|
Lake Vida
Lake Vida is a hypersaline lake in Victoria Valley, the northernmost of the large McMurdo Dry Valleys, on the continent of Antarctica. It is isolated under year-round ice cover, and is considerably more saline than seawater. It came to public attention in 2002 when microbes frozen in its ice cover for more than 2,800 years were successfully thawed and reanimated. Introduction Lake Vida is one of the largest lakes in the McMurdo Dry Valley region and is a closed-basin endorheic lake. The permanent surface ice on the lake is the thickest non-glacial ice on earth, reaching a depth of at least . The ice at depth is saturated with brine that is seven times as saline as seawater. The high salinity allows the brine to remain liquid at an average yearly water temperature of . The ice cap has sealed the saline brine from external air and water for thousands of years creating a time capsule for ancient DNA. This combination of lake features make Lake Vida a unique lacustrine ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Dry Valleys
The McMurdo Dry Valleys are a row of largely snow-free valleys in Antarctica, located within Victoria Land west of McMurdo Sound. The Dry Valleys experience extremely low humidity and surrounding mountains prevent the flow of ice from nearby glaciers. The rocks here are granites and gneisses, and glacial tills dot this bedrock landscape, with loose gravel covering the ground. It is one of the driest places on Earth and has not seen rain for nearly two million years. The region is one of the world's most extreme deserts, and includes many features including Lake Vida, a saline lake, and the Onyx River, a meltwater stream and Antarctica's longest river. Although no living organisms have been found in the permafrost here, endolithic photosynthetic bacteria have been found living in the relatively moist interior of rocks, and anaerobic bacteria, with a metabolism based on iron and sulfur, live under the Taylor Glacier. The valleys are located within the McMurdo Valleys Antarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Doran
Peter T. Doran, Ph.D. is Professor of Geology and Geophysics and John Franks Endowed Chair at Louisiana State University. Prior to 2015, he was faculty in Earth and Environmental Sciences at the University of Illinois at Chicago. Doran specializes in polar regions, especially Antarctic climate and ecosystems. Doran was the lead author of a research paper about Antarctic temperatures that was published in the journal ''Nature'' in January 2002. Because he and his colleagues found that some parts of Antarctica had cooled between 1964 and 2000, his paper has been frequently cited by opponents of the global warming theory, such as Ann Coulter and Michael Crichton. In an opinion piece in the July 27, 2006 ''New York Times'', Doran characterized this as a "misinterpretation" and stated, "I have never thought such a thing ... I would like to remove my name from the list of scientists who dispute global warming." (The temporary phenomenon is related to the "hole" in the ozone. As th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
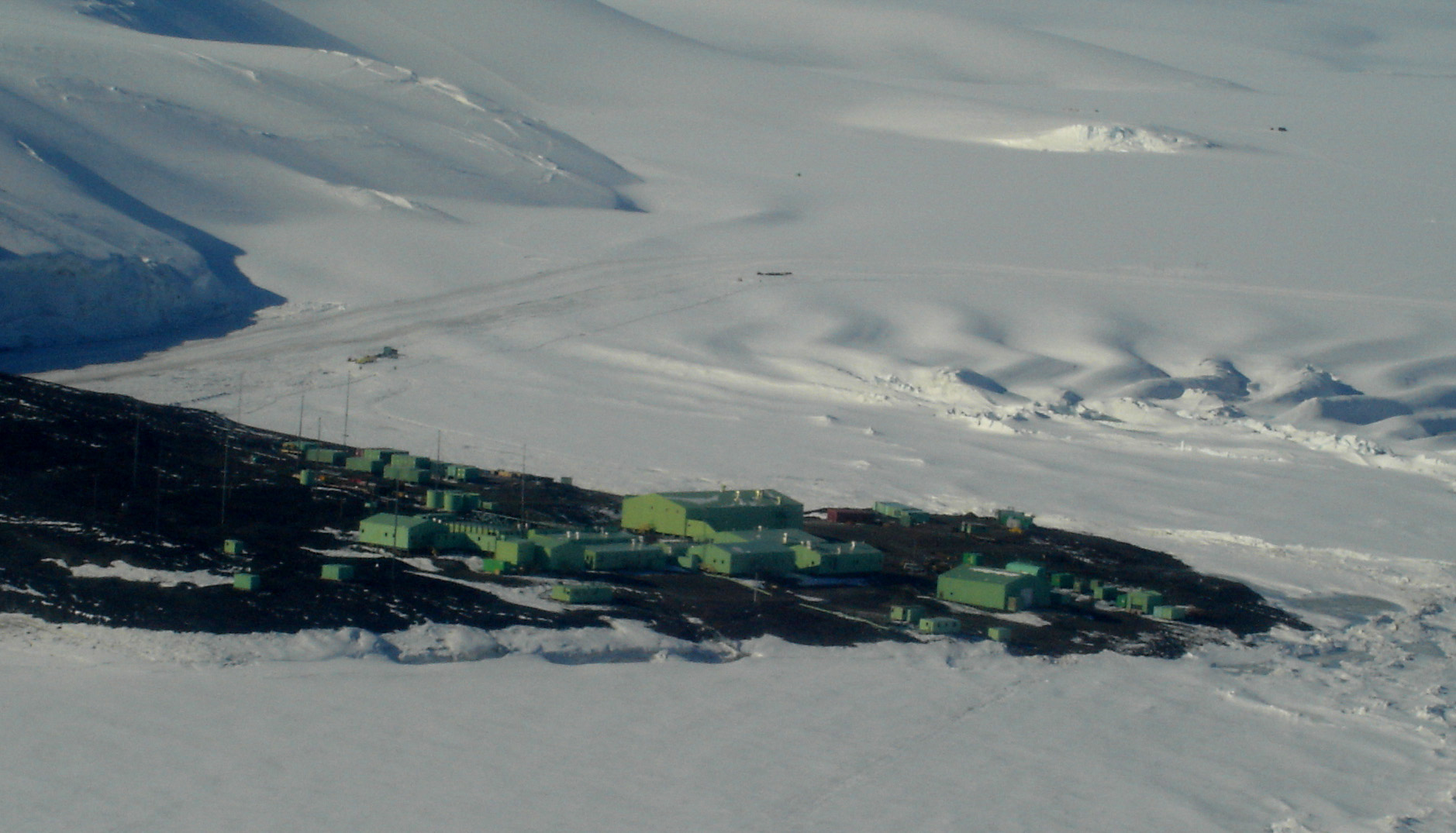
Scott Base
Scott Base is a New Zealand Antarctica, Antarctic research station at Pram Point on Ross Island near Mount Erebus in New Zealand's Ross Dependency territorial claim. It was named in honour of Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy, RN, leader of two United Kingdom, British expeditions to the Ross Sea area of Antarctica. The base was set up as support to field research and the centre for research into earth sciences, and now conducts research in many fields, operated by Antarctica New Zealand. The base is from the larger U.S. McMurdo Station via Pegasus Road. History Scott Base was originally constructed in support of the UK inspired and privately managed Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (TAE). The New Zealand government provided support for the TAE and also for the International Geophysical Year (IGY) project of 1957, five of whose members were attached to the Expedition. In February 1956, 10 months before the TAE and IGY parties were due to head to the Antarctic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
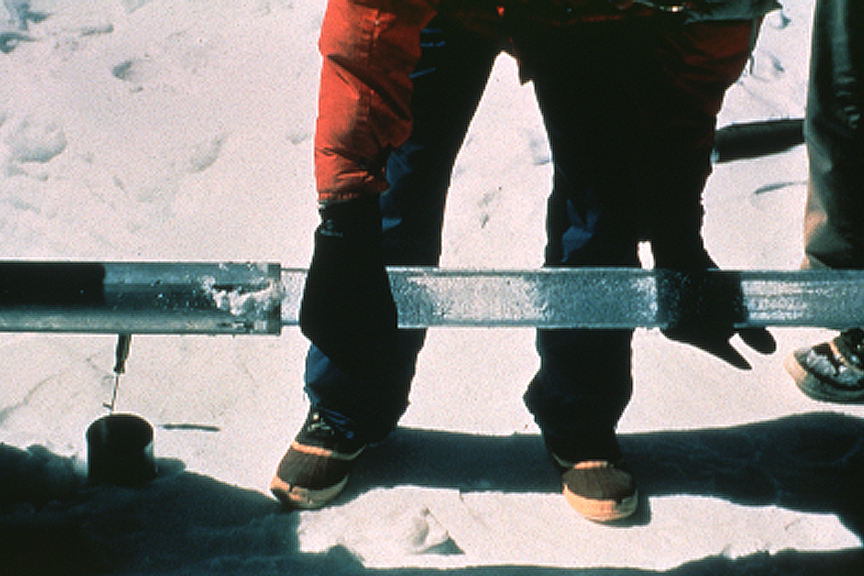
Ice Core
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier. Since the ice forms from the incremental buildup of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper ones, and an ice core contains ice formed over a range of years. Cores are drilled with hand augers (for shallow holes) or powered drills; they can reach depths of over two miles (3.2 km), and contain ice up to 800,000 years old. The physical properties of the ice and of material trapped in it can be used to reconstruct the climate over the age range of the core. The proportions of different oxygen and hydrogen isotopes provide information about ancient temperatures, and the air trapped in tiny bubbles can be analysed to determine the level of atmospheric gases such as carbon dioxide. Since heat flow in a large ice sheet is very slow, the borehole temperature is another indicator of temperature in the past. These data can be combined to find the climate model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geochemistry
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the entire Solar System, and has made important contributions to the understanding of a number of processes including mantle convection, the formation of planets and the origins of granite and basalt. It is an integrated field of chemistry and geology. History The term ''geochemistry'' was first used by the Swiss-German chemist Christian Friedrich Schönbein in 1838: "a comparative geochemistry ought to be launched, before geognosy can become geology, and before the mystery of the genesis of our planets and their inorganic matter may be revealed." However, for the rest of the century the more common term was "chemical geology", and there was little contact between geologists and chemists. Geochemistry emerged as a separate discipline after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology, and parasitology. Eukaryotic microorganisms possess membrane-bound organelles and include fungi and protists, whereas prokaryotic organisms—all of which are microorganisms—are conventionally classified as lacking membrane-bound organelles and include Bacteria and Archaea. Microbiologists traditionally relied on culture, staining, and microscopy. However, less than 1% of the microorganisms present in common environments can be cultured in isolation using current means. Microbiologists often rely on molecular biology tools such as DNA sequence based identification, for example the 16S rRNA gene sequence used for bacteria identification. Viruses have been variably classified as organisms, as they have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Recovery And Reinvestment Act Of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) (), nicknamed the Recovery Act, was a stimulus package enacted by the 111th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama in February 2009. Developed in response to the Great Recession, the primary objective of this federal statute was to save existing jobs and create new ones as soon as possible. Other objectives were to provide temporary relief programs for those most affected by the recession and invest in infrastructure, education, health, and renewable energy. The approximate cost of the economic stimulus package was estimated to be $787 billion at the time of passage, later revised to $831 billion between 2009 and 2019. The ARRA's rationale was based on the Keynesian economic theory that, during recessions, the government should offset the decrease in private spending with an increase in public spending in order to save jobs and stop further economic deterioration. The politics around the stimulus w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life On Mars
The possibility of life on Mars is a subject of interest in astrobiology due to the planet's proximity and similarities to Earth. To date, no proof of past or present life has been found on Mars. Cumulative evidence suggests that during the ancient Noachian time period, the surface environment of Mars had liquid water and may have been habitable for microorganisms, but habitable conditions do not necessarily indicate life. Scientific searches for evidence of life began in the 19th century and continue today via telescopic investigations and deployed probes. While early work focused on phenomenology and bordered on fantasy, the modern scientific inquiry has emphasized the search for water, chemical biosignatures in the soil and rocks at the planet's surface, and biomarker gases in the atmosphere. Mars is of particular interest for the study of the origins of life because of its similarity to the early Earth. This is especially true since Mars has a cold climate and lacks pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also the word for a book that catalogues the animals in such a manner. The term was first used b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude/longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme was the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction. There are two forms of reproduction: asexual and sexual. In asexual reproduction, an organism can reproduce without the involvement of another organism. Asexual reproduction is not limited to single-celled organisms. The cloning of an organism is a form of asexual reproduction. By asexual reproduction, an organism creates a genetically similar or identical copy of itself. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle for biologists. The two-fold cost of sexual reproduction is that only 50% of organisms reproduce and organisms only pass on 50% of their genes.John Maynard Smith ''The Evolution of Sex'' 1978. Sexual reproduction typically requires the sexual interaction of two specializ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thawing
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which increases the substance's temperature to the melting point. At the melting point, the ordering of ions or molecules in the solid breaks down to a less ordered state, and the solid "melts" to become a liquid. Substances in the molten state generally have reduced viscosity as the temperature increases. An exception to this principle is the element sulfur, whose viscosity increases in the range of 160 °C to 180 °C due to polymerization. Some organic compounds melt through mesophases, states of partial order between solid and liquid. First order phase transition From a thermodynamics point of view, at the melting point the change in Gibbs free energy ''∆G'' of the substances is zero, but there are non-zero changes in the enthalpy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)