|
Lévy Flight
A Lévy flight is a random walk in which the step-lengths have a Lévy distribution, a probability distribution that is heavy-tailed. When defined as a walk in a space of dimension greater than one, the steps made are in isotropic random directions. Later researchers have extended the use of the term "Lévy flight" to also include cases where the random walk takes place on a discrete grid rather than on a continuous space. The term "Lévy flight" was coined by Benoît Mandelbrot, who used this for one specific definition of the distribution of step sizes. He used the term Cauchy flight for the case where the distribution of step sizes is a Cauchy distribution, and Rayleigh flight for when the distribution is a normal distribution (which is not an example of a heavy-tailed probability distribution). The particular case for which Mandelbrot used the term "Lévy flight" is defined by the survivor function of the distribution of step-sizes, ''U'', being :\Pr(U>u) = \begin 1 &: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Walk
In mathematics, a random walk is a random process that describes a path that consists of a succession of random steps on some mathematical space. An elementary example of a random walk is the random walk on the integer number line \mathbb Z which starts at 0, and at each step moves +1 or −1 with equal probability. Other examples include the path traced by a molecule as it travels in a liquid or a gas (see Brownian motion), the search path of a foraging animal, or the price of a fluctuating stock and the financial status of a gambler. Random walks have applications to engineering and many scientific fields including ecology, psychology, computer science, physics, chemistry, biology, economics, and sociology. The term ''random walk'' was first introduced by Karl Pearson in 1905. Lattice random walk A popular random walk model is that of a random walk on a regular lattice, where at each step the location jumps to another site according to some probability distribution. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
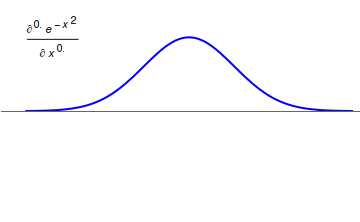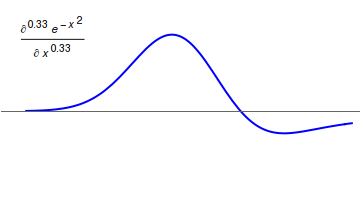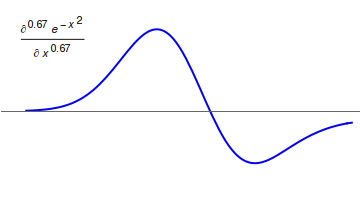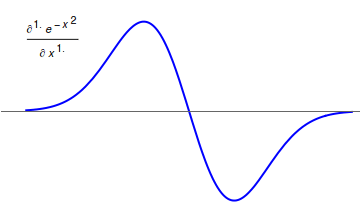
Fractional Calculus
Fractional calculus is a branch of mathematical analysis that studies the several different possibilities of defining real number powers or complex number powers of the differentiation operator D :D f(x) = \frac f(x)\,, and of the integration operator J The symbol J is commonly used instead of the intuitive I in order to avoid confusion with other concepts identified by similar I–like glyphs, such as identities. :J f(x) = \int_0^x f(s) \,ds\,, and developing a calculus for such operators generalizing the classical one. In this context, the term ''powers'' refers to iterative application of a linear operator D to a function f, that is, repeatedly composing D with itself, as in D^n(f) = (\underbrace_n)(f) = \underbrace_n (f)\cdots))). For example, one may ask for a meaningful interpretation of :\sqrt = D^\frac12 as an analogue of the functional square root for the differentiation operator, that is, an expression for some linear operator that, when applied ''twice'' to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silky Shark
The silky shark (''Carcharhinus falciformis''), also known by numerous names such as blackspot shark, gray whaler shark, olive shark, ridgeback shark, sickle shark, sickle-shaped shark and sickle silk shark, is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae, named for the smooth texture of its skin. It is one of the most abundant sharks in the pelagic zone, and can be found around the world in tropical waters. Highly mobile and migratory, this shark is most often found over the edge of the continental shelf down to . The silky shark has a slender, streamlined body and typically grows to a length of . It can be distinguished from other large requiem sharks by its relatively small first dorsal fin with a curving rear margin, its tiny second dorsal fin with a long free rear tip, and its long, sickle-shaped pectoral fins. It is a deep, metallic bronze-gray above and white below. With prey often scarce in its oceanic environment, the silky shark is a swift, inquisitive, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lévy Flight Foraging Hypothesis
The Lévy flight foraging hypothesis is a hypothesis in the field of biology that may be stated as follows: ''Since Lévy flights and walks can optimize search efficiencies, therefore natural selection should have led to adaptations for Lévy flight foraging.'' Background The movement of animals closely resembles in many ways the random walks of dust particles in a fluid. This similarity led to interest in trying to understand how animals move via the analogy to Brownian motion. This conventional wisdom held until the early 1990s. However, starting in the late 1980s, evidence began to accumulate that did not fit the theoretical predictions. In 1999, a theoretical investigation of the properties of Lévy flights showed that an inverse square distribution of flight times or distances could optimize the search efficiency under certain circumstances. Specifically, a search based on an inverse-square Lévy walk, consisting of a constant velocity search following a path whose length i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from grc, , translit=kryptós "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security (data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications. Cryptography prior to the modern age was effectively synony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Mathematics
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling of financial markets. In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that require advanced quantitative techniques: derivatives pricing on the one hand, and risk and portfolio management on the other. Mathematical finance overlaps heavily with the fields of computational finance and financial engineering. The latter focuses on applications and modeling, often by help of stochastic asset models, while the former focuses, in addition to analysis, on building tools of implementation for the models. Also related is quantitative investing, which relies on statistical and numerical models (and lately machine learning) as opposed to traditional fundamental analysis when managing portfolios. French mathematician Louis Bachelier's doctoral thesis, defended in 1900, is considered the first scholarly work on mathematical fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics focused on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, and were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals, and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning that there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause a tornado in Texas. Small differences in initial conditions, such as those due to errors in measurements or due to rounding error ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |