|
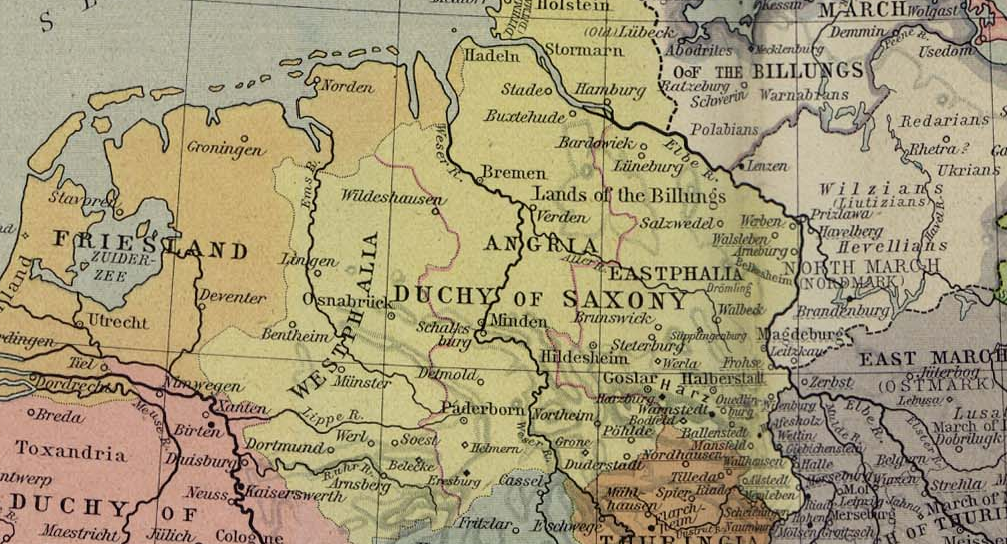
Lothair Udo II, Margrave Of The Nordmark
Lothair Udo II (c. 1025 – 1082) was Margrave of the Nordmark from 1057 until his death and also Count of Stade (as Lothair Udo III). He was the only son of Lothair Udo I of the Udonids and Adelaide of Rheinfelden. The power base of his family lay around Harsefeld and Stade, but through advantageous marriages, they had control of almost the entire eastern third of the Duchy of Saxony in lands and rights. In 1044, William became Margrave of the Nordmark. In 1056, the Saxons were defeated by the Liutizi at the Battle of Pritzlawa (Havelmündung), and William was killed. The Emperor Henry III and Lothair Udo I died the same year. Lothair Udo II came into a very strong position and became margrave the next year. Lothair initially placed himself in opposition to the Billung family and Adalbert of Bremen. Adalbert had won great influence over the young King Henry IV and he designed to extend the influence of the Archdiocese of Hamburg-Bremen over the various small counties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margrave Of The Nordmark
The Northern March or North March (german: Nordmark) was created out of the division of the vast ''Marca Geronis'' in 965. It initially comprised the northern third of the ''Marca'' (roughly corresponding to the modern state of Brandenburg) and was part of the territorial organisation of areas conquered from the Wends. A Lutician rebellion in 983 reversed German control over the region until the establishment of the March of Brandenburg by Albert the Bear in the 12th century. Slavic background During the Migration Period, many Germanic peoples began migrating towards the Roman frontier. In the northeast they were replaced primarily by Slavic peoples (Veleti, later Lutici). The first Slavs were certainly in the Brandenburg area by 720, after the arrival of the Avars in Europe. These Slavs had come via Moravia, where they had arrived in the mid-seventh century. The remnants of the Germanic Semnoni were absorbed into these Slavic groups. The group of people who settled at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billung
The House of Billung was a dynasty of Saxon noblemen in the 9th through 12th centuries. The first known member of the house was Count Wichmann, mentioned as a Billung in 811. Oda, the wife of Count Liudolf, oldest known member of the Liudolfing House, was also a Billung as was Matilda of Ringelheim. In the 10th century, the property of the family was centered in the Bardengau around Lüneburg and they controlled the march named after them. In the middle of the 10th century, when the Saxon dukes of the House of Liudolfing had also become German kings, King Otto the Great entrusted more and more of his ducal authority to Hermann Billung. For five generations, the House of Billung ruled the Duchy of Saxony. The house submerged into the Welf and Ascania dynasties when Duke Magnus died in 1106 without sons; the family's property was divided between his two daughters. His daughter Wulfhilde married Henry IX, Duke of Bavaria, a member of the House of Welf; his daughter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto II, Duke Of Swabia
Otto II ( 995 – 7 September 1047), a member of the Ezzonid dynasty, was Count Palatine of Lotharingia from 1034 until 1045 and Duke of Swabia from 1045 until his death. Life Otto was the son of the Lotharingian count palatine Ezzo (955–1034) and his wife Matilda (979–1025), a daughter of Emperor Otto II and his consort Theophanu. He was a member of the Ezzonian dynasty. Otto's elder brother Herman became Archbishop of Cologne in 1036; his sister Richeza married the Polish king Mieszko II Lambert in 1013. Upon the death of his father in 1034, Otto succeeded him as count palatine as well as count in Deutz and in the Rhenish ''Auelgau'', as his elder brother Liudolf had died already in 1031. He also served as protector (''Vogt'') of Brauweiler Abbey near Cologne, which had been founded by his parents. In the conflict with Duke Godfrey III of Lower Lorraine, Otto remained a loyal supporter of the Salian king Henry III. In turn Henry vested him with the princeless Duch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richenza Of Swabia
Richenza (also spelled as ''Richeza'' or ''Richza'') ( – before 1083) was a German noblewoman. By her first marriage, she was Countess of Werl. By her second marriage, she was Countess of Northeim, and from 1061 to 1070, Duchess of Bavaria. She is known as Richenza of Swabia based on the theory that she was a daughter of Duke Otto II of Swabia. However, that theory is hard to maintain with the current state of research. Descent Emil Kimpen published a theory in 1933, that Richenza and Ida of Elsdorf might be daughters of Otto II of the Ezzonian dynasty, who was count palatine of Swabia and from 1061 duke of Swabia. Although Kimpen himself later rejected this theory, his students Lange and Hucke included this theory in their theses about the counts of Northeim and Stade. Extensive research into the theory about Ida of Elsdorf has not confirmed this theory. Much less research was done into the theory that her alleged sister Richenza was a daughter of Otto II. On the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Homburg
The First Battle of Langensalza was fought on 9 June 1075 between forces of King Henry IV of Germany and several rebellious Saxon noblemen on the River Unstrut near Langensalza in Thuringia. The battle was a complete success for Henry, resulting in the subjugation of the Saxons shortly before the Investiture Controversy commenced. In Germany the battle is known as the ''Schlacht bei Homburg an der Unstrut'', after a nearby ''Kaiserpfalz'' and monastery. Background The Salian king Henry IV had inherited the quarrels with the Saxons from his father Emperor Henry III, whose long and costly sojournments at the Imperial Palace of Goslar had annoyed the local nobles. From the start of his reign in 1065, 15-year-old Henry IV suffered numerous setbacks enforcing his Imperial authority in Saxony after the regency of his mother Agnes of Poitou. Attempts to restore the rights over the Harz forests were not received well by the Saxon freedmen, and efforts to extend the crownlands in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Of Nordheim
Otto of Nordheim (c. 1020 – 11 January 1083) was Duke of Bavaria from 1061 until 1070. He was one of the leaders of the Saxon Rebellion in 1073-75 and the Great Saxon Revolt of 1077-88 against King Henry IV of Germany. Life Family Otto was born about 1020, the son of Count Bernard of Nordheim (d. about 1040) and his wife Eilika. The rich and influential Saxon comital dynasty of Nordheim was first mentioned about 950, its descendance has not been conclusively established: there is possibly a relationship with the Immedinger family of legendary Duke Widukind, while according to the Magdeburg archbishop Eric of Brandenburg, Otto's grandfather Siegfried I of Nordheim was a son of Count Siegfried of Luxembourg. The Nordheim counts held large Saxon estates on the upper Leine and Werra rivers as well as on the Weser and its Diemel and Nethe tributaries and on the lower Elbe river. They also acted as ''Vogts'' (reeves) of the Corvey, Gandersheim, Helmarshausen, Bursfelde, and Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liemar, Archbishop Of Bremen
Liemar (unknown – 16 May 1101, in Bremen) was archbishop of Hamburg-Bremen from 1072 to 1101, and an important figure of the early Investiture Contest. He was a supporter of Emperor Henry IV from 1073. In 1074 the papal legates Gerald of Ostia and Hubert of Palestrina put pressure on him to hold a local synod; he resisted, was suspended, and by 1075 his views against papal interference with bishops had hardened. In 1080, he attended the Synod of Brixen that condemned Pope Gregory VII. With Benno II of Osnabrück Benno II ( – 27 July 1088) was Bishop of Osnabrück from 1068 until his death. He served as a close advisor and architect of Emperor Henry IV. In 1080 he founded the Benedictine abbey of Iburg Castle. Life He was born at Löhningen (today par ... he commissioned the anti-papal polemic of Wido of Osnabrück around 1085. Liemar was one of many bishops who was irked by Gregory VII's encroachment of episcopal autonomy. In a letter to Bishop Hezilo of Hildesheim, Liem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bardowiek
Bardowiek () is an abandoned village in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It lies in the territory of the municipality Selmsdorf. History The earliest surviving record of Bardowiek is in the Ratzeburger Hufenregister and dates from 1292. The town was virtually destroyed during the Thirty Years War, but was rebuilt after the war’s end in 1648. During the early years of the German Democratic Republic there were still approximately forty residents. However, Bardowiek found itself in the five kilometre wide closed zone, a strip of land cleared by the government directly to the east of the Inner German border. In 1960, all the farmsteads were incorporated into the farming collective of Palingen. Destruction of the former farms began in 1977 and was completed only in 1989. After the reunification, surviving former residents sought to rebuild the village. However, their aspirations have been thwarted by a succession of legal disputes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Of Zeitz
The March of Zeitz (german: Mark Zeitz) was a march of the Holy Roman Empire. It was created by Emperor Otto I in the division of the ''marca Geronis'' in 965, following the death of Gero the Great. Its capital was Zeitz. Its first and only margrave was Wigger. In 982, Zeitz was reunited with the marches of Meissen and Merseburg under Ricdag, who thus temporarily reunited all of the southern ''marca Geronis'' save the Saxon Ostmark. In 983, Zeitz was overrun by the Sorbs and the marcher territory fell into the hands of the Slavs. Nevertheless, the march of Zeitz, along with the later March of Lusatia, was a recurring division of the Meissen march during the reign of the Emperor Henry II. Sources * Thompson, James Westfall. ''Feudal Germany, Volume II''. New York: Frederick Ungar Publishing Co., 1928. *Bernhardt, John W. ''Itinerant Kingship and Royal Monasteries in Early Medieval Germany, c. 936–1075''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1993. {{coord missing, Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably diverse both genetically and culturally, and relations between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports of Bremerhaven and Nordenham. The latter is on the Butjadingen Peninsula. It then merges into the North Sea via two highly saline, estuarine mouths. It connects to the canal network running east-west across the North German Plain. The river, when combined with the Werra (a dialectal form of "Weser"), is long and thus, the longest river entirely situated within Germany (the Main, however, is the longest if the Weser and Werra are not combined). The Weser itself is long. The Werra rises in Thuringia, the German state south of the main projection (tongue) of Lower Saxony. Etymology "Weser" and "Werra" are the same words in different dialects. The difference reflects the old linguistic border between Central and Low German, passin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, northwest of Hamburg. Its total length is . The Elbe's major tributaries include the rivers Vltava, Saale, Havel, Mulde, Schwarze Elster, and Ohře. The Elbe river basin, comprising the Elbe and its tributaries, has a catchment area of , the twelfth largest in Europe. The basin spans four countries, however it lies almost entirely just in two of them, Germany (65.5%) and the Czech Republic (33.7%, covering about two thirds of the state's territory). Marginally, the basin stretches also to Austria (0.6%) and Poland (0.2%). The Elbe catchment area is inhabited by 24.4 million people, the biggest cities within are Berlin, Hamburg, Prague, Dresden and Leipzig. Etymolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |