|
MIQE
The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines are a set of protocols for conducting and reporting quantitative real-time PCR experiments and data, as devised by Bustin et al. in 2009. They were devised after a paper was published in 2002 that claimed to detect measles virus in children with autism through the use of RT-qPCR, but the results proved to be completely unreproducible by other scientists. The authors themselves also did not try to reproduce them and the raw data was found to have a large amount of errors and basic mistakes in analysis. This incident prompted Stephen Bustin to create the MIQE guidelines to provide a baseline level of quality for qPCR data published in scientific literature. Purpose The MIQE guidelines were created due to the low quality of qPCR data submitted to academic journals at the time, which was only becoming more common as Next Generation Sequencing machinery allowed for such experiments to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Bustin
Stephen Andrew Bustin (born 1954) is a British scientist, former professor of molecular sciences at Queen Mary University of London from 2004 to 2012, as well as visiting professor at Middlesex University, beginning in 2006. In 2012 he was appointed Professor of Allied Health and Medicine at Anglia Ruskin University. He is known for his research into polymerase chain reaction, and has written a book on the topic, entitled ''A-Z of Quantitative PCR''. This book has been called "the bible of qPCR." Education Bustin obtained his B.A. and PhD from Trinity College, Dublin in molecular genetics. Career Following the merger with St Bartholomew's Medical College and Queen Mary University of London, Bustin was promoted to Reader in Molecular Medicine in 2002, followed by the award of a personal chair as Professor of Molecular Science in 2004 at Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry. , Bustin held the position of Professor of Molecular Medicine at Anglia Ruskin University. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
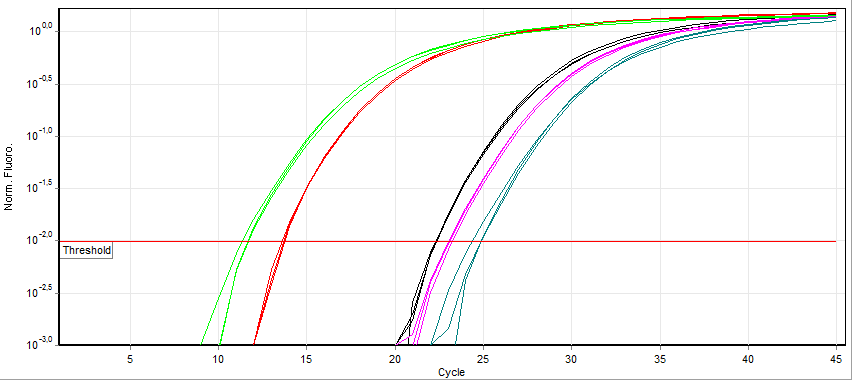
Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR, or qPCR) is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real time), not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (quantitative real-time PCR) and semi-quantitatively (i.e., above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules) (semi-quantitative real-time PCR). Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter, which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence. The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments ( MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation ''qPCR'' be used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomedicine And Laser Surgery
Photomedicine is an interdisciplinary branch of medicine that involves the study and application of light with respect to health and disease. Photomedicine may be related to the practice of various fields of medicine including dermatology, surgery, interventional radiology, optical diagnostics, cardiology, circadian rhythm sleep disorders and oncology. A branch of photomedicine is light therapy in which bright light strikes the retinae of the eyes, used to treat circadian rhythm disorders and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). The light can be sunlight or from a light box emitting white or blue (blue/green) light. Examples Photomedicine is used as a treatment for many different conditions: * PUVA for the treatment of psoriasis * Photodynamic therapy (PDT) for treatment of cancer and macular degeneration - Nontoxic light-sensitive compounds are targeted to malignant or other diseased cells, then exposed selectively to light, whereupon they become toxic and destroy these cells phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified in an outbreak in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019. Attempts to contain it there failed, allowing the virus to spread to other areas of Asia and later worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on 30 January 2020, and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. As of , the pandemic had caused more than cases and confirmed deaths, making it one of the deadliest in history. COVID-19 symptoms range from undetectable to deadly, but most commonly include fever, dry cough, and fatigue. Severe illness is more likely in elderly patients and those with certain underlying medical conditions. COVID-19 transmits when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever, cough, headache, fatigue, breathing difficulties, Anosmia, loss of smell, and Ageusia, loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days incubation period, after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected Asymptomatic, do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a target entity. The measured entity is often called the analyte, the measurand, or the target of the assay. The analyte can be a drug, biochemical substance, chemical element or compound, or cell in an organism or organic sample. An assay usually aims to measure an analyte's intensive property and express it in the relevant measurement unit (e.g. molarity, density, functional activity in enzyme international units, degree of effect in comparison to a standard, etc.). If the assay involves exogenous reactants (the reagents), then their quantities are kept fixed (or in excess) so that the quantity and quality of the target are the only limiting factors. The difference in the assay outcome is used to deduce the unknown quality or quantity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene (journal)
''Gene'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in genetics and molecular biology, focusing on the cloning, structure, function, as well as the biomedical and biotechnological importance of genes. It was established in 1976 and is published by Elsevier. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.688. Beyond Gene, there are several sub-specialty journals linked to Gene including Meta Gene, Plant Gene, Agri Gene and Gene Reports. References External links * Genetics journals Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1976 English-language journals {{genetics-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BioTechniques
''BioTechniques: the International Journal of Life Science Methods'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal published by Future Science Group. It covers laboratory methods and techniques that are of broad interest to professional life scientists, as well as scientists from other disciplines (e.g. physics, chemistry, engineering, computer sciences) interested in life science applications of their technologies. The journal was established in 1983 by Eaton Associates, which was acquired in 2001 by Informa. The journal was then acquired by Future Science Group in 2018. It is distributed in both print and online form. The journal is supported by print and website advertising, and as of January 2019, began charging article processing fees. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile App
A mobile application or app is a computer program or software application designed to run on a mobile device such as a phone, tablet, or watch. Mobile applications often stand in contrast to desktop applications which are designed to run on desktop computers, and web applications which run in mobile web browsers rather than directly on the mobile device. Apps were originally intended for productivity assistance such as email, calendar, and contact databases, but the public demand for apps caused rapid expansion into other areas such as mobile games, factory automation, GPS and location-based services, order-tracking, and ticket purchases, so that there are now millions of apps available. Many apps require Internet access. Apps are generally downloaded from app stores, which are a type of digital distribution platforms. The term "app", short for " application", has since become very popular; in 2010, it was listed as "Word of the Year" by the American Dialect Society. Apps a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bio-Rad
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. is an American developer and manufacturer of specialized technological products for the life science research and clinical diagnostics markets. The company was founded in 1952 in Berkeley, California, by husband and wife team David and Alice Schwartz, both graduates of the University of California, Berkeley. Bio-Rad is based in Hercules, California, and has operations worldwide. Business segments Bio-Rad’s life science products primarily include instruments, software, consumables, reagents, and content for the areas of cell biology, gene expression, protein purification, protein quantitation, drug discovery and manufacture, food safety, and science education. These products are based on technologies to separate, purify, identify, analyze, and amplify biological materials such as antibodies, proteins, nucleic acids, cells, and bacteria.Bio-Rad Annual Report 2016 , http://www.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/corporate/annualreport/Annual_Report_2016.p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. is a privately held independent publishing company founded by its president, Mary Ann Liebert, in 1980. The company publishes peer-reviewed academic journals, books, and trade magazines in the areas of biotechnology, biomedical sciences, medical research, and life sciences; clinical medicine, surgery, and nursing; technology and engineering; environmental science; public health and policy; law, regulation, and education. The company's headquarters is in New Rochelle, New York. The company has been described as the first to establish a specialty in genetic engineering. Publications Eschewing traditional market research, the publisher seeks out niche topics overlooked by larger publishers. As of 2000, its portfolio of more than ninety peer-reviewed journals included: Part 2 of the article appears at https://www.newspapers.com/clip/22386499/genetic_genius_part_2/. Publications focused on topics outside of the medical field include ''Westcheste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Biolabs
New England Biolabs (NEB) produces and supplies recombinant and native enzyme reagents for the life science research, as well as providing products and services supporting genome editing, synthetic biology and next-generation sequencing. NEB also provides free access to research tools such as REBASE, InBASE, and Polbase. The company The company was established in 1974 by Donald Comb as a cooperative laboratory of experienced scientists and initially produced restriction enzymes on a commercial scale. The company then began producing solution-oriented products. It received approximately $1.7 million in Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) grants between 2009 and 2013 for this research. NEB produces 230 recombinant and 30 native restriction enzymes for genomic research, as well as nicking enzymes and DNA methylases. It pursues research in areas related to proteomics, DNA Sequencing, and drug discovery. NEB scientists also conduct basic research in Molecular Biology and Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |