a human-powered watercraft originating from the Pearl River Delta region of China's southern Guangdong Province. These were made of teak, but in other parts of China, different kinds of wood are used. It is one of a family ...
*Dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek – ''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' ( ...
* Hōkūleʻa
* Nouka Baich
*Outrigger canoe
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger ...
*Polynesian Voyaging Society
The Polynesian Voyaging Society (PVS) is a non-profit research and educational corporation based in Honolulu, Hawaii. PVS was established to research and perpetuate traditional Polynesian voyaging methods. Using replicas of traditional double-hul ...
* Salisipan
* Swan boat (racing)
* Tomako
* Vaka (sailing), a word with a similar etymology
*Waka hurdling
Waka hurdling, also sometimes called waka peke (jumping waka), is a Maori sporting competition of jumping unornamented river canoes (waka tīwai) (waka (canoe)) over wooden beams set in the water. There have been attempts to revive the sport and ...
, sport
* Waka-jumping, a political term
Notes
References
* * * * * * {{Fishing vessel topics Indigenous boats Outrigger canoes Polynesian culture Māori culture Māori words and phrases Polynesian navigation Māori waka