|
Lubny
Lubny ( uk, Лубни́, ), is a city in Poltava Oblast (province) of central Ukraine. Serving as the administrative center of Lubny Raion (district), the city itself is administratively incorporated as a city of oblast significance and does not belong to the raion. Population: History Lubny is reputed to be one of the oldest cities in Ukraine, allegedly founded in 988 by knyaz (prince) Vladimir the Great (Volodymyr) of Kyiv. The first written record, however, dates from 1107. Initially, it was a small wooden fortress above the Sula River. The fortress quickly grew, and in the 15th or 16th century, it was owned by the powerful Wisniowiecki family. The town was ruled by Magdeburg rights and had a coat of arms. In 1596, Lubny was the site of the last battle of Severyn Nalyvaiko against the Poles. In the 17th century the city was one of the largest in the area. In 1638 it had 2,646 inhabitants. After Khmelnytsky Uprising, between 1648 and 1781, the town was the headquarters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubny Raion
Lubny ( uk, Лубни́, ), is a city in Poltava Oblast (province) of central Ukraine. Serving as the administrative center of Lubny Raion (district), the city itself is administratively incorporated as a city of oblast significance and does not belong to the raion. Population: History Lubny is reputed to be one of the oldest cities in Ukraine, allegedly founded in 988 by knyaz (prince) Vladimir the Great (Volodymyr) of Kyiv. The first written record, however, dates from 1107. Initially, it was a small wooden fortress above the Sula River. The fortress quickly grew, and in the 15th or 16th century, it was owned by the powerful Wisniowiecki family. The town was ruled by Magdeburg rights and had a coat of arms. In 1596, Lubny was the site of the last battle of Severyn Nalyvaiko against the Poles. In the 17th century the city was one of the largest in the area. In 1638 it had 2,646 inhabitants. After Khmelnytsky Uprising, between 1648 and 1781, the town was the headquarters o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubny Regiment
The Lubny Regiment ( uk, Лубенський полк, translit=Lubens’kyi polk, russian: Лубенский полк) was one of ten territorial-administrative subdivisions of the Cossack Hetmanate. The regiment's capital was the city of Lubny, now in Poltava Oblast of central Ukraine. Other major cities of the regiment were Pyriatyn, Hlynsk and Romny. The Lubny Regiment was founded in 1649, and was combined with the Myrhorod Regiment in 1658. During combination, 7 sotnias from the Myrhorod Regiment, 4 from the Kropyvna Regiment, and 2 from the Poltava Regiment were added into the Lubny Regiment. After reformation, the regiment consisted of a total of 13 sotnias, and later on in the 18th century — of 23 sotnias. According to documents of 1723, the regiment consisted of 2,687 land cossacks, and 3,968 horseback cossacks. In 1781, the regiment was officially abolished, and its territory was reformed into the Kiev and Chernigov Governorate The Chernigov Governorate (rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeremi Wiśniowiecki
Prince Jeremi Wiśniowiecki ( uk, Ярема Вишневецький – Yarema Vyshnevetsky; 1612 – 20 August 1651) nicknamed ''Hammer on the Cossacks'' ( pl, Młot na Kozaków), was a notable member of the aristocracy of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Prince of Wiśniowiec, Łubnie and Chorol in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the father of the future King of Poland, Michael I. A notable magnate and military commander with Ruthenian and Moldavian origin, Wiśniowiecki was heir of one of the biggest fortunes of the state and rose to several notable dignities, including the position of voivode of the Ruthenian Voivodship in 1646. His conversion from Eastern Orthodoxy to Roman Catholicism caused much dissent in Ruthenian (Ukrainian) lands (part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). Wiśniowiecki was a successful military leader as well as one of the wealthiest magnates of Poland, ruling over lands inhabited by 230,000 people. Biography Youth Jeremi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
