|
Lincolnshire Limestone (England)
The Lincolnshire Limestone Formation is a geological formation in England, part of the Inferior Oolite Group of the (Bajocian) Middle Jurassic strata of eastern England. It was formed around 165 million years ago, in a shallow, warm sea on the margin of the London Platform and has estuarine beds above and below it. The maximum known thickness is 40.2 metres, at around TF9730, while four kilometres further west it is 18.3 metres thick at its outcrop in the upper Witham valley. It fades out in the south, around Kettering in Northamptonshire. There are two sub-divisions, the Upper and Lower Lincolnshire Limestone Members respectively. The dividing marker is the 'Crossi' bed which is distinguished by the fossils of ''Acanthothris crossi'' it contains. The Crossi bed forms the top of the Lower Lincolnshire limestone. The bottom of the Lower Lincolnshire limestone has some of the characteristics of the underlying Lower Estuarine Series, in that it tends to contain more than usual amoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Lincolnshire
The ceremonial county of Lincolnshire (composed of the shire county of Lincolnshire, plus the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire and North-East Lincolnshire) is the second largest of the English counties and one that is predominantly agricultural in character. Despite its relatively large physical area, it has a comparatively small population (of less than 1 million people). The unusually low population density that arises gives the county a very different character from the much more densely populated an urbanised counties of south-east and northern England, and is, in many ways, key to understanding the nature of the county (and perhaps even its people). Classification For the purposed of a general geographical classification the county can be broken down into a number of sub-regions: *The Lincolnshire coast. *Lincolnshire Fens: a region of flat, marshy land (much of it reclaimed from the sea) that predominates in the southern and south-eastern areas of the county (most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy Of The United Kingdom
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers ( strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first geologic ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Bytham Quarry
Castle Bytham quarry is a disused quarry located close to the centre of the village of Castle Bytham, Lincolnshire, England. It is famous for the exposure of ''Laeviuscula'' Zone ammonite fauna has allowed the dating of the Upper Lincolnshire limestone - can be zoomed to show the quarries formation to the Bajocian era, and thereby dating other deposits around Europe. When the quarry was opened in the 1850s a Bronze Age arrowhead and a Saxon burial were found in the overburden. Although Ironstone quarrying was common to the west and north, this quarry was worked for Limestone. A kiln adjacent to the railway line was used to produce slaked lime for the agricultural trade and a small amount of cement. The quarry was worked by the ''Castle Lime company'. The quarry has been left to return to nature since its closure and is now a recognised Site of Special Scientific Interest or SSSI. It has most recently been used as a temporary car park for the annual Castle Bytham Mid-Summer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Types Of Limestone
This is a list of types of limestone arranged according to location. It includes both formal stratigraphic unit names and less formal designations. Africa Egypt *Tura limestone, used for the Great Pyramid casing stones *Mokattam limestone; Great Pyramid core stones and head of the Great Sphinx are of the "Member III" stratum * Galala marble (a type of limestone, not a true marble) Asia India * * Israel (West Bank) * * Europe Austria * Belgium *, (not a "true marble"; Devonian limestone) * * Croatia * France * *, or "Paris stone" (city buildings are widely faced with it) **, or Oise, limestone (variety of Lutetian) * *, in the Loire Valley Germany * * Gibraltar * Ireland * , not a "true marble"; fossiliferous Carboniferous limestone. Italy * , not a "true marble"; fossiliferous limestone United Kingdom England: * (not a "true marble"; Carboniferous limestone) * * * , the famous London Stone is made of this. * (not a "true slate"; thin-bedded limestone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
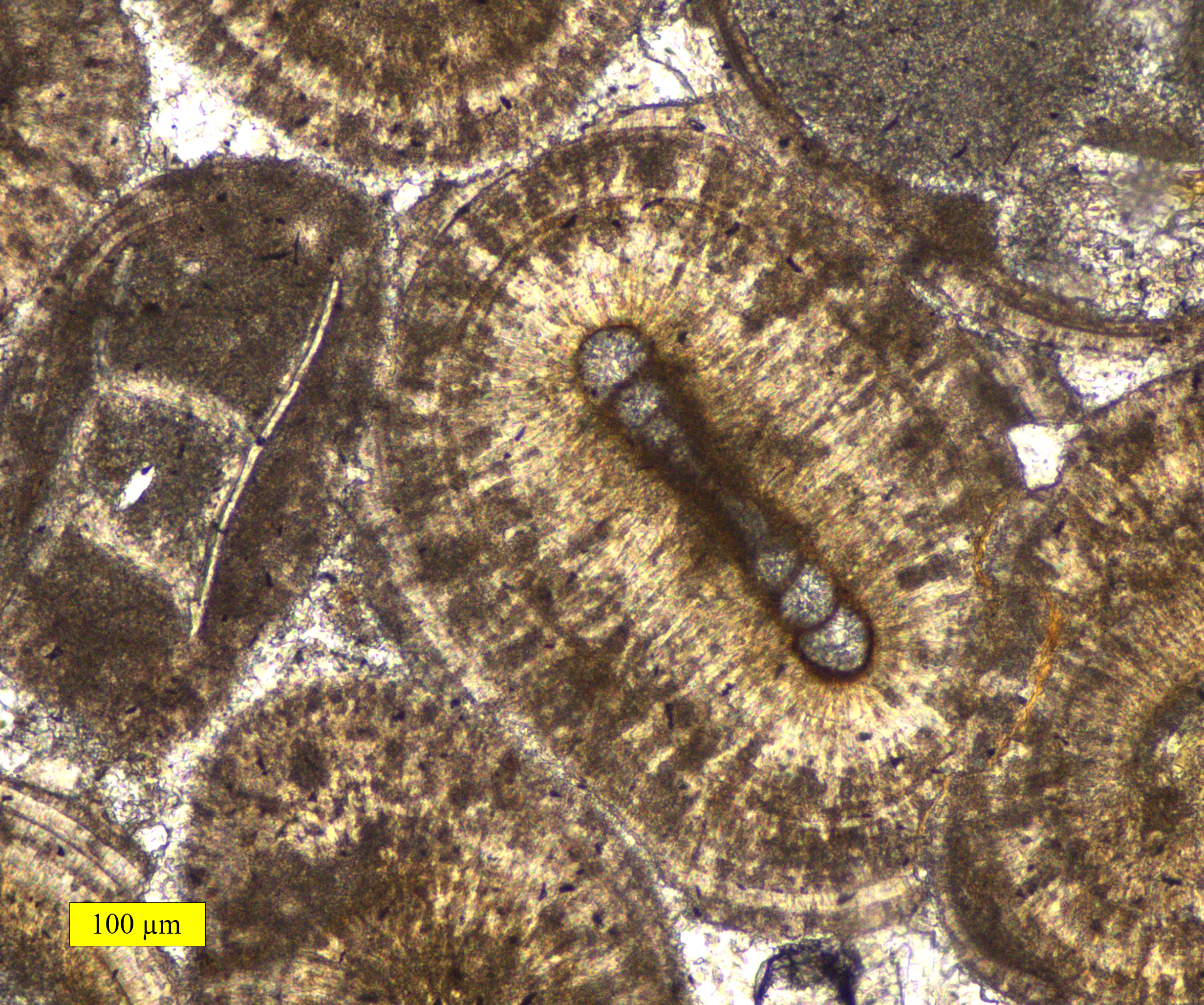
Oolite
Oolite or oölite (''egg stone'') is a sedimentary rock formed from ooids, spherical grains composed of concentric layers. The name derives from the Ancient Greek word for egg (ᾠόν). Strictly, oolites consist of ooids of diameter 0.25–2 millimetres; rocks composed of ooids larger than 2 mm are called pisolites. The term ''oolith'' can refer to oolite or individual ooids. Composition Ooids are most commonly composed of calcium carbonate ( calcite or aragonite), but can be composed of phosphate, clays, chert, dolomite or iron minerals, including hematite. Dolomitic and chert ooids are most likely the result of the replacement of the original texture in limestone. Oolitic hematite occurs at Red Mountain near Birmingham, Alabama, along with oolitic limestone. They are usually formed in warm, supersaturated, shallow, highly agitated marine water intertidal environments, though some are formed in inland lakes. The mechanism of formation starts with a small fragment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ooid
Ooids are small (commonly ≤2 mm in diameter), spheroidal, "coated" (layered) sedimentary grains, usually composed of calcium carbonate, but sometimes made up of iron- or phosphate-based minerals. Ooids usually form on the sea floor, most commonly in shallow tropical seas (around the Bahamas, for example, or in the Persian Gulf). After being buried under additional sediment, these ooid grains can be cemented together to form a sedimentary rock called an ''oolite''. Oolites usually consist of calcium carbonate; these belong to the limestone rock family. Pisoids are similar to ooids, but are larger than 2 mm in diameter, often considerably larger, as with the pisoids in the hot springs at Carlsbad (Karlovy Vary) in the Czech Republic. Formation An ooid forms as a series of concentric layers around a nucleus. The layers contain crystals arranged radially, tangentially or randomly. The nucleus can be a shell fragment, quartz grain or any other small fragment. Most mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collyweston Stone Slate
The Collyweston Slater pub in Collyweston with a Collyweston slate roof Collyweston stone slate is a traditional roofing material found in central England. It is not a proper slate but a limestone found in narrow beds. It is considerably heavier than true slate. The slates are quarried near the village of Collyweston in Northamptonshire, near Stamford and close to the borders of Lincolnshire and Rutland. Traditionally the mined stone was left outside for three winters until the frost revealed layers that could be broken ("clived") into flat slates. In the late 1990s, English Heritage (now Historic England) worked with the Burghley Estate and Sheffield Hallam University to develop an artificial system to reproduce the freeze-thaw cycle needed for production of slates. In 2012, when new slates were needed to reroof parts of Apethorpe Palace, further testing was commissioned by English Heritage to develop the artificial frosting and new Collyweston slates have been produced. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Estuarine Series
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009 The Lower Estuarine Series, also called in more modern publications, the Grantham Formation, is a relatively complex but generally thin set of geological strata which are usually considered as a group. It forms a lower part of the (Bajocian) Inferior Oolite Group, which lies in the Middle Jurassic. Where found, it is normally above the Northampton sand and below the Lower Lincolnshire Limestone Member. The group is found in the East Midlands of England and was formed when the London-Brabant Island was drifting through the low northern latitudes, in conditions represented today by the Sahara Desert , photo = Sahara real color.jpg , photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972 , map = , map_image = , location = , country = , country1 = , .... The land was eroded by wind action and by occasional downpours which carried the debris to the marg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire (; abbreviated Northants.) is a county in the East Midlands of England. In 2015, it had a population of 723,000. The county is administered by two unitary authorities: North Northamptonshire and West Northamptonshire. It is known as "The Rose of the Shires". Covering an area of 2,364 square kilometres (913 sq mi), Northamptonshire is landlocked between eight other counties: Warwickshire to the west, Leicestershire and Rutland to the north, Cambridgeshire to the east, Bedfordshire to the south-east, Buckinghamshire to the south, Oxfordshire to the south-west and Lincolnshire to the north-east – England's shortest administrative county boundary at 20 yards (19 metres). Northamptonshire is the southernmost county in the East Midlands. Apart from the county town of Northampton, other major population centres include Kettering, Corby, Wellingborough, Rushden and Daventry. Northamptonshire's county flower is the cowslip. The Soke of Peterborough fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |