|
M31-RV
M31-RV is a possible red cataclysmic variable star located in the Andromeda Galaxy (M31) that experienced an outburst in 1988, which is similar to the outburst V838 Monocerotis experienced in 2002. Such objects have been called luminous red novae or intermediate-luminosity red transients. During the outburst, both V838 Mon and M31-RV reached a maximum absolute visual magnitude of -9.8. In 2006, the area around M31-RV was observed using the Hubble Space Telescope, but only red giants were seen. It is thought that the star either became too dim for Hubble to see, or the star is a companion of one of the red giants, or the star is one of the red giants themselves. M31-RV reached a peak visual magnitude of 17 before fading rapidly and showing dust formation. The most likely explanation states that these outbursts occur during stellar merger events. See also * AE Andromedae AE Andromedae (AE And) is a luminous blue variable (LBV), a type of variable star. The star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V838 Monocerotis
V838 Monocerotis (Nova Monocerotis 2002) is a spectroscopic binary star system in the constellation Monoceros (constellation), Monoceros about 19,000 light years (6 parsec, kpc) from the Sun. The previously unremarked star was observed in early 2002 experiencing a major outburst, and was possibly one of the List of largest known stars, largest known stars for a short period following the outburst. Originally believed to be a typical nova eruption, it was then identified as the first of a new class of eruptive variables known as luminous red novae. The reason for the outburst is still uncertain, but several conjectures have been put forward, including an eruption related to stellar death processes and a merger of a binary star or planets. The eruption occurred on one of two B3 main sequence stars in a close binary orbit. The erupting star became a very cool supergiant and for a while engulfed its companion. By 2009 the temperature of the supergiant had increased (since 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AE Andromedae
AE Andromedae (AE And) is a luminous blue variable (LBV), a type of variable star. The star is one of the most luminous variables in M31, the Andromeda Galaxy. Discovery The star was discovered to be variable in 1928, with a photographic magnitude range of 14.7-15.6, at the Harvard College Observatory and designated HV 4476. A year later it was given the variable star designation AE Andromedae. At that time it was the brightest stellar object in M31 and maintained a similar brightness for about 20 years. Early in the investigations leading to the definition of LBVs, AE And was identified as similar to the five Hubble–Sandage variables: Var A, Var B, Var C, and Var 2 in M33, and Var 19 in M31 (=AF Andromedae). On the basis of color–color comparisons, it was assigned as spectral type B and described as related to the P Cygni variables. Observations from 1960 to 1970 showed irregular variations in the B (blue) magnitude between 16.2 and 17.6, with very similar V magnitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminous Red Novae
Luminous may refer to: * Luminous flame, a flame emitting visible light Music * Luminous (group), a South Korean boy band * ''Luminous'' (EP), an EP by Cesium 137 * ''Luminous'' (John Hicks and Elise Wood album), 1985–88 * Luminous (The Horrors album) * Luminous, an album by Chris Murphy * Luminous, an album by Bill Nelson * "Luminous" (ClariS song), 2012 * Luminous (Jedward song), 2012 Other uses * ''Luminous'' (book), a 1998 short story collection by Greg Egan * Luminous (typeface), a foundry type made by Ludwig & Mayer * Luminous Studio, a video game engine developed by Square Enix * Project Luminous, a project by the Walt Disney Corporation that became the sub franchise ''Star Wars: High Republic'' See also * * * Luminance * Luminescence * Luminosity * ''Lumines (pronounced as "Loo-min-ess") is a puzzle video game series developed by Q Entertainment. The core objective of the games is to survive by rotating and aligning 2×2 blocks varying between two colors to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M-type Supergiants
Type M or M type may refer to: Science and technology * Type M, a xD-Picture Card * Type M, a name for the 15 amp BS 546 electrical plug * Vaio Type M, a kind of Vaio computer from Sony * M-type asteroid * m-type filter, an electronic filter * M-type star * M-types, an implementation of inductive type Other uses * Audi Type M, a 1920s car * Beretta 92FS Compact Type M, a pistol * MG M-type, a sports car See also * M class (other) M class or M-class may refer to: Military * M-class cruiser, a planned German light cruiser class * M-class destroyer, several classes of destroyer ** Admiralty M-class destroyer, a class of British destroyers built 1913–1916 and served in World ... * Class M (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux. Its brightest star, Alpha Andromedae, is a binary star that has also been counted as a part of Pegasus, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Merger
A stellar collision is the coming together of two stars caused by stellar dynamics within a star cluster, or by the orbital decay of a binary star due to stellar mass loss or gravitational radiation, or by other mechanisms not yet well understood. Astronomers predict that events of this type occur in the globular clusters of our galaxy about once every 10,000 years. On 2 September 2008 scientists first observed a stellar merger in Scorpius (named V1309 Scorpii), though it was not known to be the result of a stellar merger at the time. Any stars in the universe can collide, whether they are "alive", meaning fusion is still active in the star, or "dead", with fusion no longer taking place. White dwarf stars, neutron stars, black holes, main sequence stars, giant stars, and supergiants are very different in type, mass, temperature, and radius, and so react differently. A gravitational wave event that occurred on 25 August 2017, GW170817, was reported on 16 October 2017 to be asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the line of sight to the observer. The word ''magnitude'' in astronomy, unless stated otherwise, usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale dates back to the ancient Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, whose star catalog listed stars from 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined in a way to closely match this historical system. The scale is reverse logarithmic: the brighter an object is, the lower its magnitude number. A difference of 1.0 in magnitude corresponds to a brightness ratio of \sqrt /math>, or about 2.512. For example, a star of magnitude 2.0 is 2.512 times as bright as a star of magnitude 3.0, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Giants
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or lower. The appearance of the red giant is from yellow-white to reddish-orange, including the spectral types K and M, sometimes G, but also class S stars and most carbon stars. Red giants vary in the way by which they generate energy: * most common red giants are stars on the red-giant branch (RGB) that are still fusing hydrogen into helium in a shell surrounding an inert helium core * red-clump stars in the cool half of the horizontal branch, fusing helium into carbon in their cores via the triple-alpha process * asymptotic-giant-branch (AGB) stars with a helium burning shell outside a degenerate carbon–oxygen core, and a hydrogen-burning shell just beyond that. Many of the well-known bright stars are red giants because they are l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Magnitude
Absolute magnitude () is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse Logarithmic scale, logarithmic Magnitude (astronomy), astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it were viewed from a distance of exactly , without Extinction (astronomy), extinction (or dimming) of its light due to absorption by Interstellar medium, interstellar matter and cosmic dust. By hypothetically placing all objects at a standard reference distance from the observer, their luminosities can be directly compared among each other on a magnitude scale. As with all astronomical magnitude (astronomy), magnitudes, the absolute magnitude can be specified for different wavelength ranges corresponding to specified Filter (optics), filter bands or passbands; for stars a commonly quoted absolute magnitude is the absolute visual magnitude, which uses the visual (V) band of the spectrum (in the UBV phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
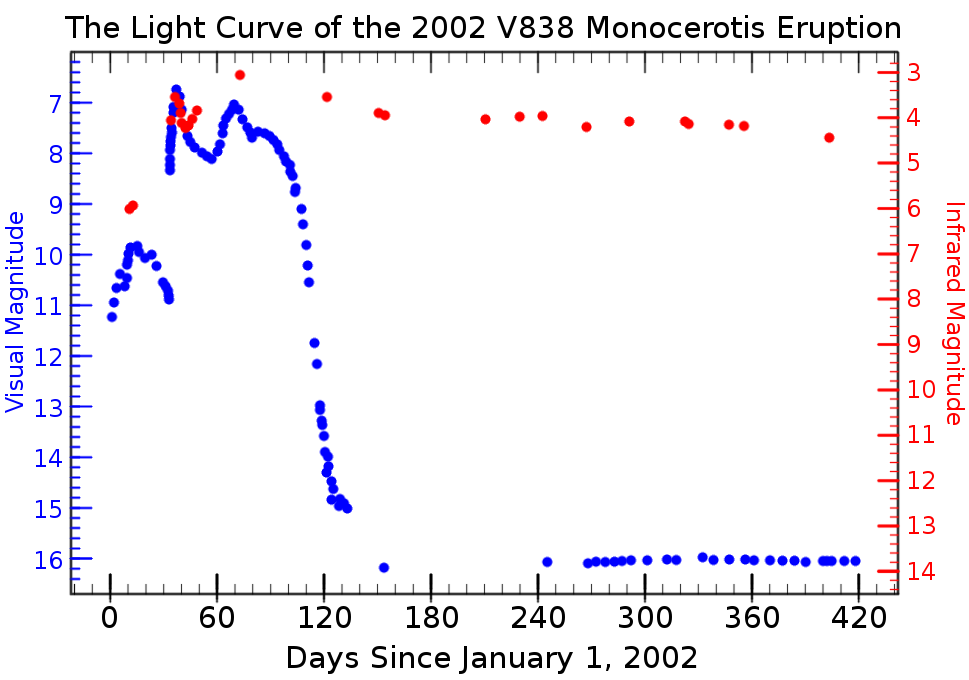
Light Curve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and transiting extrasolar planets, or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, a cataclysmic variable star, a supernova or a microlensing event or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of the light curve, together with other observations, can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces it or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the apparent magnitude of a variable star over time are commonly used to visualise and analyse their behaviour. Although the categorisation of variable star types is increasingly done from their s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