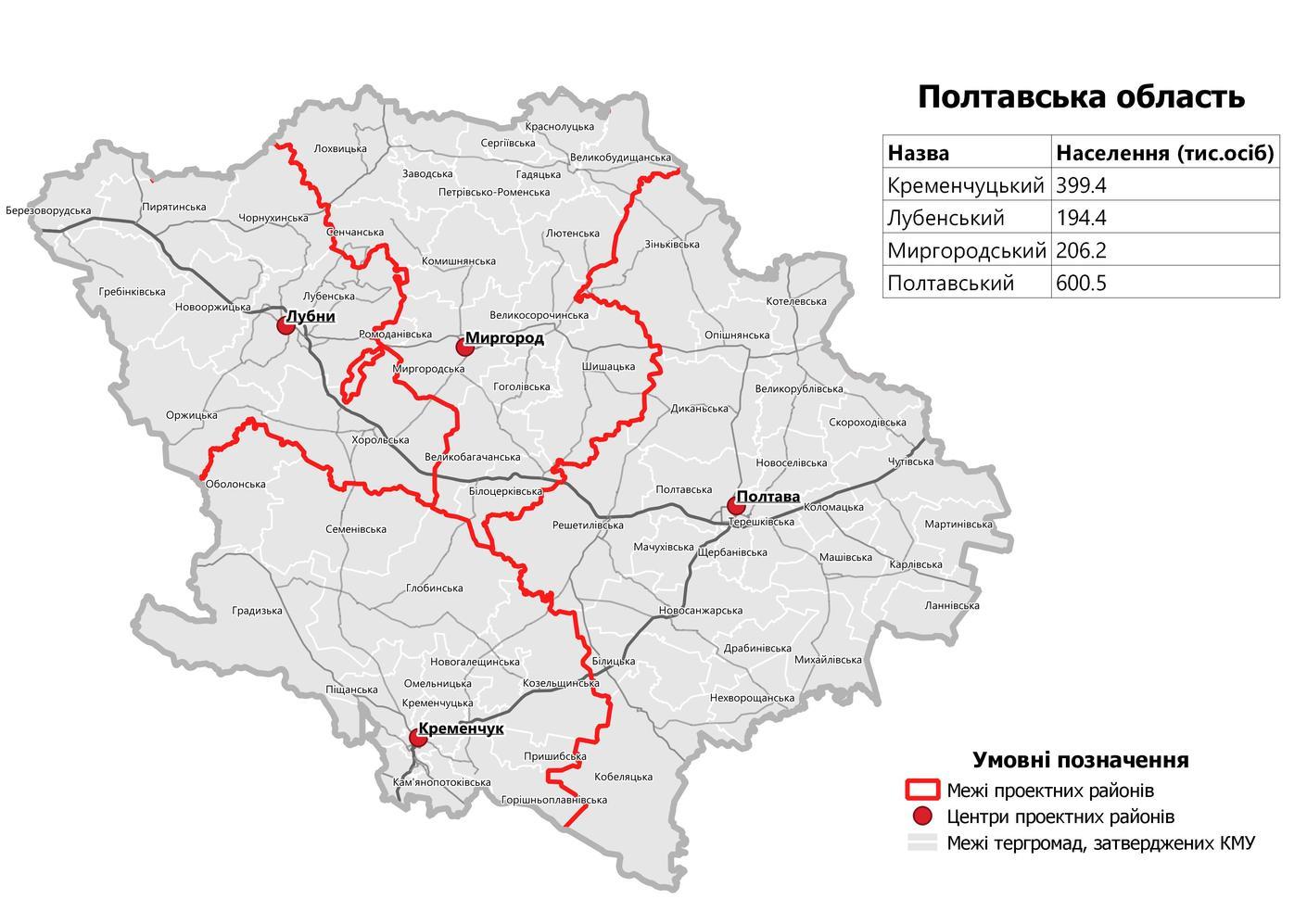
Poltava Oblast
Poltava Oblast ( uk, Полта́вська о́бласть, translit=Poltavska oblast; also referred to as Poltavshchyna – uk, Полта́вщина, literally 'Poltava Country') is an oblast (province) of central Ukraine. The administrative center of the oblast is the city of Poltava. Most of its territory is part of the historic Cossack Hetmanate (its southern regions: Poltava, Myrhorod, Lubny, and Hadiach). Population: Two other important cities there are Horishni Plavni and Kremenchuk. History During the 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine, the town of Myrhorod was bombed. However as of April 2022, there has been no ground fighting and the province remains completely under Ukrainian control. Geography Poltava Oblast is situated in the central part of Ukraine. Located on the left bank of Dnieper, Poltava region was part of the Cossack Hetmanate. It has an area of 28,800 km2. The oblast borders upon Chernihiv, Sumy, Kharkiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Kirovohrad, Cherkasy and K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poltava Governorate
The Poltava Governorate (russian: Полтавская губерния, Poltavskaya guberniya; ua, Полтавська Губернія, translit=Poltavska huberniia) or Poltavshchyna was a Governorate (Russia), gubernia (also called a province or government) in the historical Left-bank Ukraine region of the Russian Empire. It was officially created in 1802 from the disbanded Little Russia Governorate (1796–1802), Malorossiya Governorate, which was split between the Chernigov Governorate and Poltava Governorate with an administrative center of Poltava. Administrative division It was administered by 15 : *Gadyachsky Uyezd (Gadyach – Гадячъ) (Hadiach) *Zenkovsky Uyezd (Zinkiv, Zenkov – Зеньковъ) (Zinkiv) *Zolotonoshsky Uyezd (Zolotonosha – Золотоноша) *Kobelyaksky Uyezd (Kobeliaky – Кобеляки) *Konstantinogradsky Uyezd (Konstantinograd – Константиноградъ) (modern Krasnohrad) *Kremenchugsky Uyezd (Kremenchug – Кре� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raions Of Ukraine
Raions of Ukraine (often translated as "districts"; Ukrainian: ра́йон, tr. ''raion''; plural: райо́ни, tr. ''raiony'') are the second level of administrative division in Ukraine, below the oblast. Raions were created in a 1922 administrative reform of the Soviet Union, to which Ukraine, as the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, belonged. On 17 July 2020, the Verkhovna Rada (Ukraine's parliament) approved an administrative reform to merge most of the 490 raions, along with the "cities of regional significance", which were previously outside the raions, into just 136 reformed raions. Most tasks of the raions (education, healthcare, sport facilities, culture, and social welfare) were taken over by new hromadas, the subdivisions of raions. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severyn Nalyvaiko
Severyn (Semeriy) Nalyvaiko (, , in older historiography also ''Semen Nalewajko'', died 21 April 1597) was a leader of the Ukrainian Cossacks who became a hero of Ukrainian folklore. He led the failed Nalyvaiko Uprising for which he was tortured and executed in Warsaw. The Decembrist poet Kondraty Ryleyev wrote a poem about him."Nalyvaiko, Severyn" ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'', vol. 3 (1993). Biography Nalyvaiko was born in the town of not far from into a |
City Of Regional Significance (Ukraine)
City of regional significance ( uk, місто обласного значення, ''misto oblasnoho znachennia'') in Ukraine was a type of second-level administrative division or municipality, the other type being raions (districts). In the first-level division of oblasts, they were referred to as ''cities of oblast significance''; in the first-level autonomous republic of Crimea, they were ''cities of republican significance''. The designation was created with the introduction of oblasts in 1932. It was abolished in a 2020 reform that merged raions together and integrated the city municipalities into them. Such city municipality was complex and usually combined the city proper and adjacent populated places. The city of regional (oblast) significance was governed by a city council known as ''mis'krada'', which was chaired by a mayor. There were instances where a municipality might have included only the city alone (city proper), while in others instances a municipality might ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiev Viceroyalty
Kiev Viceroyalty was created in the process of the Catherine's reform initiated by hers November 7, 1775 edict when the new administrative unit namestnichestvo (viceroyalty) was introduced. Description On September 16, 1781, an edict was issued to transform the Governorate into a Viceroyalty (''Kievskoye namestnichestvo''),Сергей Тархов, "Изменение административно-территориального деления России в XIII-XX в."pdf, ''Логос'' сс. 65–101, (Ivan Fundukley. ''Statistical Description of Kiev Governorate''. St. Petersburg, 1852) Governors of Viceroyalty Governor-Generals (Viceroys) * 1782—1796 — Petr Rumyantsev ** 1791—1793 — Mikhail Krechetnikov Michael N. Krechetnikov (russian: Михаил Никитич Кречетников, 1729, Moscow, Russian Empire – 9 May 1793, Medzhybizh, Podolie Vice-Royalty, Russian Empire) was a Russian military commander and General of Infantry (Genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sula River
The Sula ( uk, Сула́; russian: Су́ла) is a left tributary of the Dnieper with a total length of 363 km and a drainage basin of 19,600 km². The river flows into the Dnieper through the Kremenchuk Reservoir, with which it forms a large delta with numerous islands, on which rare kinds of birds live. An important tributary is the Uday, smaller ones being Orzhytsya, Sliporid, Romen and Tern. Large cities located on the river are Romny, Lokhvytsia and Lubny. The river's name evokes slow or muddy waters considering the words it is related to: Lithuanian/ Latvian ''sulà'' "birch sap", Old Prussian ''sulo'' "curdled milk", Norwegian dialectal ''saula'' "dirt", Sanskrit '' súrā'' "spiritous liquor", and Avestan ''hurā'' "intoxicating drink, kumis". Another etymology of the hydronym A hydronym (from el, ὕδρω, , "water" and , , "name") is a type of toponym that designates a proper name of a body of water. Hydronyms include the proper names of rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyezd
An uezd (also spelled uyezd; rus, уе́зд, p=ʊˈjest), or povit in a Ukrainian context ( uk, повіт), or Kreis in Baltic-German context, was a type of administrative subdivision of the Grand Duchy of Moscow, the Russian Empire, and the early Russian SFSR, which was in use from the 13th century. For most of Russian history, uezds were a second-level administrative division. By sense, but not by etymology, ''uezd'' approximately corresponds to the English "county". General description Originally describing groups of several volosts, they formed around the most important cities. Uezds were ruled by the appointees ('' namestniki'') of a knyaz and, starting from the 17th century, by voyevodas. In 1708, an administrative reform was carried out by Peter the Great, dividing Russia into governorates. The subdivision into uyezds was abolished at that time but was reinstated in 1727, as a result of Catherine I's administrative reform. By the Soviet administrative reform of 1923 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |